Abstract
Diagnosing amyloidosis can be challenging due to its clinical heterogeneity, need for multiple specialists to make a diagnosis, and lack of a single diagnostic test for the disease. Patients are often diagnosed late, in advanced stage, and after exhibiting multiple symptoms and signs for a long period. It is important to develop a clinical suspicion of amyloidosis, particularly in those with multisystemic symptoms and high-risk patient populations such as those with precursor hematologic conditions. A systematic approach to the workup of suspected amyloidosis is key, including a comprehensive clinical assessment, laboratory tests to assess organ involvement, advanced imaging studies, screening for plasma cell disorder, and tissue biopsy when necessary. After making a diagnosis of amyloidosis, accurate typing of amyloid deposits, differentiating between localized and systemic amyloidosis, and appropriately staging the disease is important. Early diagnosis is crucial for improving patient outcomes and quality of life in light chain amyloidosis.
Learning Objectives
Identify concerning symptoms and signs that should trigger a suspicion of amyloidosis
Describe a systems approach to the diagnosis of amyloidosis
Outline key steps after a diagnosis of amyloidosis is made
Introduction
Diagnosing amyloidosis can be challenging. Amyloidosis encompasses a group of diseases characterized by abnormal protein accumulation in organs and tissues, leading to heterogeneous and diverse clinical manifestations. There are different presentations in amyloidosis, including hereditary versus acquired, localized versus systemic, and primary versus secondary. Delayed diagnosis is unfortunately all too common in amyloidosis, with patients experiencing symptoms for several months to years and consulting multiple specialist physicians before amyloidosis is considered and confirmed.1 There are multiple subtypes of systemic amyloidosis, with light chain (AL), transthyretin (ATTR), and secondary (AA) being the most common (Table 1).
Summary of common systemic amyloid types
| Amyloid type . | Precursor protein . | Cause . | Organ pattern . | Primary treatment* . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AL | Immunoglobulin light chain | Secondary to a clonal plasma cell or lymphoproliferative disorders | Heart Kidneys Liver PNS ANS Soft tissue | Chemotherapy, autologous stem cell transplantation to control underlying clonal disorder |
| ATTRwt | Wild-type transthyretin | Aging | Heart Soft tissue | Tafamidis |
| ATTRv | Mutated transthyretin | Hereditary | Heart PNS ANS GI tract | Patisiran, inotersen, vutrisiran for neuropathy Tafamidis for cardiomyopathy |
| AA | Serum amyloid A protein | Chronic inflammation | Kidneys Liver Heart ANS | Suppress inflammation (eg, colchicine for FMF, anakinra for periodic fever syndromes, canakinumab for CAPS, biologics for autoimmune diseases) |
| Amyloid type . | Precursor protein . | Cause . | Organ pattern . | Primary treatment* . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AL | Immunoglobulin light chain | Secondary to a clonal plasma cell or lymphoproliferative disorders | Heart Kidneys Liver PNS ANS Soft tissue | Chemotherapy, autologous stem cell transplantation to control underlying clonal disorder |
| ATTRwt | Wild-type transthyretin | Aging | Heart Soft tissue | Tafamidis |
| ATTRv | Mutated transthyretin | Hereditary | Heart PNS ANS GI tract | Patisiran, inotersen, vutrisiran for neuropathy Tafamidis for cardiomyopathy |
| AA | Serum amyloid A protein | Chronic inflammation | Kidneys Liver Heart ANS | Suppress inflammation (eg, colchicine for FMF, anakinra for periodic fever syndromes, canakinumab for CAPS, biologics for autoimmune diseases) |
Refers to controlling amyloidogenic precursor. Treatment of amyloidosis additionally requires strong supportive care management.
ANS, autonomic nervous system; CAPS, cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome; FMF, familial Mediterranean fever; GI, gastrointestinal; PNS, peripheral nervous system.
