Abstract
In recent years, the treatment paradigm for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has moved away from chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) toward the use of novel targeted agents. Commercially available drugs, including Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitors and the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax, often used in combination with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies, are now the mainstay of therapy both in the frontline and in relapsed settings. As the landscape for CLL management evolves, therapeutic endpoints need to be redefined. Detection of measurable residual disease (MRD) is a sensitive tool to identify disease burden following treatment with several therapeutic regimens in CLL (including CIT, venetoclax-based regimens, and cellular therapies), and it has demonstrated prognostic value. Despite recent advances, the utility of MRD-directed therapy and attempts to eradicate it in routine clinical practice remain debated. There is little comparative data from clinical trials on the best assay to determine undetectable MRD (U-MRD) and whether its monitoring can lead to changes in treatment strategies. Our review discusses the definitions of MRD, assays for its detection, and its impact on long-term survival outcomes for patients with a CLL diagnosis.
Learning Objectives
Review the definitions, terminology, and methods for detection of measurable residual disease (MRD) in CLL
Review current data using undetectable measurable residual disease and its potential prognostic role for survival outcomes
Discuss potential clinical applications of current findings from clinical trial data and areas for further study
Introduction
Treatments for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have shifted from chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) to novel targeted therapies with the approval of the first-in-class Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi), ibrutinib,1 the second-generation covalent BTKis acalabrutinib2 and zanubrutinib,3 and the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax.4-7 Despite improvements in survival outcomes, CLL remains incurable, and patients may ultimately require treatment with multiple lines of therapy.
Measurable residual disease (MRD) has been used in several hematologic malignancies with demonstrated prognostic value. In CLL, MRD has demonstrated prognostic value, prompting the study of several MRD response adapted therapies. In this review, we define MRD, discuss MRD assays, and examine clinical outcomes with novel targeted therapies (Table 1) and novel doublet/triplet combination currently under development (Table 2). Finally, we discuss the role of MRD testing in clinical practice.
Summary table of U-MRD rates and outcomes of pivotal clinical trials in patients with treatment-naive and relapsed/refractory CLL
| Trial . | Phase . | Treatment setting . | Treatment . | MRD endpoint . | MRD detection method . | MRD detection level . | % U-MRD PB . | % U-MRD BM . | PFS/mPFS . | OS/mOS . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLL823 | 3 | TN | FC FCR | Secondary | Flow cytometry ASO-PCR | 10−4 | 35% 63% | 28% 44% | 32.9 mo 56.8 mo | 86 mo NR |
| NIH24 | 2 | TN/RR | I | Exploratory | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 10.2% | 8% | 5-year: TP53 cohort: 58.2% Elderly cohort: 81.2% | 5-year: TP53 cohort: 75.7% Elderly cohort: 83.85% |
| E191221 | 3 | TN | IR FCR | Exploratory | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 7.9% 30.3% | NA | 5-year: 78% 51% | mOS: NR NR |
| ELEVATE-TN25 | 3 | TN | A AO CO | Exploratory | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 7% 49% 61% | 0% 61% 10.9% | 48 mo: 77.9% 87% 25.1% | mOS: NR NR NR |
| CLL147 | 3 | TN | VO CO | Secondary | ASO-PCR | 10−4-10−6 | 39.6 mo: 81% 49.5% | 17.1% 56.9% | 5-year: 62.6% 27% | 5-year: 87% 87% |
| FLAIR27 * | 3 | TN | FCR IR | Secondary | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 75% 10% | 46% 4% | mPFS: 67 mo NR | mOS: NR NR |
| CAPTIVATE: MRD28 * | 2 | TN | IV + Placebo IV + I | Secondary | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 75% | 68% | 4-year: 88% 95% | 4-year: 100% 98% |
