Abstract
Rigosertib (ON 01910.Na) is a member of a broader class of unsaturated sulfone kinase inhibitors capable of inducing profound mitotic spindle abnormalities, abnormal centrosome localization, G2-M cell cycle phase arrest and mitotic catastrophe, culminating in apoptosis. Rigosertib is a Ras mimetic that interferes with phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI-3K)/Akt, reactive oxygen species and Ras/Raf/polo-like kinase (PLK) signaling pathways. Although broadly cytotoxic against malignant cells, it is remarkably non-toxic for non-neoplastic cells. For this reason, this is a particularly attractive compound to test against neoplastic diseases of the bone marrow such as MDS and acute leukemia.
This is a report of an unexpected reduction in monoclonal IgG, during a subject participation in a Phase III, randomized study of rigosertib, in patients with MDS who have either failed to respond, or progressed after receiving hypomethylating agents (ONTIME Trial).
A 75-year-old man with CMML-2 had a CBC on day 1 of the trial that demonstrated leukocytosis, with absolute monocytosis, 7% blasts in the peripheral blood, Hgb of 9.4 gm/dl, and platelets of 7 K. He was transfusion dependent for both pRBCs and platelets. His chemistry panel demonstrated a high total protein of 9.9 (NL: 6.0 - 8.2 G/DL) with low albumin at 2.4 (NL: 3.5 - 5.0 G/DL); therefore, an SPEP/IPEP was performed, reporting the presence of monoclonal IgG kappa. Quantitative immunoglobulins showed an elevated IgG of 3594 mg/dl (NL: 596 - 1584 MG/DL). Serum free light chains were remarkable for an elevated Kappa fraction at 38.94 (NL: 0.33 - 1.94 MG/DL).
On day 1 of cycle 5 of rigosertib, he was started on pulse decadron for 2 months, after which his disease progressed to AML, and he died shortly thereafter. Neither his bone marrow biopsies, nor his hematological parameters demonstrated a response to treatment with rigosertib.
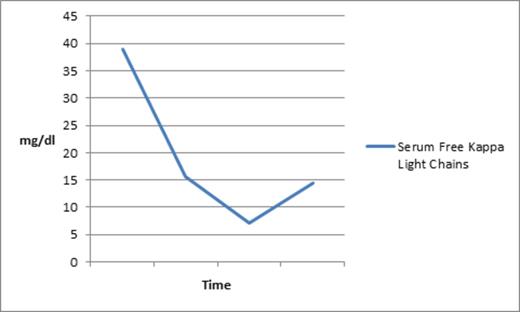
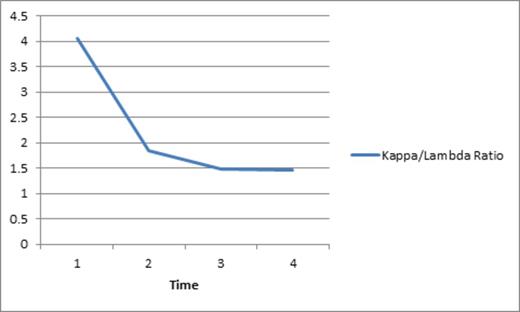
In contrast and interestingly, his total protein, serum kappa light chain load, and total IgG, all were drastically reduced shortly after initiation of rigosertib, as can be seen in the graph below depicting a substantial drop in his kappa light chain as well as the kappa/light chain ratio. Importantly, reduction in the monoclonal protein was noted prior to initiation of pulse decadron.
Even though his initial bone marrow biopsy did not note a monoclonal plasma cell population, a subsequent bone marrow reported a low-level involvement with a plasma cell dyscrasia, with kappa light chain restriction. His final bone marrow biopsy confirmed progression to AML, but the previously seen plasma cell dyscrasia was no longer present.
Conclusion: We are not aware of prior reports describing a similar effect of rigosertib on M-proteins. However, in vitro studies with rigosertib have demonstrated antitumor effects and induction of apoptosis in myeloma cell lines1. This observation merits further exploration of this agent in multiple myeloma.
References:
1. Reddy MV, et al. Discovery of a Clinical Stage Multi-Kinase Inhibitor Sodium (E)-2-{2-Methoxy-5-[(2',4',6'-trimethoxystyrylsulfonyl)methyl]phenylamino}acetate (ON01910.Na): Synthesis, Structure-Activity Relationship, and Biological Activity. J Med Chem, 2011, 54(18):6254-76.
Decrease in serum free kappa light chains following initiation of rigosertib.
Decrease in serum free kappa light chains following initiation of rigosertib.
Decrease in kappa/lambda ratio following initiation of rigosertib.
Decrease in kappa/lambda ratio following initiation of rigosertib.
Shammo:Onconova: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.