Abstract
Red blood cells infected withPlasmodium falciparum(IRBCs) undergo changes primarily in their membrane composition that contribute to malaria pathogenesis. However, all manifestations (eg, anemia) cannot be accounted for by IRBCs alone. Uninfected erythrocytes (URBCs) may play a role, but they have been under-researched. We wanted to document changes in the erythrocyte membrane that could contribute to URBC reduced life span and malaria-associated anemia. Human erythrocytes were cultured withP falciparumand washed at the trophozoite stage. IRBCs and URBCs were separated on Percoll density gradient, thus obtaining erythrocyte fractions of different densities/ages. IRBC- and URBC-purified membranes were analyzed and compared with control normal erythrocytes (NRBCs) of the same age, from the same donor, kept in the same conditions.P falciparumaccelerated aging of both IRBCs and URBCs, causing a significant shift in the cell population toward the denser (old) fraction. Protein, phospholipid, and cholesterol content were reduced in IRBCs and young URBCs. Young and medium uninfected fractions had higher levels of lipid peroxidation and phospholipid saturation (because of the loss of polyunsaturated fatty acids, PUFAs) and lower phosphatidylserine. In IRBCs, thiobarbituric reactive substances (TBARSs) were higher, and PUFAs and phosphatidylserine lower than in NRBCs and URBCs. In comparison, trophozoite membranes had lower phospholipid (particularly sphingomyelin and phosphatidylserine) and cholesterol content and a higher degree of saturation. Parasite-induced peroxidative damage might account for these modifications. In summary, we demonstrated that membrane damage leading to accelerated senescence of both infected and uninfected erythrocytes will likely contribute to malaria anemia.
Introduction
Clinical malaria is a consequence of Plasmodium invading and developing inside red blood cells (RBCs). Infection is accompanied by profound changes in the host cell that are well documented for Plasmodium falciparum, the parasite that causes the life-threatening form of malaria. P falciparum particularly affects lipid composition of the infected red blood cell (IRBC) (cholesterol level, phospholipid pattern, organization, and degree of saturation)1,2 but also its deformability and antigenic, osmotic, and transport properties.3,4 Known consequences are sequestration and stiffness (involved in organ damage, eg, cerebral malaria) and removal. If these changes are well researched for IRBCs, little is known concerning the possible alterations in the membrane composition and structure of uninfected RBCs (URBCs) from patients with malaria or P falciparum in vitro cultures.1,5
Knowing whether URBCs are affected as well and how is important because some of the clinical manifestations of falciparum malaria cannot be accounted for by IRBCs alone. For instance, falciparum malaria causes different degrees of anemia6 that is only partly due to direct destruction of IRBCs by the growing parasite or their removal by the spleen. Severe anemia, which occurs particularly in young children and pregnant woman living in malaria endemic areas, is a case-defining condition for severe and complicated malaria. URBCs in patients with malaria have a shorter life span, but the reasons for this situation are not completely understood.7 The presence of circulating monocytes containing URBCs suggests that during malaria infection uninfected erythrocytes develop membrane modifications that activate monocytes to phagocytize them.8 One possibility is that URBCs are seen as senescent cells by the organism and are thus removed.
To assess whether premature removal of RBCs may be related to changes in membrane structure or composition consistent with an accelerated aging, or both, we undertook a systematic comparison of the membrane composition of normal RBCs (NRBCs) versus URBCs and IRBCs from in vitro–cultured P falciparum. Because RBC aging is accompanied by increased cell density,9 we fractionated RBCs on a Percoll/sorbitol gradient in groups of different densities, corresponding to different ages. Each URBC and IRBC fraction was analyzed for membrane lipid composition, stage of lipid peroxidation, and sensitivity to oxidative stress and was compared with the corresponding fraction of NRBCs.
Parasite membranes from trophozoite-stage P falciparum were studied in parallel. We reasoned that a better knowledge of the lipid composition of trophozoites membranes would help in solving the paradox of parasites, which grow in an iron-porphyrin rich environment, accumulating hemozoin that is toxic for host membranes10,11 and yet survive.
Materials and methods
Reagents
RPMI 1640 medium was purchased from Gibco BRL (Grand Island, NY); human A-positive red blood cells and plasma were kindly provided by the Blood Bank of the National Cancer Institute (Milano, Italy).
Standard phospholipids (PLs), 1,1,3,3-tetraethoxypropane, acetyl thiocholine, NADP+, and thiobarbituric acid were purchased from Sigma (Milan, Italy); silica gel, acid washed was purchased from BDH (Milan, Italy); silica gel plates (Kieselgel 60, high performance thin-layer chromatography [HPTLC]) were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany); standard fatty acid methyl esters were purchased from Alltech (Deerfield, IL).
Parasite cultures
Freshly collected complete human blood with CPD (citrate/phosphate/dextrose) as anticoagulant was banked at 4°C for less than 15 days and used for parasite cultures. Approval was obtained from the Istituto di Fisiologia Generale e Chimica Biologica institutional review board for these studies. P falciparum cultures were carried out according to the method of Trager and Jensen12 with slight modifications. Briefly, a chloroquine (CQ)–sensitive P falciparum strain (D10) was maintained at 5% hematocrit at 37°C in complete culture medium (RPMI 1640 supplemented with NaHCO3 24 mM, 10% heat-inactivated A-positive human plasma, 20 mM HEPES (N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid), and 2 mM glutamine). All cultures were maintained in a standard gas mixture, consisting of 1% O2, 5% CO2, 94% N2. When parasitemia exceeded 5%, subcultures were taken; the culture medium was changed every second day.