| CAPTIVATE: Fixed Duration29,30 | 2 | TN | IV | Secondary | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 77% | 60% | 95% at 24 mo | 98% at 24 mo |
| GLOW32 | 3 | TN | IV CO | Secondary | NGS | 10−4, 10−5 | 43.4% 18.6% | 40.6% 7.6% | 30 mo: 86.7% 35.5% | mOS: NR NR |
| MDACC31 | 2 | TN | IV | Secondary | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | NA | 75% | 3-year: 93% | 3-year: 96% |
| CLL1333 | 3 | TN | FCR/BR VR VO VIO | Primary | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 52% 57% 86.5% 92.2% | 37.1% 43% 72.5% 77.9% | 3 year: 75.5% 80.8% 87/.7% 90.5% | 3-year: 95% 96.5% 96.3% 95.3% |
| MURANO34 | 3 | RR | BR VR | Secondary | ASO-PCR Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 13.3% 62.4% | 1.5% 27.3% | mPFS: 17 mo 53.6 mo | 60 mo: 62.2% 82.1% |
| CLARITY35 * | 2 | RR | IV | Primary | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 53% | 36% | NR | 100% |
| CLL3X36 | 2 | RR | Allogeneic HSCT | Secondary | Flow cytometry ASO-PCR | 10−4 | 10-year: 34% | 10-year: 51% | ||
| TRANSCEND-004 CLL41 | 1-2 | RR | Lisocabtagene maraleucel | Secondary | NGS | 10−4 | 63% | 59% | 17.97 mo | 43.17 mo |
| Trial . | Phase . | Treatment setting . | Treatment . | MRD endpoint . | MRD detection method . | MRD detection level . | % U-MRD PB . | % U-MRD BM . | PFS/mPFS . | OS/mOS . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLL823 | 3 | TN | FC FCR | Secondary | Flow cytometry ASO-PCR | 10−4 | 35% 63% | 28% 44% | 32.9 mo 56.8 mo | 86 mo NR |
| NIH24 | 2 | TN/RR | I | Exploratory | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 10.2% | 8% | 5-year: TP53 cohort: 58.2% Elderly cohort: 81.2% | 5-year: TP53 cohort: 75.7% Elderly cohort: 83.85% |
| E191221 | 3 | TN | IR FCR | Exploratory | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 7.9% 30.3% | NA | 5-year: 78% 51% | mOS: NR NR |
| ELEVATE-TN25 | 3 | TN | A AO CO | Exploratory | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 7% 49% 61% | 0% 61% 10.9% | 48 mo: 77.9% 87% 25.1% | mOS: NR NR NR |
| CLL147 | 3 | TN | VO CO | Secondary | ASO-PCR | 10−4-10−6 | 39.6 mo: 81% 49.5% | 17.1% 56.9% | 5-year: 62.6% 27% | 5-year: 87% 87% |
| FLAIR27 * | 3 | TN | FCR IR | Secondary | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 75% 10% | 46% 4% | mPFS: 67 mo NR | mOS: NR NR |
| CAPTIVATE: MRD28 * | 2 | TN | IV + Placebo IV + I | Secondary | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 75% | 68% | 4-year: 88% 95% | 4-year: 100% 98% |
| CAPTIVATE: Fixed Duration29,30 | 2 | TN | IV | Secondary | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 77% | 60% | 95% at 24 mo | 98% at 24 mo |
| GLOW32 | 3 | TN | IV CO | Secondary | NGS | 10−4, 10−5 | 43.4% 18.6% | 40.6% 7.6% | 30 mo: 86.7% 35.5% | mOS: NR NR |
| MDACC31 | 2 | TN | IV | Secondary | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | NA | 75% | 3-year: 93% | 3-year: 96% |
| CLL1333 | 3 | TN | FCR/BR VR VO VIO | Primary | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 52% 57% 86.5% 92.2% | 37.1% 43% 72.5% 77.9% | 3 year: 75.5% 80.8% 87/.7% 90.5% | 3-year: 95% 96.5% 96.3% 95.3% |
| MURANO34 | 3 | RR | BR VR | Secondary | ASO-PCR Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 13.3% 62.4% | 1.5% 27.3% | mPFS: 17 mo 53.6 mo | 60 mo: 62.2% 82.1% |
| CLARITY35 * | 2 | RR | IV | Primary | Flow cytometry | 10−4 | 53% | 36% | NR | 100% |
| CLL3X36 | 2 | RR | Allogeneic HSCT | Secondary | Flow cytometry ASO-PCR | 10−4 | 10-year: 34% | 10-year: 51% | ||
| TRANSCEND-004 CLL41 | 1-2 | RR | Lisocabtagene maraleucel | Secondary | NGS | 10−4 | 63% | 59% | 17.97 mo | 43.17 mo |
Indicates a trial that used MRD to guide treatment decisions.
A, acalabrutinib; AO, acalabrutinib-obinutuzumab; ASO-PCR, allele-specific oligonucleotide polymerase chain reaction; BM, bone marrow; BR, bendamustine-rituximab; CO, chlorambucil-obintuzumab; FC, fludarabine-cyclophosphamide; FCR, fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplant; I, ibrutinib; IV, ibrutinib-venetoclax; IR, ibrutinib-rituximab; mOS, median OS; mPFS, median PFS; MRD, measurable residual disease; NA, not available; NGS, next-generation sequencing NR, not reached; OS, verall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; PB, peripheral blood; RR, relapsed/refractory; TN, treatment-naive; U-MRD, undetectable-MRD; VR, venetoclax-rituximab.
