Abstract
Abstract 1340
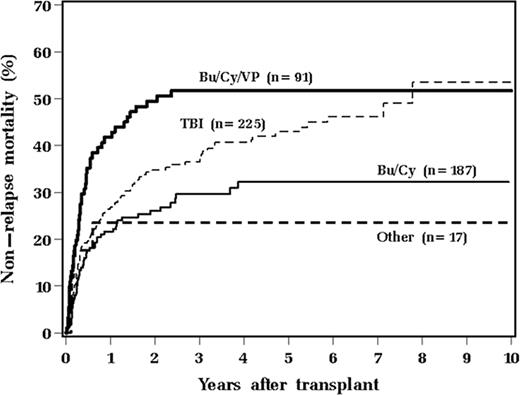
We analyzed results of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from 1/2000 to 1/2009 in 520 adult patients, receiving either bone marrow or peripheral stem cells, in order to identify factors associated with non-relapse mortality (NRM). Median age at transplant was 47 years (range 18–70). Median follow up was 43 months (range 5–122 months). Two hundred eighty four (55%) patients were male. Diagnoses included: acute myeloid leukemia 210 (40%), acute lymphoblastic leukemia 68 (13%), myelodysplastic syndrome 66 (13%), non-Hodgkin or Hodgkin lymphoma 64 (12%), chronic myelogenous leukemia 45 (9%), or other (13%). High scores (≤3) on hematopoietic cell transplant-specific comorbidity index were identified in 162 (31%) patients. For preparative regimens, 187 (36%) received BuCy (busulfan 1mg/kg oral given every 6 hours × 16 doses days -8 to -4, followed by cyclophosphamide 60mg/kg × 2 days -3 to -2), 91 (18%) received BuCyVP (busulfan 1mg/kg oral every 6 hours × 16 doses days -9 to -5, followed by etoposide 60mg/kg days -5 to -4, then cyclophosphamide 60mg/kg days -3 to -2), 225 (43%) received TBI-based therapy, and 17 (3%) received other therapy. Two hundred ninety five (57%) underwent related transplant. A majority (67%) received stem cells derived from bone marrow.
Factors associated with poor overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival (RFS) on multivariate analysis included male recipient (p=0.001, p=0.003, respectively), older age at transplant (p=0.048 for RFS), high comorbidity score (p<0.001, p<0.001), more prior chemotherapy regimens (per 1 regimen increase, p=0.22, p=0.02 respectively), and BuCyVP compared to BuCy (p=0.007, p=0.021).
Long-term follow-up of a large cohort of patients indicates that compared to BuCy, BuCyVP is associated with significantly higher NRM and lower OS and RFS.
Sweetenham:Pfizer: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.