After 3 to 4 days of culture at the trophozoite stage, cells were washed twice with serum-free culture medium, resuspended to 25% hematocrit, and fractionated onto a Percoll/4% sorbitol (wt/vol) gradient.13 This procedure allowed the separation of IRBCs at the top of the gradient (density = 1.078) and URBCs in 3 bands of different density and age: young (density = 1.091), medium (density = 1.104), and old (density = 1.117). As control, NRBCs were cultured for 3 to 4 days in the same conditions, and were density-separated in 4 discrete bands: very young (density = 1.078), young (density = 1.091), medium (density = 1.104), and old (density = 1.117). The cell number in each fraction was counted with a hemocytometer, whereas the mean corpuscular volume (MCV) was determined by using an automated Coulter.
Preparation and analysis of erythrocyte ghosts
NRBC and URBC ghosts were prepared by hypotonic lysis and extensive washing in 20 volumes of 5 mM NaHPO4 buffer pH 8.0. IRBC ghosts were purified from parasite by lysis with 0.07% saponin in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at 37°C for 10 minutes and washed according to the method of Hsiao et al.5 Final washing of RBC ghosts was performed with 10 mM Tris (tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane) HCl buffer, pH 7.4. Parasite released from saponin lysis was washed twice with PBS, lysed with 5 mM phosphate buffer pH 8.0, and centrifuged at 100 000g for 30 minutes to pellet trophozoite membranes.
RBCs and trophozoite membranes were subjected to total lipid extraction and partitioning in accordance to Folch et al.14 Total lipid extract was used for lipid analysis: PL phosphorus was determined according to Bartlett,15 whereas cholesterol (Cho) was quantified by densitometric analysis after separation by HPTLC in hexane/diethyl ether/acetic acid (90:10:1, by volume) and visualization with a solution of p-anisaldehyde/acetic acid/sulfuric acid (1:100:2, by volume). An aliquot of the total lipid extract was fractionated in the different lipid components by silicic acid column chromatography.16 Compositional analysis of PL was performed by HPTLC separation in chloroform/methanol/acetic acid/water (60:40:4:2, by volume) and quantification by densitometric analysis after spraying with a specific phosphate ester reagent.17 PL fatty acid composition was determined by gas liquid chromatography and stage of lipid peroxidation and sensitivity to oxidative stress of ghosts as TBARS production as previously reported.11
Other analyses
Protein content and acetyl cholinesterase (AChE) activity were determined in the ghost pellet accordingly to Peterson18 and Vander Jagt et al,19 respectively. An aliquot of the different RBC fractions was lysed with 0.1% Triton X-100, and the hemolysate was used for the determination of hemoglobin by its Soret band absorption at 412 nm and glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) activity.20 An aliquot of RBC ghosts and parasite homogenate was ruptured by sonication at 40 W (3 times for 5 seconds each) with cooling and was assayed for glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH)19 and parasite lactate dehydrogenase (pLDH) using 3-acetyl pyridine NAD (APAD) as a coenzyme in the reaction leading to the formation of APADH (ϵM = 9.1) and pyruvate from lactate. To exclude possible interferences of saponin in the enzymatic assays, an aliquot of NRBCs lysed with 0.07% saponin was subjected to the different enzyme determinations.
Statistical analysis
For the assessment of changes occurring after exposure to P falciparum, URBCs or IRBCs were compared with populations of NRBCs by using the Student paired t test. The 2-sample independent-group t test was used for comparison of medium or old RBCs to young RBCs of the same type. For the assessment of the percentage distribution in the 4 density fractions, the data were analyzed by the 2-way analysis of variance, with one factor for repeated measurements (URBCs versus NRBCs) and one factor for independent measurements (days).
Results
Density fractionation of RBCs from control and P falciparum cultures
NRBCs banked for different times at 4°C were cultured for 72 hours at 37°C and then separated by Percoll gradient. In agreement with published data,9 a progressive shift toward medium and older fractions was seen with aging (data not shown).
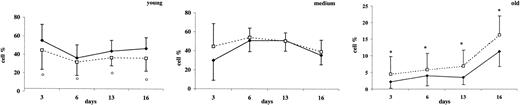
The rate at which such changes occur varied from donor to donor. Therefore, we selected for further study RBCs stored for 15 days or less and always compared with RBCs from the same donor to avoid intersubject variability. As shown in Figure 1, RBCs cocultured with P falciparum (URBCs) showed modifications in density that resulted in a significant increase in the number of cells sedimenting in the old fraction, with a corresponding decrease of the young fraction. The modifications induced by P falciparum were not significantly different among RBCs banked for different days.
Density fractionation of control and uninfected erythrocytes. Cells were banked at 4°C for the indicated time and then maintained at 37°C for 72 hours in the presence or not of P falciparum parasite before fractionation on Percoll/sorbitol gradient. Data were analyzed by 2-way analysis of variance. ⋄indicates control RBCs (NRBCs); □, uninfected RBCs (URBCs). Young URBCs versus young NRBCs, ○ indicates P < .01; old URBCs versus old NRBCs, *P < .003.
