Abstract
Abstract 4851
Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma (PMBL) is an uncommon disease, characterized by aggressive and invasive course but with a good prognosis after anthracycline-based chemotherapy. In the PET era the role of consolidation radiotherapy is under debate and, despite CD20 expression, the efficacy of Rituximab is still unclear.
We retrospectively analyzed the outcome of 36 consecutive patients (pts) affected by PMBL treated in the last 10 years at our institution. We focused on anti-CD20 antibody efficacy when added to chemotherapy and on the role of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) in PET positive pts after first-line treatment.
From June 2000 to March 2011 36 pts with biopsy proven PMBL referred to our institution. Median age was 35 years (range: 18–68); 21 pts (58%) were female and a mediastinal bulk at diagnosis was documented in 33 pts (92%). B-symptoms were reported in 16 cases (44%) and an extra-nodal involvement in 19 cases (53%). Age-adjusted IPI score was ≥ 2 in 12 pts (33%). For all patients first line treatment consisted in a third generation anthracycline-based chemotherapy (VACOP-B), with the addiction of 6 Rituximab doses in 15 pts (42%). Pts obtaining complete remission (CR) with negative PET after (R)-VACOP-B were consolidated by radiotherapy (RT), while pts in partial remission (PR) with residual FDG uptake underwent a second-line chemotherapy with 3 DHAP cycles followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT).
In the whole cohort, after first-line therapy overall response rate (ORR) was 97%, with a CR rate of 39%. RT was therefore performed in 14 PET-negative pts. 2/14 pts experienced early relapse and only one of them obtained a second CR after salvage therapy, while the non-responding patient died because of progressive disease. Twenty-one pts (58%) showed a residual FDG uptake after (R)-VACOP-B and underwent second-line therapy. Nineteen pts responding to second-line therapy achieved ASCT, while 2 pts progressed and died after salvage therapy. ORR after ASCT was 86% with a CR rate of 71%. Post-ASCT RT was performed in 10 pts, 7 CR and 3 PR; two PR pts converted to CR after RT. With a median follow-up of 66 months (range: 13–142) 2-year overall survival (OS) and progression free survival (PFS) were respectively 94% and 89%.
Among the 15 pts receiving first-line chemotherapy containing Rituximab, ORR after R-VACOP-B was 93% with a CR rate of 40%. RT was therefore performed in 6 PET-negative pts. 1/6 pts experienced early relapse and died of progressive disease. One patient showed progressive disease after R-VACOP-B and underwent second-line therapy with ASCT, obtaining CR. Eight pts (53%) showed a residual FDG-uptake after R-VACOP-B and underwent second-line therapy and ASCT. ORR and CR rate after ASCT were 100% and 75% respectively. Two pts in PR after ASCT converted to CR after RT.
Among the 21 pts receiving chemotherapy without Rituximab, ORR after VACOP-B was 100% and CR rate was 38%. RT was therefore performed in 8 PET-negative pts; one of them experienced early relapse and obtained a second CR after salvage therapy. Thirteen pts (62%) showed a residual FDG-uptake after VACOP-B and underwent second-line therapy. Eleven pts responding to second-line therapy achieved ASCT, while 2 pts progressed and died after salvage therapy. ORR and CR rate after ASCT were 77% and 69% respectively.
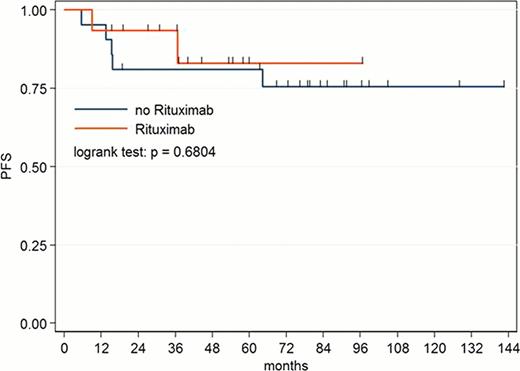
No statistically significant difference in ORR, CR rate, OS and PFS (Figure 1) was found between pts treated with Rituximab plus chemotherapy and pts treated with chemotherapy alone.
These data substantially confirm the satisfactory outcome of PMBL, with a 2-year OS and PFS of 94% and 89% for the entire cohort. We registered a residual FDG uptake after first line chemotherapy in a proportion of pts higher than expected (58%). This subgroup of pts clearly take advantage from second line chemotherapy followed by ASCT, obtaining a CR rate of 71%. The addiction of Rituximab to first line chemotherapy instead does not seem to improve PMBL pts outcome in this small and retrospectively analyzed population. The role of immunotherapy in this rare lymphoma subtype and the chance to safely avoid RT consolidation in PET negative pts need to be further investigated in wider prospective trial.
PFS of PMBL pts treated with first line chemotherapy with or without addiction of Rituximab
PFS of PMBL pts treated with first line chemotherapy with or without addiction of Rituximab
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.