Amyloid consults are challenging due to the nonspecific nature of symptoms, which can easily be mistaken for symptoms of other diseases or attributed to normal aging2 ; a need for tissue biopsy to make a definitive diagnosis (we will review a clinical scenario where this is no longer needed); multiple types of amyloidosis,3 each affecting different organ systems and possibly warranting a different workup; and finally a perception that given limited treatment options, making a diagnosis may not change patient outcomes. While this article will not delve into treatment of amyloidosis, it is no longer true that treatment options for amyloidosis are limited—significant progress has been made in recent years. The US Food and Drug Administration approved patisiran and inotersen for treatment of polyneuropathy associated with hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTRv) in 2018, tafamidis and tafamidis meglumine for ATTR cardiomyopathy in 2019, daratumumab combined with cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone for newly diagnosed light chain (AL) amyloidosis in 2021, and vutrisiran for ATTRv polyneuropathy in 2022. New treatments continue to emerge. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the subtype and, in AL amyloidosis, stage of disease. With prompt diagnosis and appropriate management, we can help improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Hematologists are frequently consulted when amyloidosis is suspected. Furthermore, they may already be involved in the care of patients with precursor hematologic conditions that can progress to systemic AL amyloidosis. In these situations, having a primer for efficient and accurate workup toward early detection is crucial. Expert reviews and consensus recommendations offer excellent algorithmic approaches to suspected amyloidosis,4-6 which are not reiterated in this article.
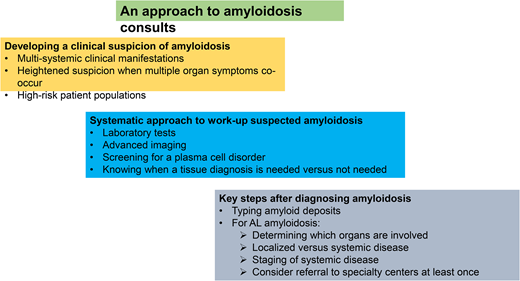
Developing a clinical suspicion of amyloidosis
The clinical manifestations of amyloidosis are myriad and often nonspecific; indeed it is one of the medical conditions earning the nickname of the great imitator or the great masquerader.7 The symptoms and presentation of amyloidosis depend on the organs involved and specific amyloid syndromes that occur. Common syndromes include cardiomyopathy with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, nephrotic range proteinuria, organomegaly due to amyloid deposition (eg, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, macroglossia, salivary gland enlargement, pseudohypertrophy of muscles), neuropathy—both peripheral and autonomic, gastrointestinal manifestations, purpura, and constitutional symptoms (fatigue, weight loss). Many patients go for several months to years with a growing constellation of symptoms and seeing multiple physicians and health care providers, often misinterpreting and misattributing symptoms to aging.1,2,8 While scans can now identify cardiac amyloidosis at early stages, such as bone scintigraphy (PYP scan) and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, and monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) can also be readily identified with blood tests, the cost-effectiveness of screening populations is unknown. The likelihood of harboring systemic amyloidosis increases incrementally in the presence of multiple organ symptomatology, and a patient with multisystemic symptoms warrants active investigation for amyloidosis. Nearly universally, patients with a diagnosis of AL amyloidosis harbor multisystemic symptoms and diagnoses preceding the AL diagnosis.9,10
High-risk patient populations
Hematologists are aware of and well-versed in screening patients with MGUS and smoldering myeloma for development of active multiple myeloma. It is equally important to consider that these patients are also at risk for developing AL amyloidosis. Some lymphoproliferative disorders such as Waldenström macroglobulinemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and marginal zone lymphoma can also lead to AL amyloidosis, and hematologists caring for patients with these diseases should consider systemic amyloidosis in their differential diagnosis during follow-up. A Mayo Clinic study showed that even with a known antecedent hematologic condition, the median time from diagnosis of the clonal precursor condition to an AL amyloidosis diagnosis was 11 months.11 An N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), screening for albuminuria (urine albumin to creatinine ratio or 24-hour urine protein study), and alkaline phosphatase can serve as good screening tests for systemic amyloidosis in following these patients.12 These tests must be supplanted with a good history for symptoms and a physical examination that considers amyloid organ sequelae (Table 2). Family history is helpful to screen for hereditary ATTR amyloidosis or syndromes associated with systemic inflammation that increase the risk for AA amyloidosis. Older African Americans are a unique high-risk group, given a 3% to 4% prevalence of Val122Ile mutation of the TTR gene as well as a two to three times higher prevalence of MGUS.