Density fractionation of control and uninfected erythrocytes. Cells were banked at 4°C for the indicated time and then maintained at 37°C for 72 hours in the presence or not of P falciparum parasite before fractionation on Percoll/sorbitol gradient. Data were analyzed by 2-way analysis of variance. ⋄indicates control RBCs (NRBCs); □, uninfected RBCs (URBCs). Young URBCs versus young NRBCs, ○ indicates P < .01; old URBCs versus old NRBCs, *P < .003.
In parallel, the increase in density was associated with a decrease of the MCV and of AChE, an erythrocyte membrane-bound enzyme, and G6PDH, 2 specific markers of RBC aging (Table 1).
Markers of RBC aging in different RBC populations
. | NRBCs . | . | . | . | URBCs . | . | . | . | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
. | Very young . | Young . | Medium . | Old . | Young . | Medium . | Old . | IRBCs . | |||||
| MCV | 98.2 ± 0.5 | 92.5 ± 0.7 | 84.5 ± 0.1 | 81.2 ± 0.5 | 90.7 ± 0.4* | 84.7 ± 0.3* | 80.5 ± 0.5* | 98.2 ± 0.3* | |||||
| AchE, U/mg protein | 5.6 ± 0.9 | 4.9 ± 1.2 | 4.4 ± 0.5 | 3.1 ± 0.9 | 4.6 ± 1.5* | 4.3 ± 1* | 3.2 ± 0.5* | 3.9 ± 1† | |||||
| G6PDH, U/g Hb | 5.5 ± 1 | 4.4 ± 0.8 | 3.6 ± 1 | 2.5 ± 0.6 | NT | NT | NT | NT | |||||
. | NRBCs . | . | . | . | URBCs . | . | . | . | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
. | Very young . | Young . | Medium . | Old . | Young . | Medium . | Old . | IRBCs . | |||||
| MCV | 98.2 ± 0.5 | 92.5 ± 0.7 | 84.5 ± 0.1 | 81.2 ± 0.5 | 90.7 ± 0.4* | 84.7 ± 0.3* | 80.5 ± 0.5* | 98.2 ± 0.3* | |||||
| AchE, U/mg protein | 5.6 ± 0.9 | 4.9 ± 1.2 | 4.4 ± 0.5 | 3.1 ± 0.9 | 4.6 ± 1.5* | 4.3 ± 1* | 3.2 ± 0.5* | 3.9 ± 1† | |||||
| G6PDH, U/g Hb | 5.5 ± 1 | 4.4 ± 0.8 | 3.6 ± 1 | 2.5 ± 0.6 | NT | NT | NT | NT | |||||
AChE was assayed in RBC membranes, G6PDH in RBC hemolysate. Results are the mean (± SD) of 6 to 8 determinations. Data analyzed by paired t test: URBCs versus NRBCs of corresponding density; IRBCs versus very young NRBCs. Hb indicates hemoglobin; NT, not tested
Not significantly different
P < .01
MCV and AChE showed a similar age-related decrease in URBCs. In IRBCs, collected from the top of the gradient, AChE showed a significantly lower activity compared with that of the corresponding very young NRBC fraction, whereas the MCV was not significantly different.
To assess if parasite contamination had occurred in IRBC and URBC membranes, we measured the activities of 2 parasite marker enzymes, pLDH (the parasite-specific form of lactic dehydrogenase) and GDH (a mitochondrial enzyme present only in the parasite). In the fraction containing P falciparum trophozoites, the pLDH value was 4.1 ± 0.2 U/mg protein, and GDH was 83.3 ± 4.0 mU/mg protein. Conversely, pLDH was detectable only in trace amounts in IRBC ghosts (0.2 ± 0.1 U/mg protein), whereas GDH was not detectable in either URBCs or IRBCs.
Protein and lipid content in density fractionated RBC
Figure 2 shows the protein, PL, and Cho content in the various RBC fractions. Protein and lipid content progressively decreased as RBCs became older. In contrast, mean cell hemoglobin content did not change with age (25-30 pg/cell; data not shown). A loss of all the membrane components was found in the IRBC fraction when compared with the control fraction of corresponding density (very young NRBCs) and in the young URBC fraction compared with young NRBCs. Medium and old URBCs were not significantly different from NRBCs of the same density.
Effect of aging andP falciparumon the protein and lipid content of the different erythrocyte populations. Control (NRBCs) and uninfected RBCs (URBCs) were density separated by Percoll/sorbitol gradient and ghosts from the various fractions were obtained by lysis and extensive washing with 5 mM NaHPO4 buffer, pH 8.0; ghosts from infected RBCs (IRBCs) were obtained by lysis with 0.07% saponin (wt/vol). Lipids were extracted, and PLs were quantified by phosphorus determination and cholesterol by thin layer chromatography and densitometric analysis as de-scribed in “Material and methods.” Protein content is expressed as microgram per 107 cells, PL and Cho as micromole per 1010 cells. Data shown are the mean ± SD of 5 experiments (paired t test for comparison of IRBCs versus very young NRBCs, and young URBCs versus young NRBCs). *P < .01.
