Introduction
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant plasma cell disease and is considered a disease of older patients as the median age at diagnosis is 70 years. In recent years, the overall survival of patients with MM has improved due to the increasing number of treatment options and better supportive care. However, older patients (age >65) have not benefitted equally from the same gains. There is a paucity of information regarding clinical outcomes in this age cohort given that older patients are often under-represented in clinical trials and prospective studies. Real-world data may allows us to examine the trends in practice patterns over time and help us understand disparities in treatment options and overall patient outcomes in older patients with MM at a population level.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective population-based study using administrative data from the Institute of Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES), which maintains a central database of health records for all patients in the publicly funded health care system for the province of Ontario, Canada. All patients with newly-diagnosed multiple myeloma, identified using the ICD-O-3 code 9732/3 (Multiple Myeloma) between the years 2007-2017, were included to form the cohort. Autologous transplant within one year of diagnosis was captured in the database using a combination of physician billing codes and hospital procedure/discharge codes. Novel drugs usage for transplant ineligible patients was defined as the receipt of thalidomide, lenalidomide and bortezomib in any combination within one year of diagnosis. No treatment was defined as patients that did not receive a transplant, novel drugs or non-novel drugs (melphalan and cyclophosphamide) within one year following diagnosis.
Results
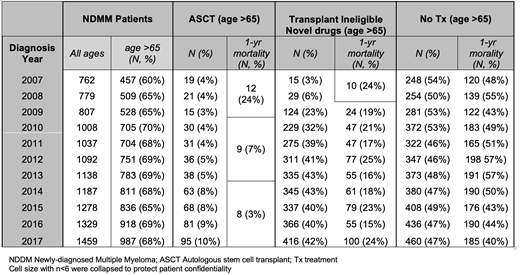
A total of 11,875 patients with newly-diagnosed myeloma were identified between the years 2007-2017. The proportion of newly-diagnosed MM patients who were older (age >65 years) increased from 60% of those diagnosed in 2007 to 68% of those diagnosed in 2017. The rates of autologous transplantation in older patients with MM increased from 4 to 10%. Overall those who underwent transplant had improved outcomes with decreasing one-year mortality from nearly 24% in 2007 down to 3% in 2017. Novel drugs were increasingly being used in older patients that were transplant ineligible with up to 42% receiving it within one year of diagnosis in 2017. In transplant ineligible older adults using novel drugs, one- year mortality ranged from 15% to 24%. The rates of older adults with newly-diagnosed MM not treated within one year of diagnosis was on average 49% although that number marginally declined from 54% in 2007 to 47% in 2017. Among those that did not receive treatment, 48% of individuals on average (range 40-57%) were not alive at one-year following diagnosis.
Conclusion
Our results demonstrate that although gains are being made in older adults with newly-diagnosed MM with increasing rates of transplantation and novel-drug usage over the last decade, there remains a sizeable cohort of older patients that do not receive any treatment within one year of diagnosis. While a limitation of our study may be the inclusion of some smouldering cases of myeloma, the mortality for older patients not treated continues to remain high with approximately half the patients not alive at one year following diagnosis. This study represents one of the largest cohort studies done to date over a decade demonstrating the ongoing low rates of no treatment and high rates of one-year mortality for older patients with MM. Further identification of factors associated with no treatment, transplantation and novel drug usage in older patients with MM are currently being explored.
Mian:Amgen: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria. Pond:Roche Canada: Employment, Other: Stock; Takeda (DSMC membership): Other: Honorarium.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.