Multisystemic symptoms, signs, and clues for amyloidosis
| . | Clinical manifestations . | Key laboratory and imaging findings . | Definition of organ involvement . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kidney | Peripheral edema, periorbital puffiness, anasarca, nephrotic syndrome | Albuminuria ≥0.5 g/24 h | Biomarker staging (refer to Table 3) |
| Heart | Dyspnea, jugular venous distension, peripheral edema, arrhythmia, HFpEF | Elevated cardiac biomarkers ECG—low voltage in limb leads, pseudoinfarct pattern, arrhythmia TEE—ventricular hypertrophy, thickened IVS, abnormal GLS | Biomarker staging (refer to Table 3) Echo wall thickness >1.5 cm |
| Liver | Hepatomegaly with cholestasis Abdominal distension | ALP elevation, elevated bilirubin in advanced infiltration Enlarged liver on imaging | Elevated ALP >1.5 times upper limit of normal Liver span >15 cm in the absence of heart failure |
| Nerves | Ascending length-dependent symmetric small-fiber peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy (orthostatic hypotension, early satiety, gastroparesis, irregular bowel movements, voiding difficulty, erectile dysfunction) | EMG/NCS may be helpful | N/A |
| GI tract | Dysphagia, early satiety, gastroparesis, GI bleeding, irregular bowel movements, weight loss, malabsorption | Anemia, hypoalbuminemia, low vitamin D | N/A |
| Spleen | Splenomegaly, functional asplenia Abdominal distension | Enlarged spleen on imaging, Howell-Jolly bodies on peripheral smear | N/A |
| Lung | Dyspnea, cough, hemoptysis | CT imaging—interstitial pattern or nodular cystic lesions | N/A |
| Skin | Cutaneous plaques, purpura | N/A | |
| Other | Periorbital purpura Macroglossia Enlarged salivary glands Hoarseness Arthropathy Pseudohypertrophy of muscles Jaw claudication Carpal tunnel syndrome | Low factor X activity | N/A |
| . | Clinical manifestations . | Key laboratory and imaging findings . | Definition of organ involvement . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kidney | Peripheral edema, periorbital puffiness, anasarca, nephrotic syndrome | Albuminuria ≥0.5 g/24 h | Biomarker staging (refer to Table 3) |
| Heart | Dyspnea, jugular venous distension, peripheral edema, arrhythmia, HFpEF | Elevated cardiac biomarkers ECG—low voltage in limb leads, pseudoinfarct pattern, arrhythmia TEE—ventricular hypertrophy, thickened IVS, abnormal GLS | Biomarker staging (refer to Table 3) Echo wall thickness >1.5 cm |
| Liver | Hepatomegaly with cholestasis Abdominal distension | ALP elevation, elevated bilirubin in advanced infiltration Enlarged liver on imaging | Elevated ALP >1.5 times upper limit of normal Liver span >15 cm in the absence of heart failure |
| Nerves | Ascending length-dependent symmetric small-fiber peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy (orthostatic hypotension, early satiety, gastroparesis, irregular bowel movements, voiding difficulty, erectile dysfunction) | EMG/NCS may be helpful | N/A |
| GI tract | Dysphagia, early satiety, gastroparesis, GI bleeding, irregular bowel movements, weight loss, malabsorption | Anemia, hypoalbuminemia, low vitamin D | N/A |
| Spleen | Splenomegaly, functional asplenia Abdominal distension | Enlarged spleen on imaging, Howell-Jolly bodies on peripheral smear | N/A |
| Lung | Dyspnea, cough, hemoptysis | CT imaging—interstitial pattern or nodular cystic lesions | N/A |
| Skin | Cutaneous plaques, purpura | N/A | |
| Other | Periorbital purpura Macroglossia Enlarged salivary glands Hoarseness Arthropathy Pseudohypertrophy of muscles Jaw claudication Carpal tunnel syndrome | Low factor X activity | N/A |
N/A: No specific definition for organ involvement but rather based on symptoms and key laboratory and/or imaging findings.
ALP, alkaline phosphatase; CT, computerized tomography; ECG, electrocardiogram; EMG, ; GI, gastrointestinal; GLS, ; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; IVS, ; NCS, ; TEE, transthoracic echocardiogram.