Effect of aging andP falciparumon the protein and lipid content of the different erythrocyte populations. Control (NRBCs) and uninfected RBCs (URBCs) were density separated by Percoll/sorbitol gradient and ghosts from the various fractions were obtained by lysis and extensive washing with 5 mM NaHPO4 buffer, pH 8.0; ghosts from infected RBCs (IRBCs) were obtained by lysis with 0.07% saponin (wt/vol). Lipids were extracted, and PLs were quantified by phosphorus determination and cholesterol by thin layer chromatography and densitometric analysis as de-scribed in “Material and methods.” Protein content is expressed as microgram per 107 cells, PL and Cho as micromole per 1010 cells. Data shown are the mean ± SD of 5 experiments (paired t test for comparison of IRBCs versus very young NRBCs, and young URBCs versus young NRBCs). *P < .01.
PL and Cho decreased similarly, with the result that the Cho/PL molar ratio was unchanged. These differences could not be seen when NRBCs and URBCs were compared before density fractionation (data not shown).
PL distribution and fatty acid pattern
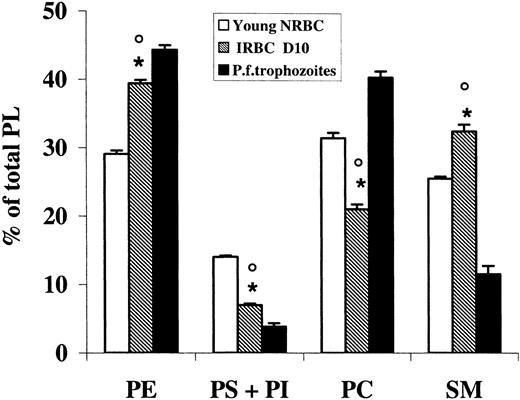
Data on the PL composition of ghosts from NRBCs and URBCs after density fractionation are summarized in Table 2. Phosphatidylinositol (PI), quantified with phosphatidylserine (PS), was present in all fractions in a very low percentage (< 1%). In NRBCs, aging caused a decrease in PS and an increase in phosphatidylcholine (PC) and sphingomyelin (SM) content. A similar trend was present in URBCs, although in each fraction the percentage of PS was significantly lower compared with the NRBC fraction of the same age. SM was higher in all URBC fractions, although significantly different only in the young age. When IRBCs were tested, very low levels of PS and PC were found, whereas PE was higher in NRBCs (Figure 3). P falciparum trophozoites too had very low levels of PS but differently from IRBCs, PC was one of the most represented PL species, and SM was low.
Phospholipid distribution of control and uninfected human erythrocyte ghosts
. | NRBCs . | . | . | URBCs . | . | . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
. | Young . | Medium . | Old . | Young . | Medium . | Old . | ||||
| PE | 29.1 ± 0.5 | 30.0 ± 0.3 | 28.2 ± 0.6 | 29.2 ± 0.9 | 30.0 ± 0.7 | 30.0 ± 1.3 | ||||
| PS + PI | 14.0 ± 0.2 | 11.4 ± 0.5* | 10.1 ± 0.3* | 11.1 ± 0.3† | 9.7 ± 0.2*† | 7.0 ± 0.4*† | ||||
| PC | 31.4 ± 0.8 | 32.9 ± 0.5§ | 34.4 ± 1.2* | 30.6 ± 1.0 | 32.9 ± 1.3 | 34.2 ± 0.5§ | ||||
| SM | 25.5 ± 0.3 | 25.7 ± 0.8 | 27.3 ± 0.4§ | 29.1 ± 0.4‡ | 27.4 ± 0.9 | 28.8 ± 0.6 | ||||
. | NRBCs . | . | . | URBCs . | . | . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
. | Young . | Medium . | Old . | Young . | Medium . | Old . | ||||
| PE | 29.1 ± 0.5 | 30.0 ± 0.3 | 28.2 ± 0.6 | 29.2 ± 0.9 | 30.0 ± 0.7 | 30.0 ± 1.3 | ||||
| PS + PI | 14.0 ± 0.2 | 11.4 ± 0.5* | 10.1 ± 0.3* | 11.1 ± 0.3† | 9.7 ± 0.2*† | 7.0 ± 0.4*† | ||||
| PC | 31.4 ± 0.8 | 32.9 ± 0.5§ | 34.4 ± 1.2* | 30.6 ± 1.0 | 32.9 ± 1.3 | 34.2 ± 0.5§ | ||||
| SM | 25.5 ± 0.3 | 25.7 ± 0.8 | 27.3 ± 0.4§ | 29.1 ± 0.4‡ | 27.4 ± 0.9 | 28.8 ± 0.6 | ||||
Lipids were extracted from erythrocyte ghosts, and PLs were purified from other lipid components as described in “Material and methods.” Individual PL species were separated by HPTLC and quantified by densitometric analysis. PE indicates phosphatidylethanolamine; PS, phosphatidylserine; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PC, phosphatidylcholine; and SM, sphingomyelin
Results represent the percentage of total PLs, and are the mean (± SD) of 3 to 6 determinations made in duplicate
Data were compared by using the 2-sample independent t test for within group comparisons (versus young RBCs), and the paired t test for between-group comparisons (cells of the same age)
P < .01 versus young RBCs of the same group
P < .01 versus NRBCs of the same age
P < .05 versus NRBCs of the same age
P < .05 versus young RBCs of the same group
Phospholipid distribution of infected erythrocyte (IRBC) ghosts and P falciparum trophozoite membranes compared with control erythrocytes (NRBCs). PL was extracted, purified, and analyzed by HPTLC separation and densitometric analysis as described in “Materials and methods.” Results represent the percentage of total PLs and are the mean (± SD) of 3 determinations made in duplicate. IRBCs were compared with trophozoites (unpaired t test, *P < .01) and young NRBCs (paired t test, ○P < .01).
