Abstract
Polycythemia vera, essential thrombocytosis (ET), and primary myelofibrosis (PMF) are grouped together as myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) because of shared clinical, pathologic, and molecular features. The 2005 discovery of the driver mutation JAK2V617F, found in more than 70% of individuals with MPNs and 98% of those with PV, has transformed the diagnosis and management of MPNs. Although PV is the most common phenotype associated with JAK2V617F, roughly 60% of individuals with ET or PMF also have the mutation, and JAK2V617F is now recognized as a common lesion in clonal hematopoiesis (CH). JAK2V617F+ CH and MPN are indolent disorders that evolve over time, with transitions to different disease phases, transformation to bone marrow failure or leukemia, and high thrombosis rates. Genomic assessment has taken center stage as an important tool to define disease phenotype, disease burden, prognosis, and even thrombosis risk of MPNs. Genomics has also unveiled the causes and factors that modify the risk of acquiring and expanding CH and MPNs and points to new pathways for targeted therapies to treat and ultimately prevent them. Genomic assessment of patients with MPNs, like other cancers, enables the clinician to capitalize on large population data sets to inform the individual patient of risk, identify treatment, and improve outcomes.
Learning Objectives
Understand the the role of JAK2V617F mutational burden in MPN presentation
Understand the thrombosis risk associated with JAK2V617F mutation burden
Clinical case
A 65-year-old computer engineer presented to a vascular medicine specialist for evaluation and management of left lower extremity deep venous thrombosis (DVT) after a traumatic ankle fracture in 2018. In 2014, he developed a pulmonary embolism on postoperative day 2 after a radical prostatectomy for early-stage prostate cancer and was treated for 6 months with warfarin. His vascular medicine specialist noted thrombocytosis, not only at the time of the DVT, but also for several years prior; submitted a JAK2V617F mutation assay that was positive with a variant allele fraction (VAF) of 49%; and referred him to a hematologist (Table 1). A bone marrow biopsy in 2020 showed hypercellular marrow with panmyelosis, compatible with a myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) with normal cytogenetics, and a next-generation sequencing panel revealed the JAK2V617F mutation with a variant allele fraction (VAF) of 63% and a TET2 frameshift mutation with a VAF 30%. The patient fulfilled the 2016 World Health Organization (WHO) criteria for the diagnosis of polycythemia vera (PV). Phlebotomy and cytoreduction were initiated,1 and systemic anticoagulation was continued.
Serial laboratory values in the 7 years before 2020 MPN diagnosis
| . | Reference range . | 2013 . | 2014* . | 2017 . | 2018† . | 2020 . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC count | 4.50-11.00 X 109/L | 6.27 | 8.0 | 7.34 | 8.12 | 8.96 |
| RBC count | 4.50-5.90 X 106/uL | 5.14 | 5.12 | 5.29 | 5.52 | 6.19 |
| Hemoglobin | 13.9-16.3 g/dL | 15.6 | 15.2 | 15.9 | 16.4 | 18.1 |
| Hematocrit | 41.0%-53.0% | 46.5 | 44.0 | 47.3 | 51.3 | 56.4 |
| Mean corpuscular volume | 80-100 fL | 88 | 87 | 89 | 90 | 91 |
| RBC distribution width | 11.5%-14.5% | 13.4 | 14.5 | 15.0 | 15.3 | 16.5 |
| Platelet count | 150-350 X 109/L | 438 | 521 | 467 | 468 | 589 |
| JAK2V617F VAF | <0.8% | — | — | — | 49 | 61 |
| . | Reference range . | 2013 . | 2014* . | 2017 . | 2018† . | 2020 . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC count | 4.50-11.00 X 109/L | 6.27 | 8.0 | 7.34 | 8.12 | 8.96 |
| RBC count | 4.50-5.90 X 106/uL | 5.14 | 5.12 | 5.29 | 5.52 | 6.19 |
| Hemoglobin | 13.9-16.3 g/dL | 15.6 | 15.2 | 15.9 | 16.4 | 18.1 |
| Hematocrit | 41.0%-53.0% | 46.5 | 44.0 | 47.3 | 51.3 | 56.4 |
| Mean corpuscular volume | 80-100 fL | 88 | 87 | 89 | 90 | 91 |
| RBC distribution width | 11.5%-14.5% | 13.4 | 14.5 | 15.0 | 15.3 | 16.5 |
| Platelet count | 150-350 X 109/L | 438 | 521 | 467 | 468 | 589 |
| JAK2V617F VAF | <0.8% | — | — | — | 49 | 61 |
RBC, red blood cell; WBC, white blood cell.