Selected ongoing clinical trials for CLL with MRD-guided primary endpoints
| Clinicaltrials.gov ID . | Study title . | Primary outcomes . |
|---|---|---|
| NCT05478512 | Front-line VenObi Combination Followed by Ven or VenZan Combination in Patients With Residual Disease: a MRD Tailored Treatment for Young Patients With High-risk CLL (VIS) | • U-MRD at month 9 • U-MRD at month 21 |
| NCT04941716 | Acalabrutinib in Combination With Venetoclax for the Treatment of Refractory or Recurrent Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia or Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma | • Rate of U-MRD |
| NCT04501939 | Cirmtuzumab Consolidation for Treatment of Patients With Detectable CLL on Venetoclax | • Percentage of subjects with U-MRD after 6 months of cirmtuzumab and venetoclax treatment |
| NCT04754035 | Clinical Study With Ibrutinib and Venetoclax for Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (IMPROVE) | • U-MRD rate evaluated by multi-color flow cytometry analysis (limit of detection 10−4) within the treatment period |
| NCT05677919 | Pirtobrutinib and Venetoclax Combined With Minimal Residual Disease Detection for Previously Untreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, MIRACLE Study | • Success of U-MRD (< 1/104) will be measured by ClonoSEQ in both PB and BM; the proportion of successes will be estimated by the number of successes divided by the total number of evaluable patients; exact binomial 95% confidence intervals for the true rate of U-MRD by ClonoSEQ in both PB and BM after cycle 15 will be calculated |
| NCT05650723 | Zanubrutinib and Venetoclax as Initial Therapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) With Response-based Obinutuzumab | • Percentage of total patients that have achieved U-MRD at cycle 16, as assessed via PB and BM aspirate • Percentage of eligible patients that have achieved U-MRD at cycle 23, as assessed via PB and BM aspirate |
| NCT05317936 | Pirtobrutinib (LOXO-305) Consolidation for MRD Eradication in Patients With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (CLL) Treated With Venetoclax | • Rate of U-MRD in the PB |
| NCT05168930 | Zanubrutinib and Venetoclax in CLL (ZANU-VEN) | • Rate of U-MRD |
| NCT03580928 | Acalabrutinib, Venetoclax, and Obinutuzumab for Initial Therapy of CLL (AVO) | • Rate of BM U-MRD complete response |
| NCT04908228 | Fixed-duration Therapy With Ibrutinib and Obinutuzumab (GA-101) in Treatment-naïve Patients With CLL (FIGHT) | • BM U-MRD (<10−4) at 30 days follow-up |
| NCT02158091 | A Phase 1b/2 Study of IPI-145 Plus FCR in Previously Untreated, Younger Patients With CLL | • Number of patients who had a U-MRD complete response (CR) 2 months after chemotherapy • Number of patients who experienced a dose limiting toxicity during phase 1 |
| NCT03708003 | Ibrutinib lead-in Followed by Venetoclax Plus Ibrutinib in Patients With RR CLL | • U-MRD CR/CRi at end of cycle 30 |
| NCT04285567 | A Study to Compare the Efficacy and Safety of a Combined Regimen of Venetoclax and Obinutuzumab Versus Fludarabine, Cyclophosphamide, and Rituximab (FCR)/Bendamustine And Rituximab (BR) in FIT Patients With Previously Untreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Without DEL (17P) or TP53 Mutation (CRISTALLO) | • Minimal residual disease (MRD response rate using NGS in the first 140 participants recruited |
| NCT05336812 | Acalabrutinib in Combination With Venetoclax or Obinutuzumab for the Treatment of Treatment-naive Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | • Rate of BM U-MRD, defined as tumor cell in 10,000 cells using standard flow-based assay, achieved after completion of therapy |
| NCT04169737 | Acalabrutinib and Venetoclax With or Without Early Obinutuzumab for the Treatment of High Risk, Recurrent, or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia or Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma | • Disease assessment of BM U-MRD (<10−4, MRD4) (TN cohort) • Disease assessment of BM undetectable-MRD4 (RR cohort) |
| NCT04010968 | Evaluation of Risk-Adapted and MRD-Driven Strategy for Untreated Fit Patients With Intermediate Risk Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (ERADIC) | • Minimal residual disease (MRD) in BM <0.01% at month 27 |
| NCT05791409 | Venetoclax Treatment (26 Cycles) With 6 Cycles or 12 Cycles of Epcoritamab in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory CLL or SLL (AETHER) | • Proportion of U-MRD in BM by NGS and no progression according to iwCLL criteria after 26 cycles (i.e., 12 weeks after cycle 26) for all intent to treat patients • Recommended phase 2 dose for the combination of venetoclax and epcoritamab based on dose limiting toxicity |
| NCT04523428 | REtreatment With VEnetoclax and Acalabrutinib After Venetoclax Limited Duration (REVEAL) | • U-MRD in BM by flow cytometry after 26 cycles (2 acalabrutinib and 24 acalabrutinib-venetoclax) |
| Clinicaltrials.gov ID . | Study title . | Primary outcomes . |
|---|---|---|
