Abstract
Background
In clinical trials, venetoclax has shown high efficacy and good tolerability in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Retrospective cohort studies have examined outcomes with venetoclax in B-cell receptor pathway inhibitor (BCRi) naïve and exposed patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL in the real world setting. However, prospective real-world data on the sequencing of new agents in the R/R setting are limited. The prospective non-interventional observational study VeRVe is assessing effectiveness, safety, and quality of life in CLL patients treated with venetoclax in Austria, Germany, and Switzerland according to local label. Here we report outcomes in patients treated with venetoclax in combination with rituximab (VenR) in BCRi-naïve and BCRi-exposed patients.
Methods
Adult patients with CLL requiring therapy treated with VenR according to local label were included in this analysis. Patient visits are scheduled at the physician's discretion and according to clinical practice. Study documentation is possible at baseline, weekly during ramp-up, monthly until the end of 6 months and 3-monthly afterwards up to a maximum of 3 years. Response assessment according to iwCLL criteria can be documented at the end of ramp-up, after 3, 12, and 24 months. Analyses were performed for subgroups of BCRi-naïve and BCRi-exposed patients.
Results
Until April 26, 2021, 94 patients treated with VenR had been enrolled in the ongoing study and had received at least one dose of venetoclax (safety population). For 72 patients, treatment response had been documented at least once (effectiveness population). Enrolled patients had a median of 1 (range 1-10) previous lines of therapy. 57 patients (61%) had previously been treated with chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) and were BCRi-naïve, 32 patients (34%) had received at least one prior BCRi and 7 (7%) had received other prior treatment options. BCRi-naïve patients had a median of 1 prior therapies (range 1-4), while BCRi-exposed patients had received a median of 3 prior therapies (range 1-10). Risk factors were more common in the BCRi-exposed group (38% of patients had a documented del(17p), 34% a TP53 mutation, and 41% an unmutated IGHV status) in comparison to the BCRi-naïve group (14% del(17p), 16% TP53 mutation and 40% unmutated IGHV). Median age at baseline was 72 and 71 years for BCRi-naïve and BCRi-exposed patients, respectively. 65% vs. 84% of BCRi-naive and BCRi-exposed patients had at least one comorbidity.
In the BCRi-exposed group, 29 patients (91%) had a BCRi as last prior therapy before VenR initiation with a median duration of prior BCRi therapy of 18 months (range 1 - 61 month). Most frequent reasons for discontinuation of prior BCRi therapy were AE/SAE (11 patients) and disease progression (12 patients).
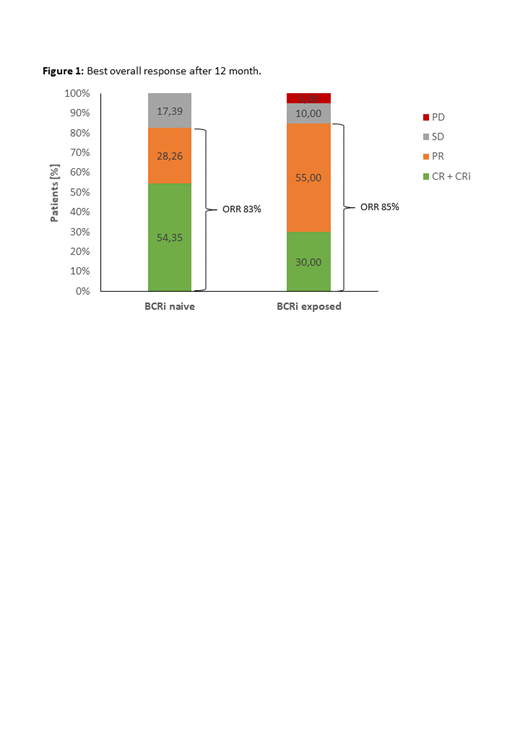
The reported best overall response at 12 months after VenR initiation was 83% (CR+CRi 55%; PR: 28%) for BCRi-naïve and 85% (CR+CRi 30%; PR: 55%) for BCRi-exposed patients (figure 1). After a median follow-up of 315 days the estimated 12-months OS and PFS rate were both 94.8% for BCRi-naïve patients, whereas the estimated 12 months OS and PFS rate for BCRi-exposed patients were 79.1% and 75.7%, respectively, with a median follow-up of 371 days. 79% / 25% of BCRi-naïve and 90% / 44% of BCRi-exposed patients had AEs / SAEs. No new safety signals were observed.
Conclusion
In this analysis of real-world use of venetoclax in R/R CLL, patients receiving venetoclax in combination with rituximab were predominantly BCRi-naïve. BCRi-exposed patients were more heavily pre-treated, exhibited more genetic high-risk factors, and a higher proportion of patients with comorbidities. Yet, these patients achieved comparable overall response rates. However, complete remissions were more common and the 12 months OS and PFS rates were higher in BCRi-naïve patients. In both groups, VenR treatment was well tolerated. VenR represents a suitable treatment option in BCRi-naïve as well as BCRi-exposed patients.
Rossi: Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Verastem: Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Cellestia: Honoraria, Research Funding. Hebart: AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria. Losem: AbbVie: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria. Wolff: Bayer: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Teva: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding. Schmidt: AbbVie: Current Employment. Famulla: AbbVie: Current Employment. Schmidt: Takeda: Honoraria; Biotest: Honoraria; Alexion: Honoraria; Sanofi-Aventis: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria. Noesslinger: Jansen: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria. Schwaner: AbbVie: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; Servier: Honoraria.