Key Points
KLR polymorphisms and HLA-C epitopes associate with NKG2A frequency and cell surface expression and predict NK cell function.
HLA-C epitope is associated with HLA-E expression, independently of HLA-E allotypes and HLA-B leader peptide.
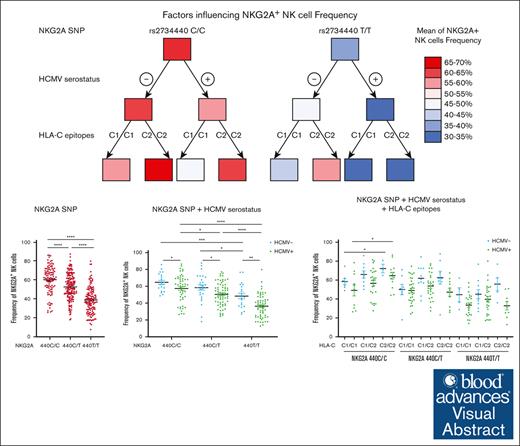
Visual Abstract
CD94/NKG2A is a heterodimeric receptor commonly found on natural killer (NK) and T cells, and its interaction with its ligand HLA-E on adjacent cells leads to inhibitory signaling and cell suppression. We have identified several killer cell lectin–like receptor (KLR)C1 (NKG2A) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that are associated with NKG2A expression on NK cells, CD8+ T cells, and Vγ9/Vδ2+ T cells. Additionally, due to strong linkage disequilibrium, polymorphisms in KLRC2 (NKG2C) and KLRK1 (NKG2D) are also associated with NKG2A surface density and frequency. NKG2A surface expression correlates with single-cell NK responsiveness, and NKG2A+ NK cell frequency is associated with total NK repertoire response and inhibitability, making the identification of SNPs responsible for expression and frequency important for predicting the innate immune response. Because HLA-E expression is dependent on HLA class I signal peptides, we analyzed the relationship between peptide abundance and HLA-E expression levels. Our findings revealed a strong association between peptide availability and HLA-E expression. We identified the HLA-C killer immunoglobulin–like receptor ligand epitope as a predictive marker for HLA-ABC expression, with the HLA-C1 epitope associated with high HLA-E expression and the HLA-C2 epitope associated with low HLA-E expression. The relationship between HLA-C epitopes and HLA-E expression was independent of HLA-E allotypes and HLA-B leader peptides. Although HLA-E expression showed no significant influence on NKG2A-mediated NK education, it did affect NK cell inhibition. In summary, these findings underscore the importance of NKG2A SNPs and HLA-C epitopes as predictive markers of NK cell phenotype and function and should be evaluated as prognostic markers for diseases that express high levels of HLA-E.
Introduction
CD94/NKG2A (NKG2A) is a heterodimeric inhibitory receptor that was originally identified in natural killer (NK) cells.1 Similar to other inhibitory NK receptors, including killer immunoglobulin–like receptors (KIRs), NKG2A has been detected on CD8+ αβ T cells2 and Vγ9/Vδ2 (Vδ2) T cells.3 Coinheritance of inhibitory receptors and their cognate HLA class I ligands lowers the threshold for effector response through a process called “education,”4,5 resulting in cells with high cytokine production and killing capacity against HLA-deficient diseased cells. The expression patterns of NKG2A and KIRs on effector T cells have remained relatively underexplored. However, emerging evidence suggests that these receptors play a significant role in T-cell function, particularly in γδ T cells,6,7 through the same mechanism of education and inhibition processes elucidated in NK cells.