| NCT05478512 | Front-line VenObi Combination Followed by Ven or VenZan Combination in Patients With Residual Disease: a MRD Tailored Treatment for Young Patients With High-risk CLL (VIS) | • U-MRD at month 9 • U-MRD at month 21 |
| NCT04941716 | Acalabrutinib in Combination With Venetoclax for the Treatment of Refractory or Recurrent Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia or Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma | • Rate of U-MRD |
| NCT04501939 | Cirmtuzumab Consolidation for Treatment of Patients With Detectable CLL on Venetoclax | • Percentage of subjects with U-MRD after 6 months of cirmtuzumab and venetoclax treatment |
| NCT04754035 | Clinical Study With Ibrutinib and Venetoclax for Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (IMPROVE) | • U-MRD rate evaluated by multi-color flow cytometry analysis (limit of detection 10−4) within the treatment period |
| NCT05677919 | Pirtobrutinib and Venetoclax Combined With Minimal Residual Disease Detection for Previously Untreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, MIRACLE Study | • Success of U-MRD (< 1/104) will be measured by ClonoSEQ in both PB and BM; the proportion of successes will be estimated by the number of successes divided by the total number of evaluable patients; exact binomial 95% confidence intervals for the true rate of U-MRD by ClonoSEQ in both PB and BM after cycle 15 will be calculated |
| NCT05650723 | Zanubrutinib and Venetoclax as Initial Therapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) With Response-based Obinutuzumab | • Percentage of total patients that have achieved U-MRD at cycle 16, as assessed via PB and BM aspirate • Percentage of eligible patients that have achieved U-MRD at cycle 23, as assessed via PB and BM aspirate |
| NCT05317936 | Pirtobrutinib (LOXO-305) Consolidation for MRD Eradication in Patients With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (CLL) Treated With Venetoclax | • Rate of U-MRD in the PB |
| NCT05168930 | Zanubrutinib and Venetoclax in CLL (ZANU-VEN) | • Rate of U-MRD |
| NCT03580928 | Acalabrutinib, Venetoclax, and Obinutuzumab for Initial Therapy of CLL (AVO) | • Rate of BM U-MRD complete response |
| NCT04908228 | Fixed-duration Therapy With Ibrutinib and Obinutuzumab (GA-101) in Treatment-naïve Patients With CLL (FIGHT) | • BM U-MRD (<10−4) at 30 days follow-up |
| NCT02158091 | A Phase 1b/2 Study of IPI-145 Plus FCR in Previously Untreated, Younger Patients With CLL | • Number of patients who had a U-MRD complete response (CR) 2 months after chemotherapy • Number of patients who experienced a dose limiting toxicity during phase 1 |
| NCT03708003 | Ibrutinib lead-in Followed by Venetoclax Plus Ibrutinib in Patients With RR CLL | • U-MRD CR/CRi at end of cycle 30 |
| NCT04285567 | A Study to Compare the Efficacy and Safety of a Combined Regimen of Venetoclax and Obinutuzumab Versus Fludarabine, Cyclophosphamide, and Rituximab (FCR)/Bendamustine And Rituximab (BR) in FIT Patients With Previously Untreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Without DEL (17P) or TP53 Mutation (CRISTALLO) | • Minimal residual disease (MRD response rate using NGS in the first 140 participants recruited |
| NCT05336812 | Acalabrutinib in Combination With Venetoclax or Obinutuzumab for the Treatment of Treatment-naive Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | • Rate of BM U-MRD, defined as tumor cell in 10,000 cells using standard flow-based assay, achieved after completion of therapy |
| NCT04169737 | Acalabrutinib and Venetoclax With or Without Early Obinutuzumab for the Treatment of High Risk, Recurrent, or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia or Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma | • Disease assessment of BM U-MRD (<10−4, MRD4) (TN cohort) • Disease assessment of BM undetectable-MRD4 (RR cohort) |
| NCT04010968 | Evaluation of Risk-Adapted and MRD-Driven Strategy for Untreated Fit Patients With Intermediate Risk Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (ERADIC) | • Minimal residual disease (MRD) in BM <0.01% at month 27 |
| NCT05791409 | Venetoclax Treatment (26 Cycles) With 6 Cycles or 12 Cycles of Epcoritamab in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory CLL or SLL (AETHER) | • Proportion of U-MRD in BM by NGS and no progression according to iwCLL criteria after 26 cycles (i.e., 12 weeks after cycle 26) for all intent to treat patients • Recommended phase 2 dose for the combination of venetoclax and epcoritamab based on dose limiting toxicity |
| NCT04523428 | REtreatment With VEnetoclax and Acalabrutinib After Venetoclax Limited Duration (REVEAL) | • U-MRD in BM by flow cytometry after 26 cycles (2 acalabrutinib and 24 acalabrutinib-venetoclax) |
BM, bone marrow; CRi, incomplete bone marrow recovery; iwCLL, International Workshop on CLL; MRD, measurable residual disease; NGS, next- generation sequencing; Obi, obinutuzumab; PB, peripheral blood; RR, relapsed/refractory; TN, treatment-naive; U-MRD, undetectable MRD; Ven, venetoclax; Zan, zanubrutinib.