Workup of suspected amyloidosis: a systems approach is needed
CLINICAL CASE
Mr. Smith, a 62-year-old male, is admitted to the medical floor with heart failure. He presented with a 6-month history of progressive fatigue, swelling in his legs, and a 30-pound weight loss. His medical history is notable for hypertension and type 2 diabetes. He was diagnosed with bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome for which he had a right carpal tunnel release 3 years ago and the left one a year ago. His primary care physician attributed these symptoms to his long work hours at the computer. A year ago, his primary care physician also identified microalbuminuria on his urinalysis with a slight elevation in his creatinine and referred him to a nephrologist for further management of chronic kidney disease. He sees a cardiologist for management of his hypertension and has had a transthoracic echocardiogram within the last year, which showed grade 2 diastolic dysfunction, moderate left ventricular hypertrophy, and an interventricular septum thickness of 1.5 cm. In the last 6 months, his cardiologist has need to stop, one by one, his 3 anti-hypertensives due to low blood pressure (BP). His BP has remained low, and he sometimes feels dizzy upon standing. Mr. Smith attributes many of his symptoms to aging, but he worries that something might be wrong. He has brought his concerns to his many doctors, and they have done additional testing pertinent to their specialty and reassured him. On physical examination, his BP is 110/70 mm Hg supine and drops to 87/54 mm Hg on standing. He has an enlarged tongue that shows lateral scalloping, and multiple bruises are seen on his arms and face, including purpura on his right eyelid. He exhibits signs of heart failure, including elevated jugular venous pressure, bilateral basal crackles on lung auscultation, and lower extremity edema. Suspecting cardiac amyloidosis, the medical team employs a systems approach to confirm the diagnosis.
Multisystemic assessment
Many symptoms and signs in this patient point to a multisystemic disease. A comprehensive assessment of his medical history and physical examination findings point to general and nonspecific symptoms—fatigue, weight loss; renal disease with proteinuria and elevated creatinine; cardiac disease with ventricular hypertrophy; coagulopathy, and orthostatic hypotension. Seemingly unrelated, but pertinent, additional information in this patient's case includes the history of bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome and macroglossia on physical examination. In working up a suspected patient with amyloidosis, in addition to the comprehensive clinical evaluation, it is important to undertake an expedited multisystemic investigative approach. This should include laboratory tests and pertinent imaging studies to assess the extent of organ involvement with amyloidosis (Table 2), screening for a plasma cell disorder, and identifying amyloidosis on a biopsy.
Laboratory tests
A comprehensive battery of tests to assess for organ amyloidosis should include a complete blood count with differential, liver function tests, renal function tests, PT/aPTT, cardiac biomarkers (NT-proBNP or BNP, troponin T or I), and a 24-hour urine protein test.
Advanced imaging
Mr. Smith had a recent transthoracic echocardiogram that showed multiple findings, including increased left ventricular wall thickness and restrictive diastolic filling pattern13 ; these should have triggered a suspicion of infiltrative cardiomyopathy. An echocardiogram with strain imaging to measure global longitudinal strain (GLS) can provide the characteristic appearance of cardiac amyloidosis, that is, abnormal GLS with apical sparing pattern.13 Other advanced noninvasive imaging studies include scintigraphy with Tc-99m-pyrophosphate (PYP scan), which is widely available in the United States and can be positive in both ATTR (nearly always) and AL cardiomyopathy (sometimes).14 Cardiac uptake is evaluated visually and scored comparing tracer uptake in the myocardium and ribs (grade 0–3), with a grade 2 or 3 pattern strongly suggestive of ATTR cardiomyopathy, with variable tracer uptake seen in AL cardiomyopathy. Using a threshold for higher visual score (a heart to contralateral ratio ≥1.5) has 97% sensitivity and 100% specificity for ATTR.15 A cardiac magnetic resonance imaging demonstrating delayed gadolinium enhancement has high sensitivity and specificity for amyloidosis.16 More advanced imaging studies such as the SAP scintigraphy scan17 and PET/CT using radionuclides such as 18F-florbetapir18 and investigational imaging techniques19 can be undertaken if available as part of clinical care or research protocols. Abdominal imaging studies can provide insight in organomegaly.
