Introduction
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is a distinct subtype of acute myeloid leukemia with a unique chromosomal translocation t(15;17), causing promyelocytic leukemia gene fusion with the retinoic acid receptor α gene (PML-RARα). Therapeutic All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) converts PML-RARα into transcriptional activator, induces APL differentiation. ATRA added during all treatment period have been reported to improve the outcomes of newly diagnosed APL. However, the benefits of maintenance therapy for patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) who achieved molecular complete remission (CRmol) are uncertain. In this study, we evaluated the efficacy and toxicity of daily ATRA monotherapy comparing with ATRA for 15 days with or without additional chemotherapy.
Materials and Methods
A retrospective data on 129 patients with newly diagnosed APL was conducted between February 2007 and August 2014. Induction and consolidation therapy were based on PETHEMA protocol. Among 113 patients (87.6%) who achieved CRmol following induction and 3 cycles of consolidation chemotherapy, 35 patients were treated daily with ATRA monotherapy (ATRAdaily), 39 with intermittent ATRA monotherapy for 15 days every 3 months (ATRA15), and 39 with ATRA plus continuous low-dose 6 mercaptopurine and methotrexate chemotherapy (ATRA/CT) for 2 years as a maintenance therapy. Event-free survival was defined as the time of CRmol to the development of events, which were defined by relapse, death, and toxicity that required hospitalization or dose reduction.
Results
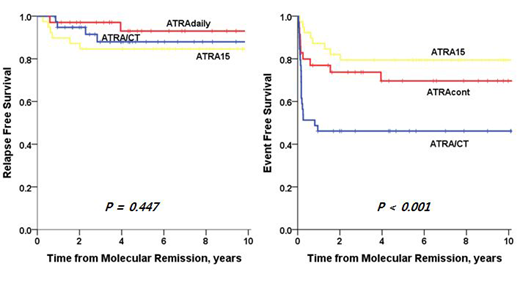
The median age of patients was 46 years (range, 18-80 years). There was no significant difference among the three groups (ATRAdaily, ATRA15, and ATRA/CT) in terms of age, sex, ECOG PS, WBC count, platelet count, fibrinogen, prothrombin time, and Sanz risk score. Among the 12 relapsed patients during maintenance therapy, 3 presented molecular relapse and 9 hematologic relapse. Six (15.4%) relapses were observed in the ATRA15 group, whereas 2 (5.7%) and 4 (10.3%) relapses were observed in the ATRAdaily and ATRA/CT groups, respectively. At a median follow-up of 75.3 months (range: 9.0-140.4 months) from CRmol, the 5-year relapse free survival (RFS) for patients receiving maintenance therapy with ATRAdaily was higher than that of the patients in the ATRA15 or ATRA/CT groups without a statistically significant difference, 93.0 ± 4.8%, 84.6 ± 5.8%, and 88.0 ± 5.7%, respectively (P = 0.447). The 5-year overall survival (OS) rate was 92.7 ± 5.1%, 94.6 ± 3.7%, and 91.2 ± 5.0% for the ATRAdaily, ATRA15, and ATRA/CT groups, respectively (P = 0.601). However, ATRA/CT group frequently had myelosuppression (n = 11, 28.2%). The 5-year EFS rate was 81.5 ± 7.6%, 86.4 ± 5.7%, and 51.7 ± 8.2% for the ATRAdaily, ATRA15, and ATRA/CT groups, respectively (P < 0.001). In the multivariate analysis, maintenance therapy in the ATRA/CT group compared to ATRAdaily showed a significantly lower EFS (HR = 2.14, 95% CI = 1.06-4.31, P = 0.023). ECOG PS ≥ 2 was also associated with lower EFS (P = 0.033). Sanz risk score was the only adverse prognostic factor for RFS, and OS (HR = 6.20, 95% CI = 1.29-29.90, P = 0.023; HR=5.30, 95% CI = 1.10-25.63, P = 0.038).
Conclusions
In conclusion, in the present study, ATRAdaily as a maintenance therapy for patients with newly diagnosed APL who achieved CRmol showed non-inferiority compared with ATRA/CT in terms of RFS and OS. In addition, ATRAdaily maintenance therapy can be a feasible and effective choice in terms of myelosuppression or hepatotoxicity. In the future, well-conducted systematic studies of long term survivorship, quality of life, and treatment-related complications are needed to confirm these observations.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.