Phospholipid distribution of infected erythrocyte (IRBC) ghosts and P falciparum trophozoite membranes compared with control erythrocytes (NRBCs). PL was extracted, purified, and analyzed by HPTLC separation and densitometric analysis as described in “Materials and methods.” Results represent the percentage of total PLs and are the mean (± SD) of 3 determinations made in duplicate. IRBCs were compared with trophozoites (unpaired t test, *P < .01) and young NRBCs (paired t test, ○P < .01).
The degree of PL unsaturation, as shown by the percentage of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and the double bond index (DBI; defined as the total number of unsaturated methylenes), decreased with age in NRBCs and URBCs and was comparatively lower in URBCs than in NRBCs (Table 3).
Phospholipid fatty acid composition of control and uninfected erythrocyte ghosts
. | NRBCs . | . | . | URBCs . | . | . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
. | Young . | Medium . | Old . | Young . | Medium . | Old . | ||||
| Fatty acid | ||||||||||
| 16:0 | 21.9±0.6 | 24.9±0.8* | 25.8±1.5* | 25.1±1.4† | 26.1±0.5 | 26.0±0.6 | ||||
| 18:0 | 19.4±2.2 | 19.1±1.2 | 18.2±1.0 | 18.6±0.1 | 18.6±0.5 | 18.6±0.8 | ||||
| 18:1, n-9 | 19.6±2.0 | 18.0±1.5 | 20.7±2.1 | 20.4±1 | 19.8±0.8 | 21.1±2.1 | ||||
| 18:2, n-6 | 11.6±0.1 | 12.7±0.3 | 12.5±0.2 | 11.1±0.1 | 12.0±0.3 | 11.8±1.4 | ||||
| 20:4, n-6 | 18.5±0.5 | 17.1±0.5* | 15.5±0.3‡ | 17.5±0.2§ | 15.5±0.2† | 15.8±0.2 | ||||
| 22:5, n-3 | 2.7±0.3 | 2.8±0.3 | 2.0±0.1 | 2.2±0.2 | 2.3±0.3 | 2.1±0.3 | ||||
| 22:6, n-3 | 5.9±0.3 | 5.4±0.5 | 4.8±0.2 | 4.8±0.8§ | 5.1±0.6 | 4.4±0.6 | ||||
| PUFA, % | 38.7 | 38.0 | 35.8 | 35.6 | 34.9 | 34.1 | ||||
| DBI | 165.7 | 158.2 | 146.5 | 152.4 | 147.9 | 144.8 | ||||
. | NRBCs . | . | . | URBCs . | . | . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
. | Young . | Medium . | Old . | Young . | Medium . | Old . | ||||
| Fatty acid | ||||||||||
| 16:0 | 21.9±0.6 | 24.9±0.8* | 25.8±1.5* | 25.1±1.4† | 26.1±0.5 | 26.0±0.6 | ||||
| 18:0 | 19.4±2.2 | 19.1±1.2 | 18.2±1.0 | 18.6±0.1 | 18.6±0.5 | 18.6±0.8 | ||||
| 18:1, n-9 | 19.6±2.0 | 18.0±1.5 | 20.7±2.1 | 20.4±1 | 19.8±0.8 | 21.1±2.1 | ||||
| 18:2, n-6 | 11.6±0.1 | 12.7±0.3 | 12.5±0.2 | 11.1±0.1 | 12.0±0.3 | 11.8±1.4 | ||||
| 20:4, n-6 | 18.5±0.5 | 17.1±0.5* | 15.5±0.3‡ | 17.5±0.2§ | 15.5±0.2† | 15.8±0.2 | ||||
| 22:5, n-3 | 2.7±0.3 | 2.8±0.3 | 2.0±0.1 | 2.2±0.2 | 2.3±0.3 | 2.1±0.3 | ||||
| 22:6, n-3 | 5.9±0.3 | 5.4±0.5 | 4.8±0.2 | 4.8±0.8§ | 5.1±0.6 | 4.4±0.6 | ||||
| PUFA, % | 38.7 | 38.0 | 35.8 | 35.6 | 34.9 | 34.1 | ||||
| DBI | 165.7 | 158.2 | 146.5 | 152.4 | 147.9 | 144.8 | ||||
PL fatty acid composition was determined by gas liquid chromatography. Results are the mean (±SD) of 4 to 8 determinations. DBI indicates double bond index (obtained by multiplying the percentage of each fatty acid by the number of double bonds in that acid)
Unpaired t test for comparison of medium and old NRBCs versus young NRBCs, P < .05
Paired t test for comparison of URBCs versus NRBCs of the same age, P < .01
Unpaired t test for comparison of medium and old NRBCs versus young NRBCs, P < .01
Paired t test for comparison of URBCs versus NRBCs of the same age, P < .05
In NRBCs, palmitic acid (C16:0) increased with age, whereas arachidonic acid (C20:4 n-6) and docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6 n-3) decreased, leading to a decrease of DBI (Table 3). In URBCs, C16:0 was significantly higher in young cells, whereas C20:4 n-6 was significantly lower in both young and medium cells as compared with the corresponding fractions of NRBCs; PUFA and DBI also decreased with age and were comparatively lower than in NRBC controls (Table 3). In IRBCs, PUFA and DBI were lower than in NRBCs and URBCs (Table 4). Saturated fatty acids (C16:0 and C18:0) were significantly higher, whereas all the unsaturated fatty acids (C18:1 n-9, C18:2 n-6, C20:4 n-6, C22:6 n-3) were significantly lower than in NRBCs and URBCs. C22:5 n-3 was not found. P falciparum trophozoites had low, yet measurable levels of C14:0 that was undetectable in RBCs, very low levels of C20:4 n-6 and C22:6 n-3, and no C22:5 n-3. Parasites showed a DBI close to IRBCs, although C18:0 and C18:2 n-6 were not statistically different from NRBCs and URBCs.