Postoperative pulmonary embolism.
DVT; bold indicates values outside of the reference range.
Introduction
PV, essential thrombocytosis (ET), and primary myelofibrosis (PMF) are grouped together as MPNs because of shared clinical, pathologic, and molecular features. The 2005 discovery of the driver mutation JAK2V617F, found in more than 70% of individuals with MPNs and 98% of individuals with PV, has transformed the diagnosis and management of PV.2 Although PV is the most common phenotype associated with JAK2V617F, roughly 60% of individuals with ET or PMF also have the mutation. MPNs are indolent disorders that evolve over time, with transitions to different disease phases, transformation to bone marrow failure or leukemia, and high thrombosis rates. Both quantitative and qualitative genomic assessments are important tools in defining disease phenotype, disease burden, prognosis, and even thrombosis risk in MPN. This case and discussion will highlight the impact of the JAK2V617F clonal burden on disease phenotype and review factors that determine progression from JAK2V617F clonal hematopoiesis (CH) to MPN.
Mutations and clonal burden
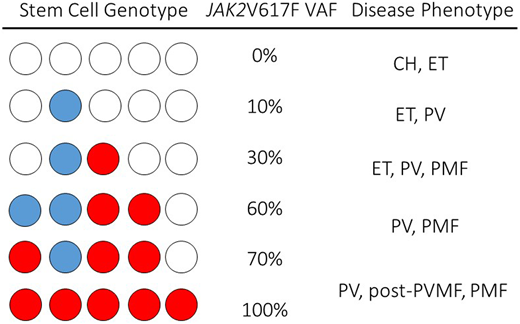
Our patient had acquired JAK2V617F, the most prevalent driver mutation in MPNs. JAK2 transmits cytokine-mediated growth signals in blood stem cells and progenitors, enabling the bone marrow factory to produce the millions of red cells, white cells, and platelets required on a daily basis.3,4 The acquired mutation JAK2V617F transmits an excessive growth signal, that induces a blood stem cell with the mutation to overproduce red cells, white cells, and platelets. Mutation of JAK2 is highly associated with acquired uniparental disomy of the chromosome 9, p region, that contains JAK2 and results in homozygosity of JAK2V617F.5 Both the JAK2V617F mutation and the mitotic recombination events occur at the hemopoietic stem cell (HSC) level, so that individual HSCs may have 1 or 2 copies of the mutation, and within a single individual, HSCs with heterozygous and homozygous mutations and unaffected HSCs may coexist.6-9 The emergence of a dominant homozygous JAK2V617F clone is a feature of many patients with PV compared with ET, suggesting that additional genetic or epigenetic events facilitate the expansion of JAK2V617F homozygous clones in PV.10 Clonal heterogeneity of JAK2V617F in the HSC compartment results in quantitative measures of JAK2V617F that range from as low as a fraction of a percent to 100% (Figure 1).
Schematic of hypothetical permutation and combination single-cell genotypes, VAFs, and associated clinical disease phenotypes in JAK2V617F+MPN.JAK2V617F can be present in a single cell as a single copy (heterozygote, blue circle) or as a double copy (homozygote, red circle) in a single-cell genome. In a single individual, multiple stem cell clones may have varied JAK2V617F genotypes, and a measured JAK2V617F may range from very low levels to 100% (center column). Clinical phenotypes associated with the JAK2V617F VAF are represented in the right column.
