Background
In patients taking oral anticoagulants and presenting with major bleeding, a rapid, effective, and safe reversal agent is urgently required. There are limited data of 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (4F-PCC) in the management of oral anticoagulant associated major bleeding.
Aims
The purpose of this study is to provide clinical experience regarding the effectiveness of 4F-PCC in the management of major bleeding induced by warfarin, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban.
Methods
A retrospective study of 43 patients who were admitted to our tertiary care center with major bleeding induced by oral anticoagulants and received 4F-PCC. The effectiveness of PCCs was assessed by using the International Society of Thrombosis and Hemostasis criteria. Descriptive statistics were utilized for analysis.
Results
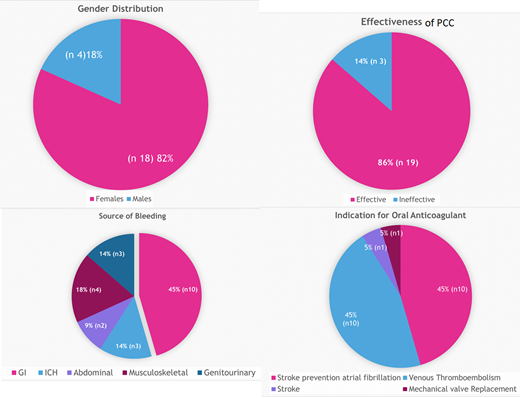
Forty-three patients were screened for inclusion into the study; notably, 21% of patients were excluded from further analysis. Of those included in this analysis (n=22), gastrointestinal bleeding accounted for (45.5%), followed by musculoskeletal bleeding (18.2%). The indication for anticoagulation was stroke prevention atrial fibrillation and VTE in the majority of the patients (45.5%), (45.5%) respectively. Patients received a mean of 2085.2 IU of PCC. Before and after 24 hours of PCC administration, the median INR resulted in a significant reduction (P;<0.001), with median aPTT (P;0.018). After final adjudication, the hemostatic effectiveness of PCC was assessed as effective in 19 patients (86.4%) and ineffective in three patients (13.6%). No major complications occurred during treatment or any serious adverse events.
Conclusions
PPC immediately and effectively reversed the effect of warfarin and rivaroxaban in patients with major bleeding and partial effect on the reversal of dabigatran.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.