Phospholipid fatty acid composition of infected erythrocyte ghosts and Plasmodium falciparum plasma membranes
. | IRBC . | P falciparum trophozoite . |
|---|---|---|
| Fatty acid | ||
| 14:0 | ND | 1.1±0.4 |
| 16:0 | 32.1±0.5* | 37.2±1.5† |
| 18:0 | 30.5±1.0* | 18.8±0.8† |
| 18:1, n-9 | 16.5±0.7‡ | 22.2±1.3† |
| 18:2, n-6 | 7.1±0.8* | 11.9±1.4‡ |
| 20:4, n-6 | 8.3±0.3* | 6.6±0.6‡ |
| 22:5, n-3 | ND | ND |
| 22:6, n-3 | 4.6±0.6§ | 2.2±0.5† |
| PUFA, % | 20.0 | 20.7 |
| DBI | 91.5 | 85.6 |
. | IRBC . | P falciparum trophozoite . |
|---|---|---|
| Fatty acid | ||
| 14:0 | ND | 1.1±0.4 |
| 16:0 | 32.1±0.5* | 37.2±1.5† |
| 18:0 | 30.5±1.0* | 18.8±0.8† |
| 18:1, n-9 | 16.5±0.7‡ | 22.2±1.3† |
| 18:2, n-6 | 7.1±0.8* | 11.9±1.4‡ |
| 20:4, n-6 | 8.3±0.3* | 6.6±0.6‡ |
| 22:5, n-3 | ND | ND |
| 22:6, n-3 | 4.6±0.6§ | 2.2±0.5† |
| PUFA, % | 20.0 | 20.7 |
| DBI | 91.5 | 85.6 |
PL fatty acid composition was determined and DBI calculated as described in Table 3. Results are the mean (±SD) of 3 determinations. ND indicates not detectable
Paired t test for comparison of IRBCs versus young NRBCs and young URBCs (Table 3), P < .01
Unpaired t test for comparison of trophozoites versus IRBC membranes, P < .01
Paired t test for comparison of IRBCs versus young NRBCs and young URBCs (Table 3), P < .05
Paired t test for comparison of IRBCs versus young NRBCs and young URBCs, P < .05 only versus young NRBCs (Table 3)
Stage of lipid peroxidation and sensitivity to oxidative stress
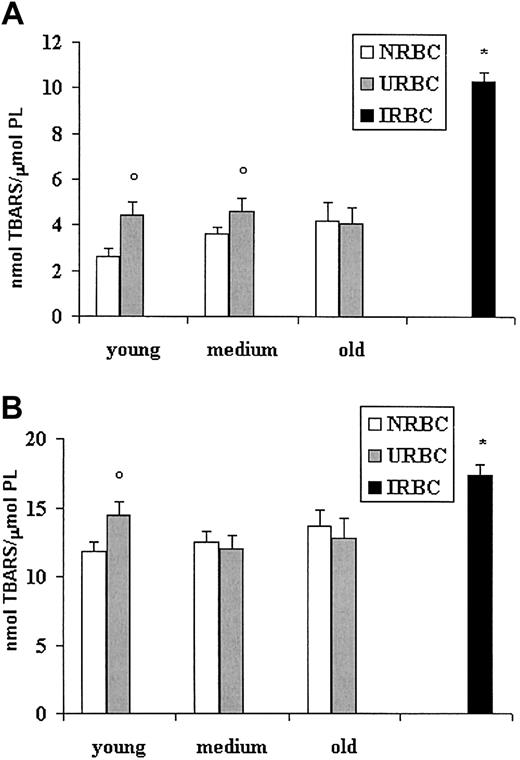
To investigate whether the modified fatty acid pattern could be related to different levels of lipid peroxidation, we examined the production of TBARSs in basal conditions or after stimulation with the prooxidant system iron/ascorbate (Figure 4). Figure 4A shows higher basal levels of TBARSs in young and medium URBC ghosts compared with NRBCs of the same age. Old URBCs were not significantly different from old NRBCs. A 3-fold increase in the level of basal peroxidation was found in IRBCs compared with NRBCs and URBCs. When challenged by iron-ascorbate, IRBC ghosts had the highest values of peroxidation, whereas, among URBCs, only ghosts from young URBCs appeared more sensitive than their age-matched controls (Figure 4B).