Schematic of hypothetical permutation and combination single-cell genotypes, VAFs, and associated clinical disease phenotypes in JAK2V617F+MPN.JAK2V617F can be present in a single cell as a single copy (heterozygote, blue circle) or as a double copy (homozygote, red circle) in a single-cell genome. In a single individual, multiple stem cell clones may have varied JAK2V617F genotypes, and a measured JAK2V617F may range from very low levels to 100% (center column). Clinical phenotypes associated with the JAK2V617F VAF are represented in the right column.
Both mutation (JAK2V617F, CALR, or MPL) and clonal burden have an influence on clinical presentation and outcome in the MPN. JAK2V617F allele burden, or variant allele fraction (VAF) at the very lowest end subtends a phenotype of clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential or ET, whereas on the higher end, it subtends phenotypes of PV or post-PV myelofibrosis (PMF; Figure 1).8,11-13 High JAK2V617F clonal burdens associate with higher white cell counts, risk of myelofibrosis transformation, and risk of splenomegaly.6 Not long after the 2005 JAK2V617F discovery, many studies observed a higher risk of thrombotic events in JAK2V617F+, compared with JAK2V617F− ET and MF.7,14 JAK2V617F is an independent predictor of thrombosis in ET, whether compared with JAK2−, or, after the discovery of mutations in the calreticulin gene (CALR), in ET, when compared with CALR mutation–positive patients.14,15 Categorical mutation status is now incorporated in the International Prognostic Score for Thrombosis in Essential Thrombocythemia (IPSET) assessment.14,16,17 In 2020, the specific effect of JAK2V617F MPNs on thrombosis risk was refined by the analysis of thrombosis in 1537 patients in China with JAK2V617F MPNs. The risk of thrombosis in patients with PV was significantly higher at diagnosis than in those with ET or PMF, and, in patients with PV, a JAK2V617F VAF greater than 50% was an independent risk factor for thrombosis, especially arterial thrombosis. In patients with PV, the incidence of thrombosis in patients with a JAK2V617F VAF ≥50% was 4.6 times higher than that in patients with a VAF <50%.18
Our patient had sustained thrombotic events years before MPN diagnosis, and his blood counts suggested that he had had a latent process for many years (Table 1). Thromboses that occur before, at presentation, or during the course of a previously diagnosed MPN have been described since the initial descriptions of these types of blood cancers.19 Recent large retrospective case series have established that most events occur at or during the years preceding MPN diagnosis; that arterial events outnumber venous events in the older population, whereas venous events outnumber arterial events in the younger MPN population; and that female sex is associated with unusual sites of venous thrombotic events, including splanchnic vein thromboses and cerebral sinus thrombosis.18,20-25 Hultcrantz and colleagues examined thrombotic events in 9 429 Swedish patients with MPNs diagnosed between 1987 and 2009 and in 35 820 matched population controls, allowing for risk estimation at the time of diagnosis and thereafter. Both arterial and venous thrombotic events occurred more frequently around the time of MPN diagnosis, but the risk of occurrence of additional events persisted throughout the lifetimes of the patients with MPN. Both advanced age and male sex added to the cumulative risk of occurrence of both arterial and venous events in patients with MPN, but the thrombotic risk was higher in the MPN group, regardless of age or sex, as compared with the non-MPN control population.24 In our patient, it is likely that the JAK2V617F mutation was evolving long before diagnosis of MPN and was exposing the patient to venous thrombosis risk at the time of cancer surgery. Indeed, mathematical modeling of JAK2V617F suggests that the mutation may be acquired up to 24 years before diagnosis of MPN.26
Clonal hematopoiesis and clonal evolution
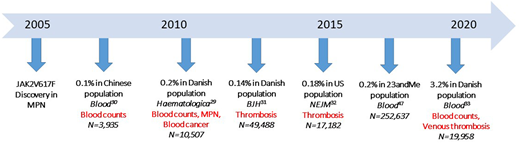
Our patient had the JAK2V617F mutation, the most common mutation in the MPNs, but also the fifth most common lesion associated with clonal hematopoiesis (CH).27,28 CH is defined as an expansion of blood stem cell clones that bear advantageous acquired somatic mutations of myeloid malignancy genes. Not long after its discovery in MPN, investigations into non-MPN populations for JAK2V617F+ CH (JAK2V617F CH) revealed associations with both elevated blood counts and thrombosis risk, even at very low JAK2V617F VAFs and without fulfilling the criteria for an MPN diagnosis. Three large general population studies from China and Denmark found that low JAK2V617F VAFs were present in 0.1% to 0.2% of the general population29-31 (Figure 2). Surprisingly, despite the absence of overt MPN, there were significantly higher platelet counts, white cell counts, and hemoglobin concentrations in individuals with JAK2V617F CH than in the controls and higher rates of both arterial and venous thrombotic events. Subsequent studies of CH demonstrated associations with arterial thrombotic events, and when segregated by specific mutated gene, JAK2V617F CH was associated with the highest relative risk of arterial events.28,32
Evaluation of JAK2V617F CH in non-MPN populations. Since 2007, more than 350 000 individuals from general population studies have been examined for JAK2V617F CH. Published reports of 353 707 unique individuals, JAK2V617F CH prevalence, and clinical associations are listed on the timeline. Significant differences in blood counts, cancer risk, and thrombosis risk between JAK2V617F CH populations and controls are indicated in red.
