Abstract
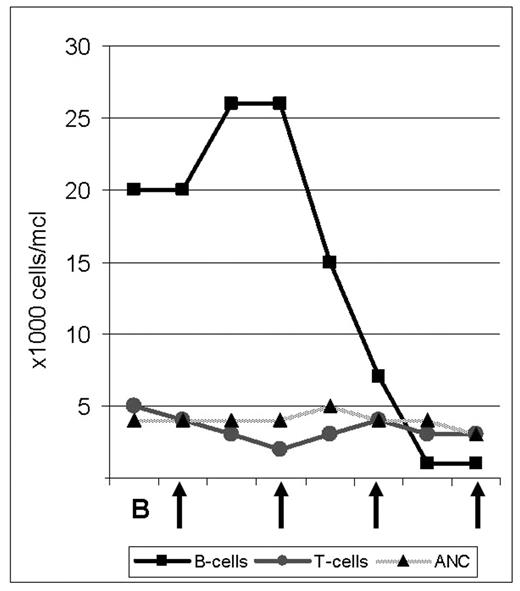
The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib is FDA approved for use in Multiple Myeloma and has shown promising single agent activity in patients with relapsed Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL), of whom 30–50% respond. We initiated a phase II study investigating the combination of bortezomib (B) with rituximab (R) and dose adjusted (DA), infusional EPOCH chemotherapy (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide) in patients with untreated MCL. Patients are treated with one cycle of B 1.5 mg/m2 i.v. on days 1, 4, 8, and 11; followed by 6 cycles of DA-EPOCH-R-B induction therapy. Patients who achieve at least PR are then randomized to receive B maintenance therapy for 18 months versus observation followed by B if progression occurs. We obtain lymph node biopsies before initiating treatment and on day 2, 12–24 hours after the first dose of bortezomib. In order to analyze the molecular effects of B on tumor cells and to identify predictors of response we plan extensive molecular studies including gene expression profiling and proteomic analysis. Here we report on the effect of single agent B in a 64 year old African American male with leukemic MCL. The patient had been well until a few months prior when he underwent unrelated surgery and was found to have mild anemia and lymphocytosis. When he presented to our institution he had a WBC of 25K/μl, absolute lymphocyte count 19K/μl, Hb 11.7g/dl and platelets 164K/μl. Blood smear revealed medium to large lymphocytes with a high n/c ratio and folded, indented nuclei with prominent nucleoli. Flow cytometry was consistent with MCL. Bone marrow examination showed up to 60% cellularity composed predominantly of an interstitial infiltrate of Cyclin D1 positive lymphocytes. Physical exam and CT scan showed minimal lymphadenopathy but a large spleen measuring 19 cm in cranio-caudal dimension. During his work-up, the lymphocyte count increased further and he became progressively anemic. After informed consent, we initiated the first cycle with single agent B. Following doses #2 and #3, the patient reported grade III–IV fatigue and was briefly hospitalized. At the same time his lymphocyte count dropped from a high of 29K/μl to 15K/μl (day 5, 24 hours after dose #2), to 3,700/μl (day 9) to 2,200/μl (day 12). Flow cytometric analysis showed that B predominantly depleted the leukemic cells; the CD19+ cells dropped from a high of 26K/μl to less than 1,000/μl (day 12 and 14) while the number of T-cells remained in the normal range (Figure). The ANC was unaffected by B and the platelet nadir was 112K/μl. The impressive single agent activity and apparent tumor selectivity of bortezomib in MCL as exemplified by this patient’s response are encouraging. Analyses to characterize the molecular effects of B in the lymphoma cells are ongoing and may help identify the molecular basis for the potent anti-tumor effects of B in MCL.
Author notes
Corresponding author