Abstract
B cell receptor (BCR) signaling plays an important pathogenic role in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) enhancing homing and homeostasis of B-CLL cells and favoring the interaction with the pro-survival stromal lymph node microenvironment. Surface expression of CD69 is required to block the cells in lymphoid compartment while Sfingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 (S1PR1) is necessary for egress of cells to blood. BCR signaling inhibitors such as Ibrutinib and Acalabrutinib, (anti-bruton tyrosine kinase) or Idelalisib (anti-Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases ) represent a significant therapeutic advance in CLL. At least some of these drugs are distinctive to lead to an initial lymphocitosis due to rapid release of cells from lymphoid organs to blood, where they die. Changes in microRNAs expression characterize clinical progression of CLL with a strong decrease of miR-181b associated with the more aggressive phase of the disease. In this study we demonstrate that miR-181b is part of the BCR pathway in that it influences the anatomical redistribution of CLL cells from lymph nodes into the blood by balancing the expression of CD69 and S1PR1.
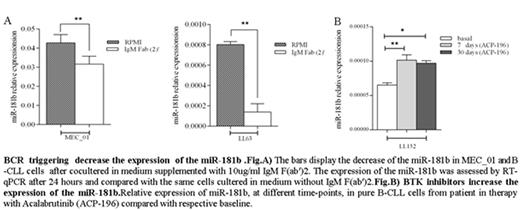
We co-cultured MEC_01 and pure B-CLL cells in medium supplemented or not with IgM F(ab')2, specific antibodies for BCR. We observed a significant decrease of miR-181b after 24 hrs of BCR stimulation compared with the same cells cultured in medium without IgM F(ab')2. To establish that this effect was due to the stimulation of the BCR, studies were performed on MEC_01 and in pure B-CLL cells treated separately with 1μM Ibrutinib or 1 μM Idelalisib, which are a potent BCR signaling inhibitors. After 1 hours of treatment the relative expression of miR-181b was assessed noting an increase of the transcription of miR, suggesting that the activation of BCR down regulate the expression of miR-181b. To confirm what we observed in vitro, RNA was isolated from B cells of the CLL patients at different time-point before and after treatment with a BTK inhibitor, Acalabrutinib (ACP-196). We observed a marked increase of miR-181b in the patients in therapy with this drugs compared with respective baseline. Since BTK inhibitors lead to the immediate release of CLL cells from lymphoid tissues to circulation, we evaluated whether this miRNA could be involved in this process. To test this hypothesis MEC01 cells were infected with either LV-miR-181b_coGFP or the LV-CTRL_coGFP after which migration was assessed in transwell assays. The Cells (5 × 105 cells/well) were seeded on top of the transwells and allowed to migrate for 4 h. S1P (100 nM) was added to the lower chamber as a chemo attractant. Transwell assay was performed to determine the migratory capacity of MEC-01 GFP+ cells, mimicking spleen (S1P-) vs blood (S1P+) compartments. Our data indicate that enhanced expression of miR-181b accelerate the migration of B-CLL cells. On the same cells we also evaluated the expression of S1PR1 and CD69. We observed that the restoration of miR-181b down regulated CD69 expression and increased the S1PR1. We also demonstrated that both proteins are direct targets and that the regulation on SIPR1 by the miR-181b occurs through a not canonical way.
In conclusion, our findings indicate miR-181b is down regulated by BCR stimulation in CLL cells and that its enhanced expression reduced CD69 while increased S1PR1 by direct targeting. This could facilitate the egress from lymphoid tissue to blood and in turn their death.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.