CLINICAL CASE
JT is a 73-year-old man with a past medical history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia who was diagnosed with CLL six years ago, when an isolated lymphocytosis was identified on preoperative blood work for an elective knee replacement. At this visit, he endorses worsening fatigue and new early satiety. His blood work demonstrates a white blood cell count of 113,000 cells/µL, a hemoglobin of 9.3 g/dL, and platelet count of 93,000 cells/µL. He now meets International Workshop on CLL (iwCLL) criteria to initiate treatment, and you discuss with him starting a continuous BTKi or treating with venetoclax-obintuzumab (VO) for one year. Before his clinical visit, he read about MRD testing, so he asks which treatment will be best and give him the deepest response.
What defines MRD?
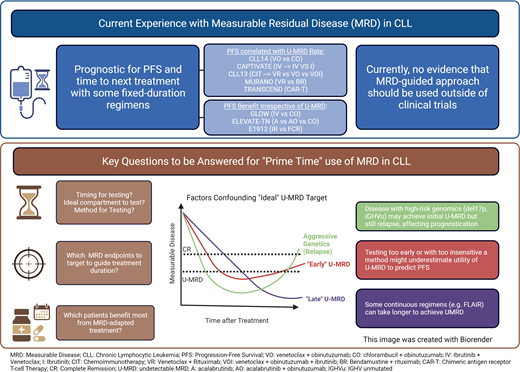
MRD is defined by the number of CLL cells detected within a sample. A recent expert panel convened to standardize nomenclature and assessment of MRD in CLL.8 Undetectable MRD (U-MRD) is the preferred term. The levels of MRD have been defined as MRD4 (10−4, or 1 in 10,000 leukocytes), MRD5 (10−5 or 1 in 100,000 leukocytes), and MRD6 (10−6 or 1 in 1,000,000 leukocytes). Given the heterogeneity of the available assays, the method utilized, the sensitivity threshold, and the tested compartment need to be reported when discussing MRD results. Identification of the tested compartment in the MRD results is important because there can be discordance between the peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM). The expert panel, as well as the iwCLL guidelines,9 define a U-MRD threshold of at least 10−4 (MRD4). Though there is no specific guidance on timing for testing and monitoring of MRD, the expert panel consensus recommendation is to consider testing at a minimum of two months after completion of fixed-duration therapy. Currently, there are no consensus guidelines on how to use MRD testing results in routine clinical practice.
How is MRD detected?
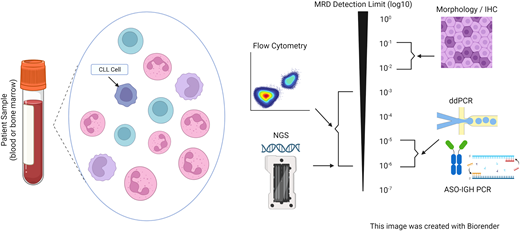
There are various methods for MRD detection (Figure 1). Flow cytometry–based assays are the most widely available and frequently used. The European Research Initiative on CLL10,11 provided consensus guidelines for harmonization of MRD detection by flow cytometry. Current recommendations are to use an antibody panel consisting of CD5, CD19, CD20, CD43, CD79b, and CD81, which can detect MRD4 by four-color flow. Six and 10-color flow cytometry can increase sensitivity, allowing for detection of MRD5.12,13 Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to the immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) gene can also be performed and can reach a sensitivity of MRD6 but requires patient-specific primers. As such, this was used in clinical trials but is not used frequently in clinical practice. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) testing and tests for rearrangements of the IGH VDJ or DJ, IgK and IgL receptor gene sequences, or translocated BCL1/IgH(J) and BCL2/IgH(J)14 have become more readily available. NGS-based assays have good concordance with flow cytometric assays, are sensitive up to MRD6, and have been incorporated into prospective clinical trials.15 These tests require baseline samples to establish clonality before initiating treatment. Emerging tests for MRD include digital droplet PCR (ddPCR)16 and cell-free DNA (cfDNA),17 which have both demonstrated excellent sensitivity but are not used routinely.
Measurable residual disease (MRD) testing modalities. ASO-IGH PCR, allele-specific oligonucleotide immunoglobulin heavy locus PCR; ddPCR, droplet digital polymerase chain reaction; IHC, immunohistochemistry; NGS, next-generation sequencing.
Measurable residual disease (MRD) testing modalities. ASO-IGH PCR, allele-specific oligonucleotide immunoglobulin heavy locus PCR; ddPCR, droplet digital polymerase chain reaction; IHC, immunohistochemistry; NGS, next-generation sequencing.
MRD with continuous treatment with targeted agents
Initial approvals of BTKi monotherapy18 have dramatically changed the treatment landscape, leading to improvements in progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) when compared to CIT.19-21 Several studies have demonstrated the prognostic value of MRD in patients treated with CIT. For patients treated with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR), U-MRD responses predict PFS, particularly for patients with MRD6 responses that have IGHV mutations.22 Given the prognostic value of U-MRD responses in predicting outcomes with CIT,23 several clinical trials have studied the role of U-MRD in patients treated continuously with BTKis.
