Abstract
Abstract 2955
The enzyme uridine diphospho glucuronosyltransferase 2B17 (UGT2B17), localized on chromosome band 4q13, glucuronidates various endogenous compounds and xenobiotics, in particular androgens. The gene UGT2B17 shows a remarkable copy number variation (CNV) and, of all genes, by far the highest difference in mRNA expression between the Asian and Caucasian normal populations. Several reports indicate a role of UGT2B17 in cancer progression and moreover, in drug response. Furthermore, UGT2B17 has immunologic effects as a minor histocompatibility antigen. However, its role in multiple myeloma has not yet been investigated.
We analyzed the UGT2B17 CNV by specific PCR in a retrospective series of 142 Caucasian patients diagnosed with multiple myeloma. Median patient age was 57.3 years at diagnosis, 40.1% were female and 59.9% male. Paraprotein was IgG in 44.4% and IgA in 22.5%. Cytogenetic aberrations (data available in 115 patients) were del13q in 40.5%, t(11;14) in 26.1%, t(4;14) in 5.3% and del17p in 7.7%. Treatment consisted of autologous or allogeneic stem cell transplantation in 72 (50.7%) patients. The remaining patients received various conventional dose regimens. We compared UGT2B17 CNV with relevant clinical and molecular markers for prognosis and with a sample of 449 healthy donors.
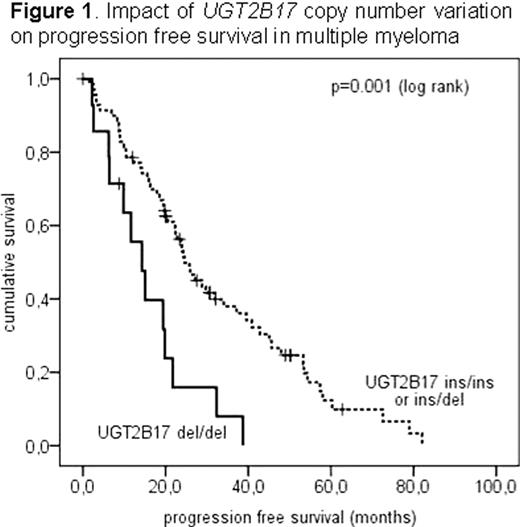
Distribution of the CNV in multiple myeloma was 15.5% double deletion (del/del), 43.0% heterozygous (ins/del) and 41.5% wild type (ins/ins). This did not differ significantly from 10.7% del/del, 46.3% ins/del and 43.0% ins/ins within healthy donors. The UGT2B17 del/del genotype was significantly associated with poor clinical outcome. Median progression free survival (PFS) was 14.3 months for del/del patients and 25.8 months for patients having one or two UGT2B17 alleles (HR 1.70; 95%CI 1.23–2.31; p=0.001) (Figure 1). Median overall survival (OS) was 43.9 months for del/del compared to 72.5 months in patients with ins/ins or ins/del (not significant). There was no significant difference in PFS or OS between wild type and heterozygous genotype. We did not observe an association of UGT2B17 CNV with any other prognostic molecular or cytogenetic markers in multiple myeloma. In subset analysis, the impact of UGT2B17 del/del was more pronounced in male patients and in patients receiving conventional dose therapy. Importantly, the impact of the deletion genotype on PFS was independent from ISS stage, sex, chromosomal aberrations, paraprotein, and stem cell therapy in multivariable analysis (HR (del/del) 2.87; 95%CI 1.62, 5.07; p<0.001).
We conclude that UGT2B17 double deletion is a novel independent prognostic marker for multiple myeloma. The enzyme has various roles in androgen and drug metabolism, cancer progression and histocompatibility. Further analyses are warranted to investigate the functional impact and potential therapeutic consequences.
Impact of UGT2B17 copynumber variation on progression free survival in multiple myeloma
Impact of UGT2B17 copynumber variation on progression free survival in multiple myeloma
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.