Abstract
Introduction:
Whilst relatively common in lymphoid malignancies, hypercalcaemia is an extremely rare complication of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). Previous case reports have described ectopic parathyroid hormone secretion, leukaemic bony invasion and the release of boneresorptivemediators as causes of hypercalcaemia in AML (GewirtzAM et al. Br JHaematology1983;31(12):1590,ZidarBL, et al.NEJM.1976;295:692). We describe a case of severe hypercalcaemia with acute kidney injury (AKI) accompanying a new diagnosis of AML, subsequently demonstrated to be secondary to leukaemic blast production of active vitamin D (calcitriol) with gross over-expression of vitamin D related genes. This represents a novel pathogenic mechanism causing hypercalcaemia in a myeloid malignancy.
Case Report:
AA, a 68 year old male presenting with fatigue and found to have circulating blasts was subsequently diagnosed with acutemyelomonocyticleukaemia(78% blasts on bone marrow biopsy). Additionally, he had marked hypercalcaemia (calcium 3.3mmol/L, normal range 2.1-2.6mmol/L) and AKI (creatinine 263umol/L, normal range 60-110umol/L). Given the rarity of AML-associated hypercalcaemia, extensive investigations were undertaken to elucidate the cause. In search of a second concurrent malignancy, AA underwent computed tomography and positron emission tomography scanning, with subsequent biopsy of FDG avid vocal cord nodules; but only benign pathology could be demonstrated. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels were appropriately suppressed (0.9pmol/L, normal range 1.6-6.9pmol/L) and levels of PTH-related peptide and serum ACE were normal (<2pmol/L, and 37units/L, normal range 20-70units/L, respectively). Inactive vitamin D, (calcidiol or 25(OH)D3) levels were also normal (88nmol/L, normal range 50-250nmol/L). However, the active vitamin D (calcitriol or 1,25(OH)2D3) level was grossly elevated beyond the upper limit of assay (>500pmol/L, upper limit of normal: 190pmol/L).
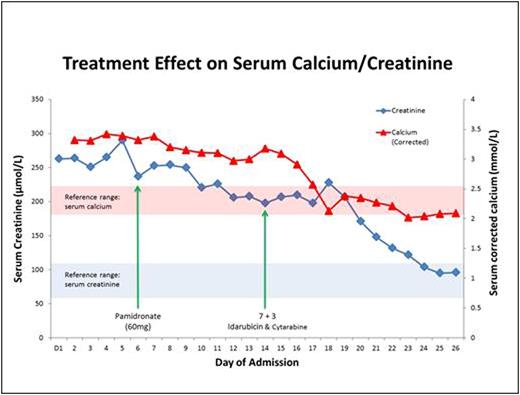
Both the hypercalcaemia and kidney injury proved refractory to multiple therapeutic strategies including aggressive hydration with an average of over 2.5L of crystalloid per day, as well as intravenouspamidronate. However, as depicted in Figure 1, there was a precipitous response following the initiation of chemotherapy (idarubicinandcytarabine, 7+3 regimen). Within several days, AA's serum calcium levels returned to normal levels, and his kidney function followed a similar pattern of improvement shortly thereafter. The rapid resolution of serum calcium levels also mirrored peripheral blast clearance, and repeat testing of calcitriol levels showed progressive improvement towards a normal concentration. AA achieved complete remission following induction chemotherapy and remains leukaemia free after consolidation chemotherapy and current maintenanceazacitidine. His hypercalcaemia has not recurred and his renal function remains normal.
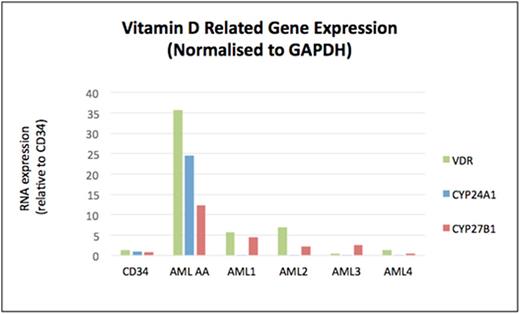
Having excluded other causes of hypercalcaemia and given the dramatic response to chemotherapy, we hypothesised that AA's AML blasts were secreting calcitriol. Accordingly, quantitative PCR was performed on AA's stored leukaemic cells for genes essential to vitamin D metabolism: the vitamin-D receptor (VDR), CYP24A1, and CYP27B1 (1-α-hydroxylase). RNA was extracted from AML cells using the QIAGEN RNeasykit. cDNAwas synthesised from 400ng of RNA using the Roche First Strand cDNASynthesis Kit. Gene expression was assessed by quantitative real-time PCR, relative to the housekeeping gene GAPDH. AA's leukaemia cells demonstrated markedly elevated expression of these vitamin-D related genes compared to healthy control CD34+ cells and four other independent primary AML cells (Figure 2, labelled AML 1-4), which were selected for absence of patient hypercalcaemia from our institution's tissue bank (Figure 2).
Conclusion:
Hypercalcaemia secondary to secretion of calcitriol can be a manifestation of lymphoid malignancies, however our case is the first documented occurrence of this phenomenon in a myeloid cancer. The PCR studies demonstrated striking overexpression of vitamin D related genes in leukaemia cells, resulting in the patient's hypercalcaemia and AKI. This finding represents a novel mechanism for a rare complication in AML.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.