Studies of treatment with continuous ibrutinib have demonstrated low rates of complete response (CR) as well as low rates of U-MRD. Despite these findings, we continue to see impressive PFS and OS, including in patients with high-risk genetic features (e.g., del17p/TP53, unmutated IGHV, complex karyotype). In a phase 2 CLL study conducted by the NIH with elderly patients or patients with TP53 aberrations, continuous treatment with ibrutinib monotherapy demonstrated a deepening of responses over time, with increased CR rates from 0% at 6 months to 28.4% at 60 months on treatment24 with low rates of U-MRD at four years: 10.2% (5/49 patients) in PB and 8% (2/25 patients) in BM. Despite the low rates of U-MRD, five-year PFS was excellent at 58.2% for patients with TP53 aberrations and 81.2% for elderly patients. Similar findings were seen in E1912, the pivotal phase 3 trial comparing ibrutinib-rituximab (IR) (with continuous ibrutinib) to six cycles of FCR in treatment-naive fit patients <65 years old with CLL. At 5.8 years of follow up, median PFS was longer for IR compared to FCR (Hazard Ratio [HR] 0.37) with small but statistically significant improvement in OS for patients with unmutated IGHV (HR 0.35; 95% CI 0.15-0.80; p = 0.01) but not for patients with mutated-IGHV (HR 0.72; 95% CI 0.15-3.47; p = 0.68).21 Patients treated with FCR had higher rates of U-MRD4 at 3, 12, 24, and 36 months compared to patients treated with IR (29.1% at 3 months, 30.3% vs 7.9% at 12 months, 23.4% vs 4.2% at 24 months, and 8.6% vs 3.7% at 36 months). An updated four-year follow-up from ELEVATE-TN, a phase 3 trial comparing acalabrutinib, acalabrutinib- obinutuzumab (AO), and chlorambucil-obinutuzumab (CO),25 also demonstrated an improvement in four-year PFS for patients treated in the acalabrutinib-containing arms,26 despite low rates of U-MRD. These results demonstrate that outcomes remain excellent with BTKis, even after years on therapy. As such, current recommendations are for continuous treatment until progressive disease or unacceptable toxicity, and therefore routine MRD testing is not recommended.
The FLAIR trial compared treatment with IR to FCR in fit patients with treatment-naive CLL without a del(17p).27 Ibrutinib was continued for six years, until U-MRD4, toxicity or disease progression. MRD in both PB and BM was assessed at 9 months and 12 months after randomization, and then every 6 months thereafter. Treatment with ibrutinib was discontinued if U-MRD was attained, and treatment duration was based on the time from randomization to U-MRD. With median follow-up of 53 months, median PFS was not reached for patients treated with IR and was 67 months for patients treated with FCR. Rates of U-MRD were lower at 9 months for patients treated with IR (3.9%) compared to patients treated with FCR (55.3%), again demonstrating that U-MRD is not necessarily associated with PFS for patients on continuous BTKi therapy. Updated results of the influence of MRD on PFS and the time to next treatment after ibrutinib discontinuation will provide a potential role for utilizing MRD testing to shorten the duration of therapy with BTKis.
MRD in frontline fixed-duration treatment of CLL with targeted treatments
MRD endpoints have been studied in clinical trials of fixed- duration treatments. CLL14 is a pivotal randomized phase 3 trial that led to the approval of VO for frontline treatment of CLL. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive VO for 12 months vs 6 months of CO. U-MRD4 rates by allele-specific oligonucleotide (ASO) PCR and four-color flow cytometry were higher with VO than CO (76% at end of treatment +3 months vs 35%). The recurrence of measurable disease was also delayed for patients treated with VO compared to CO (21 months vs 6 months), demonstrating not just the importance of reaching U-MRD at the end of treatment (EOT) but also highlighting the differences in duration of U-MRD responses by treatment.
The phase 2 CAPTIVATE trial examined patients with CLL who were ≤65 years old treated with frontline ibrutinib and venetoclax (IV). Patients received 3 months of ibrutinib lead-in treatment followed by IV for 12 months. The study consisted of both a fixed duration (FD) cohort and a randomized MRD cohort. MRD4 was measured by eight-color flow cytometry in both PB and BM and confirmed that U-MRD was defined as two separate U-MRD measurements.28 U-MRD was achieved by 75% of patients in the PB and 68% in BM at EOT. High rates of U-MRD were seen across high-risk subgroups, including in patients with del17p and unmutated IGHV. In the MRD cohort, patients with confirmed U-MRD were randomized to receive either placebo or ibrutinib. Patients with unconfirmed U-MRD were randomized to receive ibrutinib or IV. Four-year PFS was 95% in patients treated with ibrutinib and 88% in patients treated with placebo.29 In the unconfirmed MRD cohort, 30-month PFS was 95% for patients treated with ibrutinib and 97% for patients treated IV. In the FD cohort, four-year PFS rates were higher for patients with U-MRD at EOT +3 compared to those with detectable MRD (90% vs 66%), although there were no differences in OS.30 Similar results were seen in a phase 2 study of 24 months of IV treatment for patients with treatment-naive CLL with high-risk genetic features (i.e., del17p, TP53, del11q, or unmutated IGHV). Complete response rate at EOT (18 cycles of combination) was 96%, with 61% also achieving U-MRD in BM initially. With longer follow-up, 75% of patients achieved U-MRD in BM as best response with associated three-year PFS of 93%.31
The phase 3 GLOW trial studied fixed duration IV compared to CO for frontline treatment of CLL in patients ≥70 years of age or unfit for CIT.32 MRD4 and MRD5 were assessed by NGS. IV achieved higher rates of MRD5 in BM and PB at EOT +3 (40.6% and 43.4% vs 7.6% and 18.1%) and EOT +12 in PB (36.8% vs 6.7%) compared to CO. Patients treated with IV were more likely to sustain their U-MRD compared to CO, which demonstrated shorter duration or U-MRD. There were no significant differences in PFS for patients treated with IV if they were U-MRD4 vs detectable MRD4 in BM (96.3% vs 93.3%), demonstrating excellent PFS irrespective of achieving U-MRD status.
