Background: N9-GP is a glycoPEGylated rFIX designed to achieve higher FIX levels throughout the dosing interval. The paradigm™ clinical trials program included 115 participants in 5 studies, and demonstrated safety and efficacy of N9-GP in routine prophylaxis using annualized bleeding rate (ABR) as the standard primary efficacy measure. However, ABR as an outcome measure may not adequately discriminate the impact of different products and dosing regimens. Here we report peak/trough FIX activities achieved and the impact on ABR, target joint resolution, and mobility.
Methods: In the adolescent/adult trial, patients were blinded and randomized to receive N9-GP 40 IU/kg (n=29) or 10 IU/kg (n=30) once-weekly, with the goal of being able to compare the impact of high FIX peak/trough levels with those achieved with more standard prophylaxis. In the pediatric trial, all children (n=25) received 40 IU/kg once-weekly, which resulted in substantially higher FIX levels than achievable with currently available standard or extended half-life (EHL) FIX products. Post hoc analyses were performed to explore patient responses, particularly in those on prophylaxis prior to enrollment.
Results:
Factor levels: Routine prophylaxis with 40 IU/kg achieved the following mean steady state peak/trough levels according to patient age: age ≤6, 65.5%/15.4%; age 7-12, 71.4%/18.7%; age 13-17, 82.8%/23.7%; age ≥18, 97.9%/29.3%.
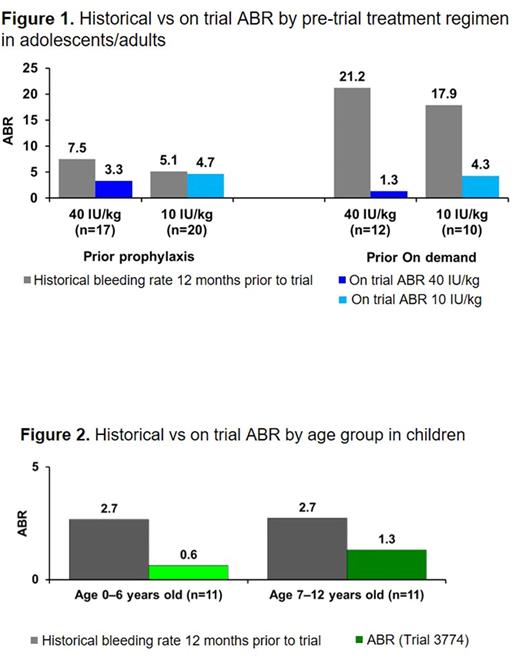
Bleeds: As previously reported, the median overall/spontaneous ABR in adolescents/adults receiving 40 IU/kg and 10 IU/kg was 1.04/0.00 and 2.93/0.97. When considering patients' prior treatment and adjusting for their historical bleeding rate, the estimated ABR in the 40 IU/kg arm was 49% lower than that of the 10 IU/kg arm. Despite ≥90% of adolescents/adults having preexisting arthropathy or target joints, 69% of those on 40 IU/kg had no spontaneous bleeds compared with 43% on 10 IU/kg. On 40 IU/kg, 59% (20/34) of spontaneous bleeds occurred in 2 patients with target joints. For the 22 adolescents/adults who continued into the ~1-year safety extension trial and remained on 40 IU/kg once-weekly, 18/22 (82%) remained spontaneous bleed-free. More than half (63%) were on standard prophylaxis prior to enrollment. Patients on prior prophylaxis randomized to 40 IU/kg reported a substantial reduction in ABR during the trial (Figure 1).
The overall median ABR for younger (age 0-6) and older (age 7-12) children was 0.0 and 2.0. While 40% had no bleeding episodes during the main phase of the trial (1+ years), 83% and 69% of younger and older children were spontaneous bleed-free. Furthermore, at follow-up (mean exposure 2.5 years; max ~3.8 years) in the extension trial, 75% and 69% remained spontaneous bleed-free. Through the extension, only 21 spontaneous bleeds were reported by 7 patients; of these, one older child with preexisting joint disease accounted for 12 of the bleeds (57%). For children, 88% were on prophylaxis prior to the trial; ABR was reduced on 40 IU/kg once-weekly in both younger and older children (Figure 2).
Resolution of target joints: More adolescents/adults randomized to 40 IU/kg vs 10 IU/kg experienced no target joint bleeds (67% vs 8%), and more target joints were resolved (90% vs 58%). Further, 56% of 9 preexisting target joints that developed on standard prophylaxis in 6 patients randomized to 40 IU/kg were bleed-free, compared with 0% of the 11 preexisting target joints in 7 patients randomized to 10 IU/kg. Two children (ages 9 and 11) had preexisting target joints on prior standard prophylaxis therapy; both were resolved during the main phase of the trial.
Quality of life: EQ-5D VAS was improved for all adolescents/adults (mean change, 8.2) and those on prior prophylaxis (9.0). Compared with baseline, fewer patients on 40 IU/kg at end of trial had any problems with walking (EQ-5D mobility: 52% baseline vs 24% end of trial; 47% baseline vs 13% end of trial on prior prophylaxis).
Conclusions: Therapy with N9-GP 40 IU/kg once-weekly leads to higher FIX activity levels throughout the dosing interval in both adolescents/adults and children compared with currently available therapies. Post hoc analyses show the impact of higher factor activity levels in greater likelihood of remaining spontaneous bleed-free over periods of years. Reductions in bleeding, target joint resolution, and improved mobility were seen even in patients treated with standard prophylaxis prior to trial enrollment.
Young: Novo Nordisk: Consultancy; CSL Behring: Honoraria. Carcao: Bayer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Baxter: Honoraria, Research Funding; Biogen: Honoraria, Research Funding; CSL Behring: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novo Nordisk: Honoraria, Research Funding; Octapharma: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Biotest: Honoraria. Kearney: Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Grifols: Research Funding; Novo Nordisk: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Bioverativ: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Seremetis: Novo Nordisk: Employment. Cooper: Novo Nordisk Inc.: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.