Evaluation of JAK2V617F CH in non-MPN populations. Since 2007, more than 350 000 individuals from general population studies have been examined for JAK2V617F CH. Published reports of 353 707 unique individuals, JAK2V617F CH prevalence, and clinical associations are listed on the timeline. Significant differences in blood counts, cancer risk, and thrombosis risk between JAK2V617F CH populations and controls are indicated in red.
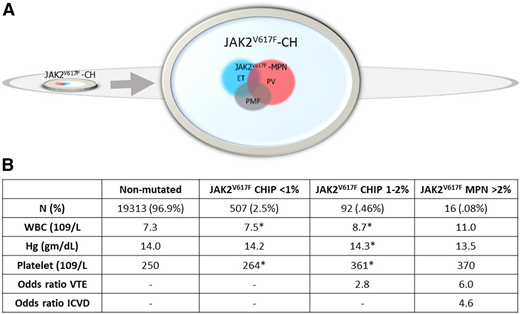
In 2019, Cordua and coworkers provided further insight into associations of JAK2V617F CH and CALR-mutation–positive CH (CALR CH) in 19 958 participants in the Danish General Suburban Population Study.33 Owing to a more sensitive assay, the researchers found a higher prevalence of JAK2V617F CH (3%) than that in prior studies (Figure 3). CALR CH was detected, but JAK2V617F CH was nearly 20-fold more prevalent. In MPN, the prevalence of JAK2V617F, although higher than that of the CALR mutation, was only fourfold more common than CALR mutation prevalence, a consistent finding across large MPN cohorts.34-36 Blood counts and thrombosis risk of the 645 CH+ individuals were significantly different than that of the CH− individuals. The 32 CALR-mutation CH individuals had higher platelet counts, whereas the 613 JAK2V617F CH individuals had significantly higher total white cell, neutrophil, red cell, and platelet counts, and a higher odds ratio of the occurrence of thrombotic events (Figure 3). Blood counts were significantly different, even when stratified by very low JAK2V617F VAF (<1%), and there was a dose-response relationship of CH <1%, compared with CH ≥1% to 2% in both blood counts and risk of venous thrombosis. In that study, JAK2V617F was detected in 613 of the 19 958 (3%) population, whereas only 14 of the 613 (2.3%) individuals with JAK2V617F had an MPN diagnosis.33 It is not known whether all individuals with JAK2V617F CH evolve to JAK2V617F+ MPN. Other large population studies of JAK2V67F CH that have had the opportunity to examine the change in allele burden over time and evolution from JAK2V617F CH to JAK2V617F MPN have found increases in VAF and evolution to an overt MPN in a substantial proportion of patients with CH.13,29 Thus, identifying factors that expand JAK2V617F CH to JAK2V617F MPN is important for understanding disease evolution, and recognizing the potential for JAK2V617F CH to be a hidden force behind elevated blood counts and thrombosis risk is important in the non-MPN population. Our patient had blood counts and VTE risk in line with those associated with JAK2V617F CH 7 years before the MPN diagnosis was made.