Screening for a plasma cell disorder
A serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation electrophoresis (IFE) are fundamental tests to detect M-proteins in the serum. The serum protein electrophoresis identifies the presence of abnormal protein bands, while the IFE determines the specific immunoglobulin class involved. The free light chain assay allows measurement of serum kappa and lambda free light chains, providing additional information. The urine protein electrophoresis and IFE on a 24-hour urine sample is an additional valuable test to detect and characterize monoclonal proteins in urine. A comprehensive screen for a plasma cell disorder should include all these tests and has 98.1% sensitivity for AL amyloidosis.20 Finally, a bone marrow aspiration and biopsy examination is needed to confirm the presence of a clonal plasma cell disorder and can provide prognostic information such as the percentage of clonal plasma cells and cytogenetic abnormalities.
Tissue diagnosis
If the PYP scan is abnormal and a plasma cell disorder screen shows no evidence of a monoclonal process, a tissue biopsy is not needed as this constellation has high specificity and sensitivity for ATTR cardiomyopathy.14 In this setting, the next step includes a genetic test to identify whether there is a pathogenic mutation in the transthyretin gene (ATTRv) or whether the gene is normal (ATTRwt). In any other scenario, it is critical to confirm amyloidosis with a tissue biopsy. Staining for amyloidosis on a bone marrow biopsy combined with a fat aspirate has a high sensitivity at high-volume specialty amyloid centers.21,22 However, outside of high-volume centers, the yield on a fat aspirate has been, anecdotally, notoriously low and may be secondary to inadequate tissue quantity, inadequate staining, or improper use of polarizing instrument.23,24 In this setting, amyloidosis is not ruled out, and additional tissue (eg, salivary gland biopsy or biopsy of the target organ) should be expeditiously obtained to confirm or rule out amyloidosis.
Key next steps after diagnosing amyloidosis
Typing amyloid deposits
While the presence of Congo red positive stain, which exhibits apple-green birefringence under polarized light microscopy, confirms the presence of amyloid, additional tests are needed to determine the specific protein or peptide involved in the amyloid deposits. Immunohistochemical staining has good performance when used with custom-made antibodies specific to different amyloid proteins.25 Other antibody-based methods, such as immunofluorescence, are used especially in nephropathology. Immuno-gold labeling has high accuracy but is not widely available.26 Proteomics using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry can directly assay the protein composition of microdissected amyloid deposits and determine the subtype.27 This technique is expensive, requires experience in evaluating results, and has a lead time of several days to obtain results.28 However, it has high accuracy and has revolutionized amyloid typing, has led to discovery of new subtypes, and can also shed light on the rare (<1%) but clinically important phenomenon of co-occurrence of two different types of amyloidosis in the same patient.29
Identify whether the patient has localized versus systemic amyloidosis
Differentiating between localized and systemic amyloidosis is an important step in management of patients with amyloidosis. While the presence of amyloid in certain organs such as the heart, kidneys, or liver or in the nervous system is always indicative of a systemic process, in some tissue, such as cutaneous, breast, pulmonary, and gastrointestinal, amyloidosis is either localized or systemic. Some other locations, such as the urinary bladder, aerodigestive tract, and orbit, are almost always localized. In a patient diagnosed with AL amyloidosis in one of these organ systems, it is important to take a systems approach with laboratory, imaging, and plasma cell disorder testing to identify whether a patient has localized or systemic amyloidosis. Localized amyloidosis can be surgically managed with debulking or managed conservatively with monitoring as patients may have local or, rarely, systemic progression.30,31
Staging of systemic AL amyloidosis
Staging of systemic AL amyloidosis is an important step to determine the extent of systemic AL disease, predicting prognosis, and guiding treatment decisions. The two commonly used staging systems include the 2004 Mayo staging system32 with the 2015 European modification33 and the 2012 revised Mayo staging system.34 In addition to the cardiac biomarkers, renal staging system is also helpful in determining renal prognosis.35 Table 3 provides the staging systems along with cross-reference among the various biomarkers. Similar staging systems for ATTR cardiomyopathy using cardiac biomarkers also exist.36,37