Lipid peroxidation of ghosts from control, uninfected, and infected erythrocytes. RBC ghosts were assayed for TBARSs before or after induction for 3 hours at 37°C with the pro-oxidant system iron-ascorbate. Results (mean ± SD) are expressed as nanomole TBARS per micromole red cell phospholipids. ○P < .01 versus NRBCs of the same age. *P < .01 versus NRBCs and URBCs. (A) TBARSs at basal conditions. (B) TBARSs after iron/ascorbate challenge.
Lipid peroxidation of ghosts from control, uninfected, and infected erythrocytes. RBC ghosts were assayed for TBARSs before or after induction for 3 hours at 37°C with the pro-oxidant system iron-ascorbate. Results (mean ± SD) are expressed as nanomole TBARS per micromole red cell phospholipids. ○P < .01 versus NRBCs of the same age. *P < .01 versus NRBCs and URBCs. (A) TBARSs at basal conditions. (B) TBARSs after iron/ascorbate challenge.
Discussion
The present study shows that P falciparum induces biochemical modifications in the membranes of both infected and uninfected erythrocytes, mimicking the physiologic cell's aging process. These effects might be produced through P falciparum–induced oxidative stress.
Cell populations obtained from the same donor that were either cultured but nonexposed to (NRBCs, control RBCs), cocultured but not infected with (URBCs), or infected with P falciparum (IRBCs) were compared. A novel protocol was used (cell storage for different times at 4°C and culture at 37°C for 72 hours, the P falciparum intraerythrocytic cycle) before Percoll fractionation, and the recovery in each fraction was quantified and compared. The implications of the methodology used in explaining our results vis-à-vis discrepancies in the literature are addressed further.
We confirmed and quantified in NRBCs the changes occurring during RBC aging21-26 : (1) decreased AChE and G6PDH activities; (2) decreased protein, PL, and Cho; (3) decreased PS; and (4) decreased PUFA and DBI. Some of these changes were more marked in cells infected with, or exposed to (notably young URBCs) P falciparum as compared with NRBCs of the corresponding density (age). The AchE activity of young URBCs, which was not different from that of homologous NRBCs when expressed per milligram of protein, was actually lower because of the lower content of protein per cell of this URBC fraction.
RBCs that are not infected (URBCs) but share the same environment with P falciparum–infected cells become older prematurely, as suggested by the increase in the number of cells sedimenting in the medium and most dense fractions and the relative decrease of the young fraction, compared with NRBCs. These findings were reproducible and independent of the donor and storage time at 4°C.
Changes induced by P falciparum to the properties of IRBCs are well documented. PL content increases because of the high biosynthetic activity27 necessary for membrane biogenesis and essential to parasite's survival, and its composition is modified.1,28
It is important to draw attention at this point to the paucity and conflicting nature of data reported in the literature when whole infected RBCs (reflecting the separate contribution of the erythrocyte and the intracellular parasite itself) are studied and when total RBC populations of infected and uninfected cells are compared with no prior fractionation.1,2,5,29,30 This variability has been attributed to different parasite species, level of parasitemia, developmental stages of the parasite, or purity of cell membranes. On the basis of our results, additional factors, which can be controlled by standardizing the experimental methodology, contribute to these discrepancies. RBCs from different donors can be very different in their lipid composition, and, within each donor, they vary with age. Aging (in vivo or during storage at 4°C) is accompanied by physical and biochemical modifications, including enzymatic activities, lipid composition, and peroxidative damage of membrane PL.21-26,31 Therefore, one should compare infected and uninfected RBCs only with control RBCs from the same donor, banked for the same number of days, and maintained under the same culture conditions; RBC fractions (separated on a density gradient) should be used instead of whole unfractionated cell population; infected and uninfected RBC fractions should be compared with control fractions of the same density (age). It is also worth noting that P falciparum shows a preference for invading young RBCs.32 We did not see any difference between whole control and URBCs before density fractionation. In the whole RBC population, the decrease in lipid and protein content because of the loss of the younger RBCs and to the lower protein and lipid content of IRBCs and young URBCs is masked by the relative increase in the old fraction. This masking helps explain why previous studies that used unfractionated RBC populations could not see differences between normal and uninfected RBCs.5,29
Our results are not influenced by contaminants. The purity of RBCs derived from P falciparum cultures was verified by measuring the activities of pLDH (the parasite-specific form of LDH assayed by the NAD analog APAD) and GDH (a mitochondrial enzyme present only in the parasite).19,33 Other features also (description to follow) support the purity of IRBCs and URBCs from parasites.
