Introduction:
Despite multiple treatment options, multiple myeloma (MM) remains an incurable disease. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T) therapy, a form of adoptive immunotherapy, has shown favorable outcomes in the treatment of hematological malignancies. The B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) which is present on myeloma cells, serves as a valid target site for CAR T cells. Early studies have shown promising outcomes in patients (pts) with relapsed and refractory MM (RRMM). However, CAR T therapy is also associated with multiple adverse effects. The main objective of this review is to evaluate the all grades of CRS and other commonly occurring adverse events (AE) associated with CAR T therapy in pts with RRMM.
Methods:
A systematic search of databases (following PRISMA guidelines) PubMed, Cochrane, Embase and, clinicaltrials.gov was performed with no restrictions of language and time period. A total of 249 articles were identified initially and after a detailed screening, we finalized 16 studies including 12 phase I and 3 phase Ib/II clinical trials and 1 retrospective analysis for data extraction.
Results:
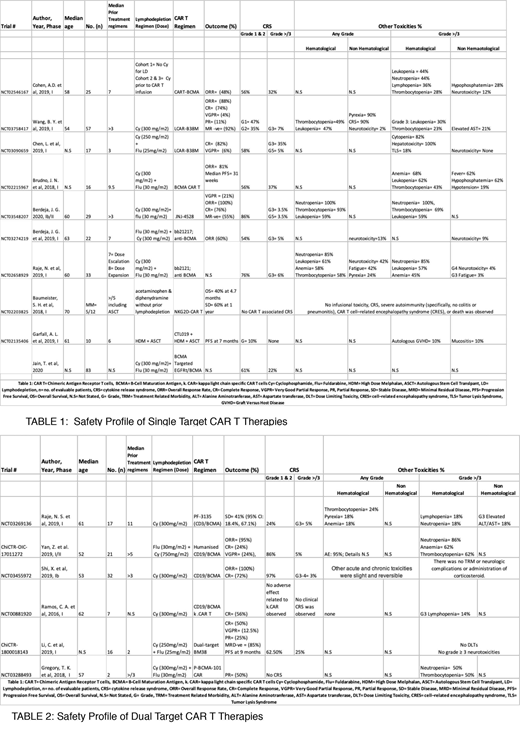
Total included trials were 15 and trial-level data collected from 392 pts is summarized in Table 1 and Table 2. Commonly used CAR T regimens for the treatment of MM were bb2121 BCMA, P BCMA 101 CAR, LCAR B38 M, and anti CD19 CAR.
Single Target; Anti BCMA CAR T (Table 1)
BCMA CAR T, LCAR-B38M:
In a phase I trial, Cohen et al. (2019) reported G1&2 CRS in 56% pts (n=25) and G3 CRS in 32% pts when treated with BCMA specific CAR T. Leukopenia, neutropenia, and lymphopenia were seen in 44%, 44% and 36% of pts, respectively.
In a phase I trial, Wang et al. (2019) reported G1 & G2 CRS in 47% and 35% pts (n=57), respectively and G3 CRS in 7% pts when treated with LCAR-B38M CAR T. Pyrexia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia were seen in 90%, 49% and 30% pts, respectively.
In a phase I trial, Chen et al. (2019) reported G1/2 CRS in 58% pts (n=17) and G3 and G5 CRS in 35% and 5% pts respectively when treated with LCAR-B38M. Hepatotoxicity and cytopenia were seen in 100% and 82% pts, respectively.
In a phase 1 trial, Brudno et al. (2018) reported G1/2 in 56% pts (n=16) and G3 in 37% pts when treated with BCMA CAR T. Anemia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia were observed in 68%, 62% and 43% pts, respectively.
JNJ-4528, bb2121
In a phase Ib/II trial, Berdeja et al. (2020) reported G1/2 CRS in 86% pts (n=29), G3 and G4 CRS in 3.5% pts each when treated with JNJ-4528 (an LCAR-B38M) CAR T. Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia and leukopenia were seen in 100%, 69% and 59% pts, respectively.
In a phase I trial, Berdeja et al. (2019) reported G1, G2 and G3 CRS in 22%, 32% and 5% pts (n=22), respectively when treated with bb2121 CAR T. Neurotoxicity was observed in 22% pts.
In a phase I trial, Raje et al. (2017) reported CRS of any grade in 76% pts (n=33) and G3 CRS in 6% pts when treated with bb2121 CAR T. Neurotoxicity, hypotension and hyponatremia were observed in 42%, 15% and 15% pts, respectively.
Dual Target CAR T (Table 2)
Anti-CD19/BCMA, PF-3135, Dual Target BM38:
In a phase Ib trial, Shi et al. (2019) reported G1/2 CRS in 97% pts (n=32) while G3/4 CRS in 3% pts when treated with anti-CD19/BCMA CAR T. Other AE were slight and reversible.
In a phase I/II trial, Yan et al. (2019) reported G1/G2 CRS in 86% pts (n=21) and G3/4 CRS in 5% pts when treated with humanized anti-CD19/BCMA CAR T. Neutropenia, Anemia and thrombocytopenia were observed in 86%, 62% and 62% pts, respectively.
In a phase I trial, Raje et al. (2019) reported G1/2 CRS in 24% pts (n=17) and G3 CRS in 5% pts when treated with PF-3515 (anti-CD3-BCMA) CAR T. Hepatotoxicity, thrombocytopenia, Neutropenia and pyrexia were observed in 18%, 24%, 18% and 18% pts, respectively.
In a phase I trial, Li et al. (2019) reported G1/2 CRS in 62% pts (n=16) and G3 CRS in 25% pts when treated with Dual-target BM38 CAR T. No dose-limiting (>/G3) toxicities were observed at a median follow up of 36 months.
Conclusion:
CAR T therapy is emerging as a treatment modality for RRMM. With promising initial results, there is evidence for multiple side effects, the most concerning and common one is CRS. The most frequently occurring CRS grade is G 1&2 (requiring symptomatic treatment), but G3 CRS is also reported which can be dose-limiting and life-threatening. Neurotoxicity, hematological abnormalities, hepatotoxicity and pyrexia are the other common side effects
Anwer:Incyte, Seattle Genetics, Acetylon Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie Pharma, Astellas Pharma, Celegene, Millennium Pharmaceuticals.: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.