Frequency of JAK2V17F in the general population and in associated laboratory and clinical phenotypes. Data are from the Danish Suburban Population Survey.33 (A) JAK2V617F was identified in 3% (615/19958) of the general population, represented as the small chip within the larger oval. The arrow indicates an enlargement of this chip and shows that JAK2V617F MPN comprised only 2.6% of the total JAK2V617F CH population, with JAK2V617F MPN phenotypes indicated as overlapping colored circles. (B) Average blood counts and associated venous thromboembolism (VTE) and ischemic cerebrovascular disease (ICVD) from the non-mutated (CALR-negative and JAK2V617F-negative) and JAK2V617F-positive populations stratified by JAK2V617F VAF). Asterisks indicate significantly different values compared with the nonmutated population (*P < .05). WBC, white blood cell.
Frequency of JAK2V17F in the general population and in associated laboratory and clinical phenotypes. Data are from the Danish Suburban Population Survey.33 (A) JAK2V617F was identified in 3% (615/19958) of the general population, represented as the small chip within the larger oval. The arrow indicates an enlargement of this chip and shows that JAK2V617F MPN comprised only 2.6% of the total JAK2V617F CH population, with JAK2V617F MPN phenotypes indicated as overlapping colored circles. (B) Average blood counts and associated venous thromboembolism (VTE) and ischemic cerebrovascular disease (ICVD) from the non-mutated (CALR-negative and JAK2V617F-negative) and JAK2V617F-positive populations stratified by JAK2V617F VAF). Asterisks indicate significantly different values compared with the nonmutated population (*P < .05). WBC, white blood cell.
Causes of CH and CH expansion to MPN
The acquisition of JAK2V617F CH, the expansion of JAK2V617F CH into MPN, and venous and arterial thromboses share smoking, older age, and a chronic inflammatory state as risk factors.29,37,38 Inflammation drives thrombotic risk by increased white cell and platelet counts, related to activation of clotting factors, endothelial cells, platelets, and white cells and to activation of hypoxia-sensing signaling pathways.39 Thromboinflammation is a concept that is particularly operational in cancer, aging, sickle cell anemia, and infection, and links inflammatory pathways to thrombotic risk.40-43 JAK2V617F is uniquely connected to inflammation, both proximally and distally: inflammatory states may predispose to acquiring JAK2V617F CH, and JAK2V617F MPN signaling also drives inflammatory pathways.44,45 For example, Pedersen et al analyzed 107 969 individuals from the Copenhagen Population Study, a cohort in which 352 individuals developed MPN and in which a subcohort of 49 143 of the study individuals had JAK2V6717F testing, as reported by Nielsen et al.13,44,46 Pedersen et al used a Mendelian randomization approach to test the role, in the acquisition of either MPN or JAK2V617F positivity, of a common loss-of-function IL-6 receptor variant associated with impaired IL-6 receptor signaling and reduced inflammation. Their results demonstrate that age- and sex-adjusted risk of acquiring any MPN is 40% lower among carriers of the loss-of-function IL-6 receptor variant. This relative risk reduction was even more prominent when examined in the JAK2V617F tested subcohort, further substantiating the concept that acquisition of JAK2V617F CH and JAK2V617F MPN subtend the same risk factors.31,44,47 The JAK2 46/1 haplotype, which is highly associated with the development of JAK2V617F+ MPN, is also associated with the acquisition of JAK2V617F CH, suggesting that JAK2V617F CH is a precursor to JAK2V617F MPN.31,47-49 The JAK2V617F mutation burden, measured prospectively in individuals with CH, is estimated to increase by roughly 0.5% per year and much more variably in individuals with JAK2V617F MPN, where disease type, age, sex, and other mutational burdens influence clonal burden and expansion.12,13,26 Serial measures of JAK2V617F in our patient demonstrate that JAK2V617F VAF increased significantly as clinical disease evolved from thrombocytosis to PV (Table 1).
