Abstract
Introduction: CTL019 (tisagenlecleucel) is a chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy (CAR-T)for the treatment of relapsed or refractory (r/r) pediatric/young adult patients (pts) with B-cellacute lymphoblastic leukemia(ALL). Current treatments for r/r pediatric ALL (pALL) include clofarabine monotherapy (Clo-M), clofarabine combination therapy (Clo-C), blinatumomab (Blin), other salvage chemotherapies (SC), and allogeneic stem cell transplant (SCT). The prognosis for r/r pALL is poor and SCT is considered as the only potentially curative option. However, less than 50% of pts with multiple relapses achieve CR from existing treatments, and even fewer are eligible for and ultimately receive SCT. CTL019 is a potentially promising treatment option for pALL pts with multiple relapses, with complete remission (CR) rates between 69-95% based on data from phase I/II trials (ELIANA, ENSIGN, and CHP959). The current study aimed to compare the life year (LY) and quality-adjusted life year (QALY) gained using CTL019 vs. comparator treatments, and estimate the value-based prices for CTL019 at different incremental (incr) cost effectiveness ratios (willingness-to-pay [WTP] thresholds) for the treatment of r/r pALL from a US third-party payer perspective.
Methods: A partitioned survival model with monthly cycle and 3% discount rate was developed to assess the incr cost effectiveness of CTL019 compared to Clo-M, Clo-C, Blin, SC, and 2nd SCT, for the treatment of r/r pALL over a 20-year time horizon. The model included three health states: event-free survival (EFS), progressive disease, and death. Efficacy inputs (overall survival [OS] and EFS) for CTL019 were based on pooled data of three phase I/II single-arm trials. Efficacy inputs for the comparators were based on publications of clinical trial and SCT registry that enrolled similar pts (although with notable differences); Kaplan-Meier curves of OS and EFS, where available, were used to reconstruct proxy patient-level data. Parametric models were fitted to extrapolate EFS and OS for each treatment until year 5. Afterwards, the model assumed no additional progression, and that all pts alive at 5 years would experience the same mortality risk consistent with long-term survivors of pALL. Pre-treatment (lymphodepleting for CTL019 and induction therapy for SCT) and treatment costs (drug, administration, and hospitalization), adverse event (AE) costs, subsequent SCT costs, and medical costs for each health state were obtained from public databases and literature. All costs were inflated to 2016 USD. Utilities for each health state and disutilities for AEs were based on literature. Incr LY, incr QALY, and incr cost per QALY gained were estimated comparing CTL019 to each comparator. Value-based prices, defined as the price that would achieve the incr cost effectiveness ratios (WTP thresholds) of $100,000, $150,000, $200,000, and, $300,000 per QALY gained, were calculated for CTL019 vs. each comparator. Deterministic sensitivity analyses (DSA) were performed to test the robustness of the results.
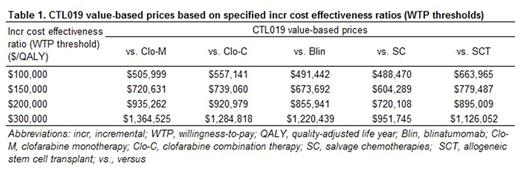
Results: Over a 20-year time horizon, treatment with CTL019 led to an increase of 4.62, 3.79, 3.68, 2.08 and 2.05 in discounted LYs and an increase of 4.29, 3.64, 3.64, 2.32 and 2.31 in discounted QALYs relative to Clo-M, Clo-C, Blin, SC, and SCT respectively. CTL019 value prices to reach a specified incr cost effectiveness ratio (WTP threshold) of $150,000/QALY ranged from $604,289 to $779,487 across comparators. The value prices ranged between $951,745 and $1,364,525 when the incr cost effectiveness ratio (WTP threshold) was set at $300,000/QALY (Table 1). Results from the DSA generally supported the base case findings, with the largest variation observed when time horizon and the parametric survival functions were varied. Compared to Clo-M, Clo-C, Blin and SC, CTL019 trials enrolled more severe pts who had failed more lines of prior therapies, which suggested that the estimated CTL019 LY and QALY benefits were conservative.
Conclusions: Compared to existing treatments, CTL019 showed promising efficacy results for the treatment of pediatric/young adult ALL pts, with incr QALY gains of 2.31-4.29. Using specified incr cost effectiveness ratios (WTP thresholds) from $100,000/QALY to $300,000/QALY, the value-based prices for CTL019 ranged from $488,470 to $1,364,525.
Hao: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Eldjerou: Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation: Employment. Yang: Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation: Other: Author is an employee of Analysis Group, which received consulting fees from Novartis for this study; Analysis Group Inc.: Employment. Qi: Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation: Other: Author is an employee of Analysis Group, which received consulting fees from Novartis for this study; Analysis Group Inc.: Employment. Globe: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.