Several data indicate that oxidative stress increases with age in RBCs and intensifies with P falciparum infection. In agreement with published data, we too found increased endogenous TBARSs in older RBCs, suggesting a higher level of lipid peroxidation in aged erythrocytes.25,34 Hydroperoxides have been shown to exert an inhibitory effect on the PL reacylating reactions35 and could contribute to the impairment of fatty acid esterification found in aged erythrocytes26,36 as well as to the loss of PUFAs and PLs observed with RBC aging in the present and previous works. However, endogenous TBARS levels were higher in IRBCs and also in young and medium URBCs compared with NRBCs of the same densities. This finding supports the view that peroxidative processes increase in RBCs during P falciparum infection.37 Membrane damage is enhanced in IRBCs, as shown by the lower unsaturation index (DBI) and the modified PL pattern, whereby PS and PC are markedly decreased. The lower DBI of IRBC ghosts (about 50% that of NRBCs) is accounted for by the loss of PUFAs and the increase of both the saturated species palmitic and stearic acid. Compared with P falciparum trophozoites, IRBCs had very similar DBI and PUFA values, but a much higher content in stearic acid and a lower content in oleic and linoleic acid, as well as higher proportions of SM and PS (as molar percentage and absolute value per milligram of protein). Low percentages of SM and PS in trophozoite membranes and in the whole infected RBCs were reported also by others.5,29 These differences, along with the lower content of PLs and Cho of trophozoite (0.6 μmol/mg protein and 0.12 /μmol/mg protein, respectively) are a further indication of the negligible contamination of parasite membrane by RBC membranes in our specimens. Also, the lower AChE activity of IRBCs, compared with the NRBCs of the same density (very young fraction), could be ascribed to P falciparum–induced oxidative stress or the reduced content of PUFAs.38-40
P falciparum accelerated also the age-related modifications of URBCs, particularly the young fraction. We found a loss in arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acid, but, differently from IRBCs, the increase in saturated species was limited to palmitic acid. On a percentage molar basis, lower PS levels were found in URBCs compared with NRBCs of the same density, which were apparently compensated by increased SM. However, because young URBCs have a lower PL content compared with the control fractions, all the PL species were reduced in absolute terms, albeit to a lower extent compared with PS.
The greater loss in PS could be partly ascribed to its richness in unsaturated fatty acids, which are most vulnerable to peroxidative breakdown, but also to its increased exposure on the outer surface of the cell membrane. Lipid asymmetry of the membrane, maintained by an aminophospholipid translocase activity, is reduced in aged erythrocytes41 or erythrocytes under oxidative stress.42 Altered membrane PL organization, particularly a greater PS exposure on the outer surface of the membrane, has been reported in both IRBCs2,43,44 and URBCs,45,46 although not confirmed by others.29,47 Oxidative stress induced by P falciparum might contribute to the loss of PS by changing the transbilayer organization of the membrane phospholipids and enhancing PS exposure on the outer surface.
Iron-ascorbate induction was studied to assess whether P falciparum infection could induce changes in RBC susceptibility to lipid peroxidation. Membranes obtained from IRBCs and young URBCs are more sensitive to peroxidation than those from NRBCs, as shown by the levels of TBARS production, despite their lower degree of unsaturation. This apparent incongruity could be related to the different lipid distribution in the membrane, promoting the presence of defect points, which facilitate radical attack. A lower content of vitamin E has been found in intact parasitized erythrocytes48 ; therefore, a depletion in endogenous antioxidant protection, in particular vitamin E, cannot be excluded and deserves further investigation.
Alterations in the organization of PLs have been shown to compromise membrane integrity and lead to early hemolysis or reticuloendothelial clearance49 or phagocytosis.41,50 Therefore, the observed abnormalities in the organization of RBC PLs may have pathophysiologic implications and possibly shorten cells' life span.
The nature of the modifications observed in IRBC and URBC plasma membranes suggests that P falciparum can exert a strong oxidative stress in RBC culture. Differently from erythrocyte membranes, parasite membranes appear to be quite resistant to oxidative stress. They are very poor in cholesterol and have a lower content of PLs, characterized by a higher level of fatty acid saturation than RBCs (see also Hsiao et al5 ). These features will very likely contribute to parasite resistance to the oxidant environment where they live and critical processes taking place in the parasite itself. The release of hemoglobin-derived heme and its oxidation and crystallization to hemozoin (malaria pigment) in the parasite food vacuole generates toxic radicals. Even hemozoin that is considered a nontoxic storage of heme for the parasites has been shown to catalyze peroxidative processes in cell culture and cell-free systems.10,11,51 Parasites seem to use different tools to cope with such an environment: (1) they are rich in antioxidant enzymes either imported from host or newly synthesized; (2) as shown here, the composition of their membranes is quite resistant to oxidative damage; and (3) to minimize contact with oxygen, they have evolved a way to survive in microaerophilic conditions. The food vacuole, the organelle where the digestion of hemoglobin occurs, is likely to be an anaerobic compartment, as we recently suggested.52
In conclusion, the results of this study show that the growth of P falciparum affects primarily the host RBCs but modifies also the surrounding uninfected RBCs, while preserving the integrity of the microorganism. These findings have implications for both a better understanding of pathologic manifestations of malaria, leading to its severe complications. The changes in URBCs can shorten the cell's life span through premature removal, thus contributing to chronic and severe anemia observed in areas of intense malaria transmission, where particularly young children and pregnant women live with large numbers of parasites in their blood. In addition, these changes may be a factor of increased RBC membrane rigidity, thus contributing to cells jamming in small vessels and hence to organ damage of severe malaria. For the parasite, under the circumstances, approaches using membrane oxidants are unlikely to be effective.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, March 20, 2003; DOI 10.1182/blood-2002-08-2437.
Supported by the Ministero Italiano dell'Università e della Ricerca Scientifica e Tecnologica (PRIN 2001) and by the University of Milano (progetto giovani ricercatori) (A.M. and S.P.)
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
We thank Dr F. Ravagnani from the Blood Unit, National Cancer Institute, Milan, Italy, for providing fresh red blood cells, G. Montorfano for technical assistance, and Dr F. Vitali, Division of Laboratory Medicine, A.O. Melegnano, Milan, Italy, for RBC MCV analysis.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal