Abstract
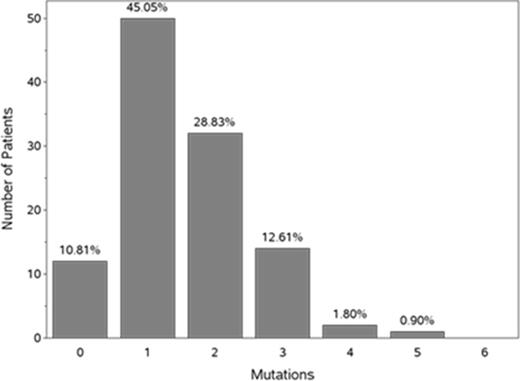
Background: The aging marrow stem cell demonstrates more somatic mutations when compared to younger marrow stem cells. These abnormalities have been noted in pts with MDS, as well as in patients with normal peripheral blood counts (Steensma et al, Blood 2015; Jaiswal et al, N Engl J Med 2014). Mutations are rarely detected in people <40 years of age, but increase each decade thereafter (Jaiswal et al, N Engl J Med 2014). Certain mutations (eg, DNMT3A, TET2, ASXL1, and SF3B1) are most prevalent in the oldest pts, and approximately 2% of pts with mutations associated with leukemia or lymphoma have age-related hematopoietic clonal expansion, which increases to 5-6% among patients ≥70 years of age (Xie et al, Nat Med 2014). In another study, 10% of elderly subjects had clonal hematopoiesis with somatic mutations and this number increased with increasing age (Genovese et al, N Engl J Med 2014). In a randomized, Phase III study with intravenous rigosertib (ONTIME) in patients with MDS failing HMA therapy, a much higher proportion of pts with bone marrow mutations was observed. The most frequent mutations were as follows: SRSF2 (28% of pts), TP53 (22%), ASXL1 (19%), SF3B1 (14%), and TET2 (14%) (Mufti et al, Blood 2014). Given that MDS is a disease of the elderly, and the importance of somatic mutations for diagnosis, prognosis, and (potentially) targeted therapy, we explored the correlation between age and type of somatic bone marrow mutation found in pts entered into ONTIME. Methods: We evaluated the bone marrow mutations in patients with MDS who were enrolled in ONTIME after failing to respond to a previous HMA. Bone marrow genomic DNA was isolated from single microscopic slides from 153 pts from ONTIME and subjected to sequence analysis of a "myeloid panel" comprising of 24 selected loci known to be frequently mutated in MDS and AML (Mufti et al, Blood 2014). We investigated these 24 myeloid abnormalities for their frequency in the identified age cohorts prior to study randomization to explore the correlation between age and the somatic mutation identified, specifically looking at pts older or younger than the mean age of pts with MDS in ONTIME (75 years). Results: Approximately 45% of patients had 1 mutation and an equal number had >1 (Figure 1).
Table 1 shows the most frequent clonal myeloid mutations in ONTIME, based on age above and below 75 years (the median age in ONTIME).
Incidence (%) of Patients with Specific Mutations, Age Above and Below 75 Years
| Mutation . | < 75 years (N=60) . | ≥ 75 years (N=51) . | Total (N=111) . | Fisher's Exact Test P-value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRSF2 | 27 | 29 | 28 | 0.83 |
| TP53 | 25 | 18 | 22 | 0.37 |
| ASXL1 | 20 | 18 | 19 | 0.81 |
| SF3B1 | 13 | 16 | 14 | 0.79 |
| U2AF1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 1.00 |
| TET2 | 12 | 16 | 14 | 0.59 |
| RUNX1 | 8 | 14 | 11 | 0.38 |
| DNMT3A | 8 | 12 | 10 | 0.75 |
| Mutation . | < 75 years (N=60) . | ≥ 75 years (N=51) . | Total (N=111) . | Fisher's Exact Test P-value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRSF2 | 27 | 29 | 28 | 0.83 |
| TP53 | 25 | 18 | 22 | 0.37 |
| ASXL1 | 20 | 18 | 19 | 0.81 |
| SF3B1 | 13 | 16 | 14 | 0.79 |
| U2AF1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 1.00 |
| TET2 | 12 | 16 | 14 | 0.59 |
| RUNX1 | 8 | 14 | 11 | 0.38 |
| DNMT3A | 8 | 12 | 10 | 0.75 |
Mutations by Months Since MDS Diagnosis and Duration of Prior HMA
| Mutation . | N . | Months from MDS Diagnosis median (range) . | Duration of HMA (mo) median (range) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| All analyzed pts | 111 | 18.5 (0.1-116) | 8.9 (1.2-65) |
| TP53 | 24 | 14.9 (0.7-116) | 13.0 (1.2-36) |
| SF3B1 | 16 | 29.4 (7.5-63) | 13.0 (1.2-36) |
| TET2 | 15 | 22.6 (0.1-63) | 11.4 (2.0-36) |
| SRSF2 | 31 | 17.2 (6.6-116) | 6.4 (3.0-35) |
| ASXL1 | 21 | 15.7 (4.9-66) | 8.2 (2.8-44) |
| DNMT3A | 11 | 15.1 (7.4-36) | 6.5 (4.2-30) |
| Mutation . | N . | Months from MDS Diagnosis median (range) . | Duration of HMA (mo) median (range) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| All analyzed pts | 111 | 18.5 (0.1-116) | 8.9 (1.2-65) |
| TP53 | 24 | 14.9 (0.7-116) | 13.0 (1.2-36) |
| SF3B1 | 16 | 29.4 (7.5-63) | 13.0 (1.2-36) |
| TET2 | 15 | 22.6 (0.1-63) | 11.4 (2.0-36) |
| SRSF2 | 31 | 17.2 (6.6-116) | 6.4 (3.0-35) |
| ASXL1 | 21 | 15.7 (4.9-66) | 8.2 (2.8-44) |
| DNMT3A | 11 | 15.1 (7.4-36) | 6.5 (4.2-30) |
Mufti:Onconova Therapeutics Inc: Research Funding. Silverman:Onconova Therapeutics Inc: Honoraria, Patents & Royalties: co-patent holder on combination of rigosertib and azacitdine, Research Funding. Best:Onconova Therapeutics Inc: Research Funding. Fructman:Onconova Therapeutics Inc: Employment. Azarnia:Onconova Therapeutics Inc: Employment. Petrone:Onconova Therapeutics Inc: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.