Abstract
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) is a heterogeneous familyof entities with a worse prognosis, stage by stage, than theirB-cell counterparts. Fasting blood glucose (FBG) level at diagnosis has recently been described as a novel, independent prognostic factor for survival in patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma (NKTCL). The goal of this study is to retrospectively investigatethe prognostic value of FBG at lymphoma diagnosis in the survival of patientswith PTCL.
A total of 250 cases of aggressive, non-primary cutaneous PTCLdiagnosed at our institution between January 1997 and December 2012 were reviewed,reevaluated according to their morphological, immunologicaland clinical characteristics, and reclassified according tothe 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Characteristics are presented descriptively. For the evaluation of FBG, patients were divided in 2 categories; those patients with an FBG at diagnosis >100 mg/dl (hyperglycemia) and those with an FBG at diagnosis <100 mg/dl (normoglycemia). Overall survival (OS) was defined as the time elapsed between lymphoma diagnosis and death or last follow-up. The Kaplan-Meiermethod was used to estimate OS curves, which were then comparedusing the log-rank test. P-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
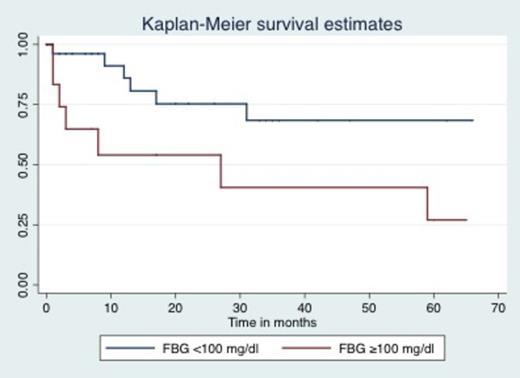
According to the new WHO classification, 104 cases (41%) were classified as adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL), 103 cases (41%) as PTCL, unspecified (PTCLU), 26 cases (11%) as anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), 10 cases (4%) as extranodal NKTCL, nasal type, 4 cases (2%) as angioimmunoblastic lymphoma (AIL), 2 cases (1%) as ALK-positive ALCL, and 1 case (0.4%) as hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma. The median age at diagnosis was 57 years (range 14-92 years); 47% of patients were >60 years. The male-to-female ratio was 1:1. ECOG performance status >1 was seen in 51%, LDH was elevated in 67%, advanced stage was seen in 73%, and >1 extranodal sites were seen in 22% of the patients. Bone marrow involvement was reported in 30% and B symptoms in 64% of patients. FBG >100 mg/dl was seen in 34% and FBG <100 mg/dl in 66%. An International Prognostic Index (IPI) score 3-5 was seen in 52%, and a Prognostic Index for PTCLU (PIT) score of 2-4 in 62%. Response evaluation was performed only in patients who received chemotherapy (n=161). The overall response rate (ORR) was 47% (n=76) with complete response (CR) in 32% (n=52) and partial response (PR) in 15% (n=24). FBG was no associated with ORR or CR (p=0.25 and p=0.43, respectively. We then evaluated FBG separately in patients with ATLL and PTCL except ATLL. In ATLL patients, the median OS was 8 months with a 3-year OS of 33%. In PTCL patients, the median OS was 17 months with a 3-year OS of 49%. FBG >100 appeared as an adverse prognostic factor only in PTCL patients with a median OS that was not reached vs. 27 months in patients with FBG <100 mg/dl (Figure; log-rank p=0.035). No difference was seen in patients with ATLL; patients with FBG >100 mg/dl has a median OS of 16 months vs. 18 months in patients with FBG <100 mg/dl (log-rank p=0.95).
Based on the results of our single-center retrospective study, FBG >100 mg/dl appears as a prognostic factor in PTCL but not in patients with ATLL. Additional studies are needed to investigate the role of hyperglycemia in patients with PTCL, and to evaluate if controlling hyperglycemia during therapy could improve the survival on such patients.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.