Recently, the CLL13 trial compared venetoclax combinations to CIT. It randomized fit patients 1:1:1:1 to receive CIT (with FCR or bendamustine-rituximab [BR]) for six cycles, 12 cycles of venetoclax-rituximab [VR], 12 cycles of VO, or 12 cycles of venetoclax-obinutuzumab-ibrutinib [VOI] with co-primary endpoints of U-MRD4 at 15 months (EOT +3) and PFS.33 Rates of U-MRD4 by flow cytometry were higher in PB and BM in the VO and VOI arms compared to CIT (72.5%, 77.9%, 37.1%, respectively). At a median follow-up of 38.8 months, three-year PFS was 76.4% for VO, 82.9% for VOI, and 65.5% for CIT. At 15 months, U-MRD was associated with improvement in PFS in the venetoclax-containing arms compared to CIT, although there were no significant differences between doublet and triplet combinations.
What potentially accounts for the above differences in the association of MRD with PFS? GLOW has a shorter follow-up than CAPTIVATE, and it may take longer to see differences in PFS with BTKi-containing regimens given their long-term PFS benefits with continuous BTKi therapy. Importantly, GLOW enrolled an older population, and several deaths were reported in the study. This suggests that the toxicity of regimens needs to be considered when choosing therapy for older patient populations and that in certain populations, attaining U-MRD may not be optimal due to the toxicity associated with the regimen.
CLINICAL CASE (continued)
JT decides that he wants to start treatment with acalabrutinib monotherapy. You discuss that in this setting, you would not recommend checking MRD testing, as outcomes do not correlate well with U-MRD status. After five years on acalabrutinib, he develops progressive disease and starts treatment with VR. He asks about MRD testing and if it should be performed now.
MRD for relapsed/refractory disease with targeted agents
Given the improvements in PFS and OS for patients with U-MRD responses to frontline CIT, MRD has been explored as an endpoint in patients treated with targeted agents for relapsed/refractory CLL. MURANO is the practice-changing phase 3 clinical trial comparing VR to BR for patients with relapsed/refractory CLL. MRD was assessed by ASO-PCR and four-color flow cytometry. In a recent update, seven-year PFS was 23% for patients treated with VR compared to 0% for patients treated with BR.34 Seven-year OS rates were 69.6% for patients treated with VR compared to 51% for patients with BR (HR 0.53). For patients with U-MRD at EOT who have not had progressive disease, median PFS was 52.5 months compared to 18 months for patients who had detectable MRD, demonstrating that patients with U-MRD at the end of VR treatment have prolonged PFS, and U-MRD status can be prognostic in this setting.
The CLARITY study is a phase 2 trial that treated relapsed CLL patients with the combination of IV and looked at the primary endpoint of MRD4 in PB and BM after 12 months of combination therapy.35 Unlike CLL14 and MURANO, where all patients discontinued treatment at 12 months irrespective of MRD status, patients could stop combination therapy anywhere from 8 to 26 months if U-MRD was confirmed. Patients continued ibrutinib treatment if they were not U-MRD4 at 26 months. At 14 months on therapy, 36% (19/53) of patients achieved U-MRD in BM, and 53% (28/53) of patients achieved U-MRD in PB at 14 months (12 months combination therapy).35 There was a deepening of U-MRD responses by month 26 (44% [11/25]). Twenty-three patients with U-MRD have stopped all therapy, and 14/18 remain U-MRD4 at 38 months. These data demonstrate that responses to IV can deepen over time; further follow up for PFS while off therapy, during the time to next treatment, can help inform if targeting U-MRD specifically with FD treatments improves outcomes.
