Abstract
Objectives To evaluate the prevalence and association with clinical features of FLT3 internal tandem duplication (FLT3-ITD) in patients with newly-diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL).
Methods A total of 103 APL patients were screened by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for FLT3-ITD.
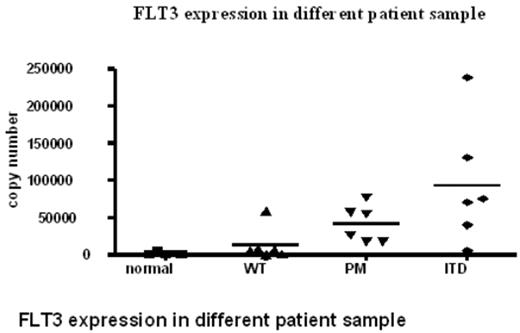
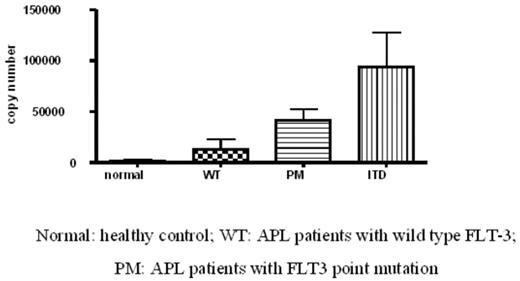
Results FLT3-ITD mutations were identified in 19.4% (20/103) patients. The FLT3-ITD was associated with short/variant form of PML-RARα isoforms (p<0.0001). Among 20 patients with FLT3-ITD, 16 patients presented with short, 2 with variant and 2 with long form of PML-RARα isoforms. The expression level of FLT3 via quantitative real-time RT-PCR was significantly increased in patients with FLT3-ITD (p<0.05). Patients with FLT3-ITD also presented significantly increased initial peripheral white blood cell (WBC) count (p<0.01), especially in patients with short/variant PML-RARα isoforms (p=0.015). For patients with long form PML-RARα, there was no significant difference in initial WBC count. For clinical outcome, 90% (18/20) of FLT3-ITD positive patients obtained complete remission and 16 evaluable patients (2 lost follow-up) remained in first remission with relatively short follow-up (median 26 months, 11-47), which was not significantly different from patients without FLT3-ITD.
Conclusion FLT3-ITDs were frequently identified in patients with newly diagnosed APL. FLT3-ITD was associated with short/variant form of PML-RARα fusion gene and increased initial WBC. No significant impact of FLT3-ITD on treatment outcome was observed with limited follow-up.
Association of FLT3-ITD and PML-RARα isoforms in patients with APL
| . | No . | FLT3-ITD+ . | FLT3-ITD− . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long | 57 | 2(3.5%) | 55(96.5%) |
| Short | 41 | 16(39.0%) | 25(61.0%) |
| Variant | 5 | 2(40%) | 3(60%) |
| Total | 103 | 20(19.4%) | 83(80.6%) |
| . | No . | FLT3-ITD+ . | FLT3-ITD− . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long | 57 | 2(3.5%) | 55(96.5%) |
| Short | 41 | 16(39.0%) | 25(61.0%) |
| Variant | 5 | 2(40%) | 3(60%) |
| Total | 103 | 20(19.4%) | 83(80.6%) |
FLT3 expression in different patient sample
FLT3 expression in different patient sample
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author