Mutations in myeloid cancer genes are common in the normal ageing population.27,28,50-53 Although several myeloid gene mutations can be responsible for CH, coronary artery disease is most closely associated with mutations in DNMT3A, TET2, ASXL1, and JAK2.28,32,54 Individuals with mutations in DNMT3A, TET2, or ASXL1 had a 1.7- to 2.0-fold increase in coronary artery disease, whereas individuals with JAK2V617F CH had a 12.1-fold increase coronary artery disease.32 The degree of elevation of the VAF of the mutated gene was also related to risk of coronary artery disease. Conversely, individuals with JAK2V617F MPN harbor the most common CH lesions that are associated with vascular disease, including TET2, DNMT3A, and ASXL1.35,55,56
A growing number of studies have indicated that loss-of-function mutations in TET2 or DNMT3A lead to the development of a generalized inflammatory state that may contribute to clonal expansion and thrombotic risk. Low-density lipoprotein receptor–deficient mice, prone to develop atherosclerosis, that were genetically engineered to lack TET2 in marrow cells acquired atherosclerotic plaques with increased size and an increased number of macrophages in the aortic walls.32 The macrophages from TET2-deficient animals generated increased levels of cytokines and chemokines and promoted IL-1β transcription.57 Individuals with TET2 CH have been shown to have significantly elevated plasma levels of IL-8. Taken together, the results of these studies highlight the interplay between inflammation, clonal expansion, and thrombotic risk and provide a rationale for targeting inflammation to reduce acquisition of CH, expansion of CH, and vascular risk in both MPN and CH populations.38,58,59
Clinical case follow-up
Our patient had both JAK2V617F and a TET2 frameshift mutation, with VAFs of 63% and 30%, respectively. Although we could not determine clinically which lesion came first, the mutation order of TET2 and JAK2 has been studied in PV and has important clinical and biological associations.60 Patients who acquired the JAK2V617F mutation first were younger and had higher thrombosis rates than those who acquired the TET2 mutation first. Mechanistically, the TET2 mutation may alter the transcriptional impact of a subsequent JAK2V617F mutation in an HSC and may mitigate proliferation compared with an HSC with JAK2V617F and normal TET2 functions.60 Our patient’s median event-free survival is estimated to be 15 years, based on a personalized risk calculator.56 The TET2 lesion slightly shortens his estimated event-free survival, and in this sense, may indicate higher inflammatory risk that shortens survival via thrombotic events or genomic instability and acquisition and expansion of additional detrimental lesions. National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines have identified age >60 and/or history of thrombosis as the first point in their treatment algorithm and recommends treatment with hydroxyurea (HU) as the first-line therapy for older, high-risk patients with PV.61 NCCN guidelines have incorporated the concept of treatment intolerance or resistance into the risk profile of PV. Patients with PV who are resistant or intolerant of HU are at an even increased risk of thrombotic events or disease progression, and in the case of HU resistance, the guidelines recommend alternative therapies.62 Although not yet realized, genomics has the potential to predict treatment resistance. Genomics may move patients proactively to therapies with a higher probability of disease control without having to demonstrate treatment failure or may identify contexts in which targeted treatments induce both hematologic and molecular remission.
Conclusions
Genomics has informed diagnostics, prognostics, and treatment of MPN; has unveiled the causes and factors that modify risk of acquiring and expanding CH and MPN; and has pointed to new pathways for targeted therapies to treat and ultimately prevent CH and MPN. The progress in MPN genomics reflects the promise of 21st century medicine: molecularly defined entities, refined risk assessment, and opportunities for targeted therapy. The molecular pathogenesis of our patient’s presentation and disease are now understood, and his thrombosis risk and symptom burden can be specifically addressed and monitored with ongoing genomic assessment. Thus, genomic assessment of patients with MPN enables clinicians to capitalize on large data sets to inform the individual of risk, identify therapies, and improve outcomes.63
Correspondence
Alison R. Moliterno, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Ross Building Room 1025, 720 Rutland Ave, Baltimore, MD 21205; e-mail: amoliter@jhmi.edu.
References
Competing Interests
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.R.M. has served as a consultant to PharmaEssentia. H.K. declares no competing financial interests.
Author notes
Off-label drug use: None disclosed.