MRD with cellular therapy
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation remains part of the treatment paradigm for fit patients with high-risk CLL and has curative potential, although it is used less frequently given the efficacy of our novel targeted therapies. There is limited prospective data on U-MRD responses to transplant. The German CLL3X trial looked at reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplant in poor-risk patients with relapsed/refractory CLL and found a U-MRD rate of 52% of patients at 12 months in those patients who were alive, including in patients with del17p. Additionally, U-MRD at 12 months was prognostic for a reduced relapse risk,36 with a six-year OS of 58% irrespective of high-risk genomic features.37
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells were initially studied in patients with CLL, with early trials demonstrating durable responses.38,39 Several products are currently under study and have demonstrated the ability to achieve U-MRD, even in high-risk patients. A study of CD19 CAR-T cell therapy in combination with ibrutinib in patients who progressed on ibrutinib therapy demonstrated a four-week overall response rate of 83% with 61% of patients having U-MRD in BM.40 A phase 1-2 study of lisocabtagene maraleucel in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL demonstrated a CR rate of 18% and overall response rate of 43%.41 U-MRD rate was 63% in the PB and 59% in BM. Median PFS for patients with U-MRD was 26.2 months compared to 2.8 months in those with detectable MRD. These data demonstrate the prognostic value for U-MRD with cellular therapies, though longer follow-up is needed with CAR T-cells to determine the durability of these responses.
CLINICAL CASE (revisited)
After two years of VR therapy, you check U-MRD using four-color flow cytometry at EOT and detect a clone in 0.02% of cells.
Is MRD ready for prime time?
U-MRD at EOT has demonstrated important prognostic value with several treatments in CLL, including CIT, venetoclax-based combinations, and cellular therapies. As such, it is reasonable to evaluate U-MRD status at the end of these finite treatments if testing is readily available. At present, the value of MRD testing on survival requires further investigation for future combination regimens because it is unclear whether MRD-guided approaches will be standardized. Currently, there is no evidence that an MRD-guided approach should be used outside clinical trials. U-MRD remains an attractive endpoint for clinical trials because median OS has not been reached for many pivotal clinical trials, and surrogate endpoints are needed.
While U-MRD is prognostic, other disease-specific factors continue to influence outcomes. Patients with high-risk genomic features such as del17p and unmutated IGHV have similar rates of U-MRD compared to those with low-risk disease, but they continue to have shorter PFS, demonstrating a potential difference in MRD kinetics based on disease biology.7,34 As of today, there is no clear evidence as to how to adapt treatment based on MRD. The BOVen study treated treatment-naive patients with CLL with the triplet of zanubrutinib, venetoclax, obinutuzumab, with 89% of patients having a U-MRD response in the PB and BM after a median of 10 cycles of therapy.42 Longer follow-up is needed, but the level of MRD seems to correlate with the durability of remission, with 94% of patients remaining U-MRD after an additional 15.8 months of follow-up. The CLARITY study was amended to increase the duration of treatment with IV, with nearly all patients discontinuing treatment by the end of two years.35 The FLAIR study also used an individualized treatment duration, but longer follow-up (especially after ibrutinib discontinuation) is needed to determine if this is an effective approach.27 The CLL17 trial of ibrutinib, IV, or VO for frontline treatment of CLL will help determine whether continuous time-limited therapy for frontline treatment is best, although translating this data into outcomes with second-generation BTKis that have become a preferred treatment will be challenging.
Despite recent consensus guidelines, there are still key unanswered questions: What level of MRD detection should be targeted? Which testing method should be used? When and how often should testing be performed, and with what compartment? Finally, is MRD the correct endpoint for all CLL patients? Outcomes with continuous BTKi therapy are excellent, and U-MRD may not be necessary to improve survival in all patients.
Conclusions
MRD remains a powerful tool for response assessment for certain FD treatment regimens, and it has the potential to become an important surrogate for PFS. Despite MRD's prognostic utility, further research and follow-up is needed to determine its role in routine clinical practice, both for prognostication and for guiding treatment decisions in routine clinical practice. Finally, U-MRD may not be a one-size-fits-all endpoint, and individualized treatment decisions will be needed that consider patient factors, treatment, and desired endpoints. Clinical trials are currently underway to begin to answer these questions, and we eagerly await these results.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
Joanna M. Rhodes: consulting: Abbvie, Genentech, Jannsen, Pharmacyclics, Beigene, AstraZeneca, Morphosys, ADCT, Epizyme, GenMab; SeaGen research support (to institution): Oncternal Pharmaceuticals, Pharmacyclics LLC, Acerta, Loxo Oncology, Velosbio, Abbvie; honoraria: MJH Life Sciences, Aptitude, Curio.
Carlos A. Lopez: no competing financial interests to declare.
Jacqueline C. Barrientos: consulting: Beigene, AstraZeneca, Pharmacyclics; Janssen Research support: Merck, Nurix, Abbvie Honoraria: Janssen, Beigene, and AstraZeneca.
Off-label drug use
Joanna M. Rhodes: nothing to disclose, no off-label drug use mentioned.
Carlos A. Lopez: nothing to disclose, no off-label drug use mentioned.
Jacqueline C. Barrientos: nothing to disclose, no off-label drug use mentioned.