Staging systems in AL amyloidosis
| . | Biomarker thresholds . | Staging . |
|---|---|---|
| 2004 Mayo stage with 2015 European modification of 2004 staging system32,33,38 | NT-proBNP ≥332 ng/L (or BNP ≥81) cTnT ≥0.035 ng/ml (or cTnI ≥0.1 or hsTnT ≥50) | Stage I: 0 markers above cutoff Stage II: 1 marker above cutoff Stage IIIa: both markers above cutoff and NT-proBNP <8500 (or BNP >700) Stage IIIb: both markers above cutoff and NT-proBNP ≥8500 (or BNP >700) |
| 2012 Mayo staging system34,38 | NT-proBNP ≥1800 ng/L (or BNP ≥800) cTNT ≥0.025 ng/ml (or hsTnT ≥40) dFLC ≥180 mg/L | Stage I: 0 markers above cutoff Stage II: 1 marker above cutoff Stage III: 2 markers above cutoff Stage IV: 3 markers above cutoff |
| 2014 Palladini renal staging system35 | eGFR ≤50 ml/min/1.73 m2 Proteinuria ≥5 g/24 h | Stage I: 0 thresholds met Stage II: either threshold met Stage III: both thresholds met |
| . | Biomarker thresholds . | Staging . |
|---|---|---|
| 2004 Mayo stage with 2015 European modification of 2004 staging system32,33,38 | NT-proBNP ≥332 ng/L (or BNP ≥81) cTnT ≥0.035 ng/ml (or cTnI ≥0.1 or hsTnT ≥50) | Stage I: 0 markers above cutoff Stage II: 1 marker above cutoff Stage IIIa: both markers above cutoff and NT-proBNP <8500 (or BNP >700) Stage IIIb: both markers above cutoff and NT-proBNP ≥8500 (or BNP >700) |
| 2012 Mayo staging system34,38 | NT-proBNP ≥1800 ng/L (or BNP ≥800) cTNT ≥0.025 ng/ml (or hsTnT ≥40) dFLC ≥180 mg/L | Stage I: 0 markers above cutoff Stage II: 1 marker above cutoff Stage III: 2 markers above cutoff Stage IV: 3 markers above cutoff |
| 2014 Palladini renal staging system35 | eGFR ≤50 ml/min/1.73 m2 Proteinuria ≥5 g/24 h | Stage I: 0 thresholds met Stage II: either threshold met Stage III: both thresholds met |
BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; cTnT, cardiac troponin T; cTnI, cardiac troponin I; hs-TnT, high-sensitivity cTnT; dFLC, difference between involved and uninvolved free light chain; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; NT-proBNP, N-terminal of propedtide of BNP.
Referral to specialty centers
Given that amyloidosis remains a rare disease, patients diagnosed with amyloidosis can benefit from evaluation at a specialty center at least once. These specialty centers have multidisciplinary physicians and health care providers who collaborate to provide comprehensive care, including accurate diagnosis, treatment options including clinical trials and stem cell transplantation, and a comprehensive approach to supportive care. Further patient and caregiver education through organizations such as the Amyloidosis Foundation, Amyloidosis Support Groups, and Amyloidosis Research Consortium are critical to provide additional support to patients and caregivers, establish collaborative care, and provide research opportunities.
Amyloidosis is not identified on workup
Amyloidosis may not be identified despite clinical manifestations, advanced imaging, and organ biopsy. While it may seem reassuring that a diagnosis of amyloidosis has been refuted, if amyloidosis remains suspected, close follow-up and reevaluation of the clinical course and symptoms is necessary. Monitoring for progressive organ dysfunction or the emergence of additional clinical features consistent with amyloidosis is crucial. Repeat investigations, including laboratory tests, imaging studies, and biopsies, may be necessary over time to capture evolving disease manifestations.
Summary
The detection and diagnosis of amyloidosis can appear daunting. A systems approach to suspecting and working up the disease can make the process easier. There are specific clinical findings that should raise the suspicion and prompt a comprehensive systematic diagnostic approach. Earlier diagnosis prior to the development of advanced end-organ damage is crucial for improving the morbidity and mortality of patients with amyloidosis.
Acknowledgments
Anita D'Souza is supported by K23 HL141445 and R01 HL166339. The content is solely the responsibility of the author and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
Anita D'Souza reports institutional research funding from AbbVie, Caelum, Janssen, Novartis, Prothena, Sanofi, Takeda, and TeneoBio; advisory board fees from BMS, Pfizer, and Janssen; and consulting fees from Prothena and Janssen.
Off-label drug use
Anita D'Souza: Nothing to disclose.