Introduction
Novel agents such as ibrutinib, lenalidomide, and venetoclax are increasingly used in patients with relapsed/refractory lymphoma. A number of patients on these oral agents require radiation therapy (RT) either for palliation of their lymphoma symptoms or for management of another malignancy. There is no available information regarding the safety and outcomes of patients receiving RT and a novel agent concurrently. There is some theoretical concern for overlap in toxicities, yet there is no consensus on holding or continuing the oral agent during RT. Our goal was to characterize toxicities in patients with lymphoma receiving both RT and a novel agent.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective study of patients with lymphoma who received RT and either ibrutinib, lenalidomide, or venetoclax at the University of Pennsylvania between 1/2009 and 6/2018. Those who received one of these agents within one month of RT were included in the study and were required to have at least one encounter at least 14 days after completing RT to assess for toxicities. Patients who received the agent for less than 7 days and those also receiving chemotherapy were excluded. Toxicities that developed during and up to 3 months following radiation were recorded according to NCI Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v.4. Concurrent administration of the novel agent was defined as receiving the agent within 5 days or less of RT, whereas sequential administration was defined as having greater than a 5-day interval between RT and the agent. Rates of grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs) were compared between the concurrent and sequential groups using Fisher's exact test.
Results
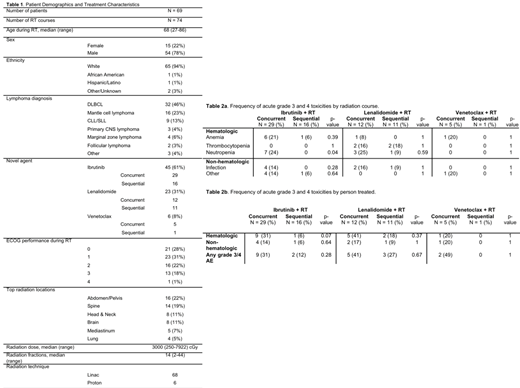
A total of 80 patients with lymphoma received one of the novel agents within one month of RT. After excluding cases where the novel agent was received for less than 7 days as well as those with inadequate follow up post-RT, a total of 69 patients with a corresponding 74 radiation courses were included (Table 1). The most common agent received was ibrutinib (61%), followed by lenalidomide (31%), and venetoclax (8%). The novel agent was administered concurrently with RT in 47 instances and sequentially in the remaining 28. Sixty-three (85%) of the RT courses were for treatment of lymphoma and the remaining 11 (15%) for other malignancies. The most common lymphoma diagnoses were DLBCL (46%), mantle cell lymphoma (23%), and CLL/SLL (13%). The median age was 68 (range: 27-86), and 79% were male. The median radiation dose was 30 Gy (range: 2-79) and the median fractions delivered was 14 (range: 2-44).
Twenty-one of 69 patients experienced acute (within 30 days of RT) grade 3/4 AEs (Table 2a and 2b). Overall, we observed similar rates of hematologic grade 3/4 AEs in our cohort as compared to historical studies of these novel agents in lymphoma patients (Barr et al., Haemotologica, 2018; Wiernik et al. J. Clin. Oncol, 2008). However, the rate of grade 3/4 neutropenia in patients receiving ibrutinib concurrently with RT (N=29) was significantly higher than in those receiving therapy sequentially (N=16) (24% vs 0%, p=0.04). There was otherwise not a significant difference in the prevalence of grade 3/4 hematologic or non-hematologic AEs in patients receiving any of the novel agents concurrently vs sequentially. Notable non-hematologic AEs in the entire cohort was infection (9%) and atrial fibrillation (4%), with the latter occurring only in the ibrutinib group. The novel agent was held or discontinued due to AEs in 15% of cases (8 patients on ibrutinib, 3 on lenalidomide) with no significant difference in rates between concurrent vs sequential administration. 59 of the 69 patients had follow-up within 30-90 days of completing RT, and only 4 of those experienced grade 3/4 AEs in that time period. Twenty patients transitioned to comfort-focused care or hospice within 2 months of completing RT.
Conclusion
To our knowledge, this is the first study to describe the safety of using novel oral agents in lymphoma patients receiving RT. Our data suggests that the use of ibrutinib with concurrent RT may be associated with an increased incidence of neutropenia, but the use of lenalidomide, and venetoclax with concurrent RT is not associated with significantly increased toxicities compared to sequential administration. Although concurrent therapy appears tolerated, further work is needed to corroborate our findings as our study is limited by the small size and heterogeneity of our cohort.
Hughes:AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genzyme: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Acerta Pharna/HOPA: Research Funding. Landsburg:Triphase: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau; Triphase: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Curis, INC: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Curis, INC: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Research Funding. Dwivedy Nasta:Roche: Research Funding; 47 (Forty Seven): Research Funding; Rafael: Research Funding; Millenium/Takeda: Research Funding; Debiopharm: Research Funding; Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; ATARA: Research Funding; Aileron: Research Funding. Gerson:Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy. Schuster:Merck: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Patents & Royalties: Combination Therapies of CAR and PD-1 Inhibitors with royalties paid to Novartis, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Loxo Oncology: Honoraria; Acerta: Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria; Nordic Nanovector: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding. Barta:Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Mundipharma: Honoraria; Takeda: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bayer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Honoraria; Merck: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Research Funding. Svoboda:AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Celgene: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kyowa: Consultancy; Merck: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.