Background: Plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) is a rare type of aggressive large B - cell Non Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) which was initially described in HIV positive individuals and later was also described in immune competent individuals. It constitutes about 2-3% of HIV associated malignancies. It was included as a distinct entity in WHO lymphoma classification in 2008.
Methods: The clinical features, HIV status, treatment details and outcomes of patients diagnosed with plasmablastic lymphoma during the period of January 2012 to December 2018 were retrospectively collected from the patient records and analyzed. The survival analysis was done by Kaplan Meier analysis and the comparison was done by Log Rank test.
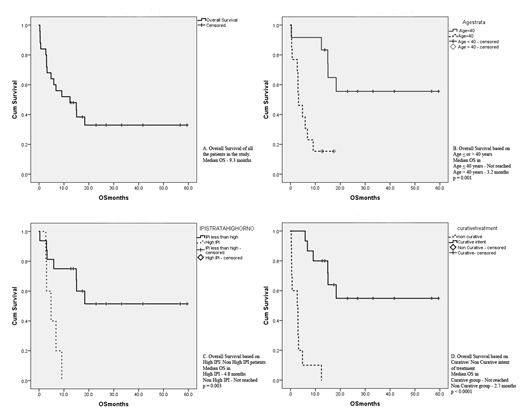
Results: Median age of 25 patients, included in the study was 41 years (Range 13 - 71 years). Males constituted 76% (n=19). HIV positivity was 72% (n=18). Stage 4 disease was present in 76% (n=19). Extra nodal involvement was seen in 96% (n=24), of which the common sites were gastrointestinal tract and bone. Out of 25 patients, 7 did not receive any treatment and 3 received metronomic oral chemotherapy due to poor performance status at presentation. Fifteen patients received chemotherapy on a curative intent. Infusional EPOCH chemotherapy was given in 13 patients. CHOP and CHOPE chemotherapy was given in one patient each. The median number of cycles was 6 (Range: 3 - 8). The overall response rate of patients treated on a curative intent was 80% (Complete response and partial response in 8 and 4 respectively). Three patients underwent high dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell rescue at first remission (2 HIV patients and 1 Non HIV patient). The median overall survival (OS) of the whole study population was 12.4 months with a median follow of 15.9 months. The Medial OS was not reached in the curative intent group and the 2 year OS of the curative group was 55% with a median follow up of 22.8 months. The factors adversely influencing the OS were Age > 40 years and High IPI (International prognostic index).
Conclusion: Plasmablastic lymphoma commonly presents as stage 4 disease with extra nodal involvement. It is more common in immunodeficient individuals especially HIV positive patients. Infusional EPOCH chemotherapy is a promising option which induces long term remission in fit patients.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.