Abstract
Abstract 4525
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation (Allo-SCT) is a treatment option in aggressive histology lymphoma (AG-NHL) patients who have either failed or relapsed after autologous SCT (ASCT) or if the potential for long term disease control after ASCT is limited. There is limited data in literature regarding the long term outcome of allo-SCT in AG-NHL.
We did a retrospective analysis of all aggressive histology patients who underwent Allo-SCT between 1989 and 2009 at our centre. A total of 41 patients with AG-NHL [diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and variants, follicular lymphoma grade 3 (FL3), biopsy proven aggressive transformation of indolent lymphoma (TRIL)] underwent Allo-SCT. All patients were in a chemosensitive remission at time of transplantation. The conditioning regimen was BU-CY in the majority (36 or 88%) of patients and 3 patients had reduced intensity transplantation (RIC) with fludarabine-based regimens. GVHD prophylaxis was cyclosporine and methotrexate until 2009 and was cyclosporine and mycophenolate mofetil after that. Alemtuzumab was used in matched unrelated donor (MUD) transplants in 5 (12%) cases.
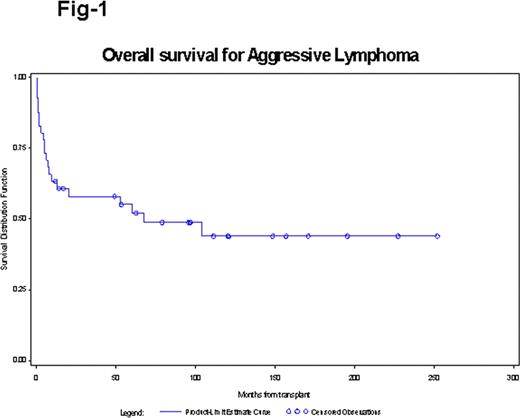
There were 22 (54%) males and 19 (46%) females. The median age at BMT was 48 years (range: 20–65). Fifteen (37%) had DLBCL, 19 (46%) had TRIL and 7 (17%) had FL3. Fifteen (37%) patients had received 2 or less lines of chemotherapy and 26 (63%) had received more than 2 lines of therapy at time of transplantation. The median number of chemo regimens was 3 (range: 1–7). The chemotherapy regimens included prior anthracyclines in 40 (98%), prior platinum in 26 (63%) and prior mini BEAM in 19 (46%). Six (15%) patients had received Rituximab and 9 (22%) had received prior RT. Seven (17%) patients had prior ASCT. Thirty-five (85%) of patients received matched related donor transplant whereas 5 (12%) received MUD transplant. The graft source was bone marrow in 33 (80%) and peripheral blood stem cells in 8 (20%). Grade 1–2 acute GVHD was seen in 53% and grade 3–4 in 9%. Chronic GVHD was seen in 51% patients. With a median follow up of 49 months and 96 months in those who are alive, five (12%) patients have relapsed, 20 (49%) patients are alive and in remission. Non relapse mortality (NRM) was 16/41 (39%) and predominantly related to infection. The overall survival (OS) and progression free survival (PFS) of the entire cohort at 60 months was 55% (Fig-1). Patients, who had achieved CR pre-allo-SCT (compared to PR) had a statistically significantly improved PFS and OS (100% survival for those who were in CR). In multivariate analysis, number of chemotherapy regimens (≤2) was associated with improved OS (p=0.015) and presence of chronic GVHD showed a trend towards significant OS (p=0.052)
With a median follow up of 96 months in survivors, myeloablative allo-SCT is associated with durable remission in patients with chemosensitive AG-NHL. Results are less favourable in patients who have received multiple prior regimens. NRM remains a significant concern with myeloablative regimens. We believe there is a role for myeloablative regimens and research should focus on ways to reduce NRM in this setting.
Gupta:Incyte: Honoraria, Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.