Recent investigations by our laboratory and others have demonstrated that KIR gene copy number and allelic variation can predict receptor expression frequency and cell surface density,8-10 in some cases impacting NK function through education or inhibitability.8,11-13
In contrast to inhibitory KIRs, the functional impact of NKG2A variations has been less explored. Characterized as an inhibitory receptor due to the presence of an immunoreceptor tyrosine–based inhibitory motif in its intracellular domain,14 NKG2A binds HLA-E on target cells15,16 and contributes to NK cell education.17,18 NKG2A is differentially expressed between CD56dim and CD56bright NK cells in terms of cell surface expression and frequency, with CD56bright NK cells almost exclusively NKG2A+ and having higher NKG2A density.19 The potential of NKG2A as a candidate checkpoint inhibitor for NK and CD8+ T cells20 is currently being investigated in clinical trials.21,22 Although there are no common protein variants of NKG2A, several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have been reported in the noncoding regions of the killer cell lectin–like receptor (KLR)C1 gene, which encodes the NKG2A protein. KLRC1 SNPs have been associated with the risk of rheumatoid arthritis23 and disease outcome in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia receiving interleukin-2-based immunotherapy.24 Recent studies have reported that HLA-E expression and NKG2A-mediated education are influenced by HLA class I leader peptide polymorphism25,26 and HLA class I expression.27 In this study, we demonstrated an association between SNPs from multiple genes in the KLR family, including KLRC1, and NKG2A expression on NK cells, CD8+ T cells, and Vδ2+ T cells, and we described how the expression of NKG2A and its cognate ligand HLA-E impact effector cell function.
Materials and methods
Sample sources and preparation
Peripheral blood samples were collected from healthy human donors after approval from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Institutional Review Board, and donors provided informed written consent. Buffy coats were obtained from healthy volunteer donors at the New York Blood Center (NYBC). The Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Institutional Review Board waived the need for additional research consent for anonymous NYBC samples. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) serostatus and self-identified ethnicity and race were provided by NYBC. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated by Ficoll gradient and cryopreserved. Genomic DNA samples were extracted using a Blood Mini Kit (Qiagen).
KLRC1, KLRC2, KLRK1, KLRD1, HLA-C, and HLA-E SNP typing and HLA sequencing
Primers were designed for sequence-specific primers polymerase chain reaction (PCR), targeting selected SNPs in various genes (Table 1). Each 20 μL reaction contained 25 to 50 ng of DNA, 0.5 μL 2ʹ-deoxynucleoside 5'-triphosphate, 2 μL PCR buffer, and 0.25 μL Taq polymerase (Roche). All reactions were run on Eppendorf Mastercycler pro-S thermocyclers using the following conditions: 94°C for 2 minutes, (94°C for 15 seconds, 55-63°C for 20 seconds, 72°C for 60-90 seconds) for 40 cycles, and 72°C for 1 minute. The annealing temperature, elongation time, and control primer concentration varied based on the primer design (Table 1). All PCR products were analyzed by gel electrophoresis on 1.5% agarose gels run for 40 minutes at 125 V and imaged with an AlphaImager (Alpha Innotech). HLA genotyping was provided by Deutsche Knochenmarkspenderdatei Life Science Lab using next-generation sequencing.28
Sequence-specific primers PCR primers used for genotyping human genomic DNA samples
| SNP . | Reaction . | Gene region . | ARMS primer sequence (forward and reverse) . | Control primer conc to use (μM) . | Annealing temperature (°C) . | Elongation time (min) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1983526 G>C | NKG2A V1 | 5' UTR (C) | GATCCTTTTACTAGGGCTTCTAGCAGAC AATCTCCACTCAAACTCCTCTCAACTGT | 1.25 short | 58 | 1 |
| NKG2A V2 | 5' UTR (G) | GATCCTTTTACTAGGGCTTCTAGCAGAG AATCTCCACTCAAACTCCTCTCAACTGT | 1.25 short | 58 | 1 | |
| rs7301582 C>T | NKG2A V3 | Intron 5 (C) | TCAAAAGTACATTAGCAGTATATGAATTTTAAACC CTTGTCATCAACTATAAGTAAAATCACTATGCTT | 0.625 short | 58 | 1 |
| NKG2A V4 | Intron 5 (T) | TCAAAAGTACATTAGCAGTATATGAATTTTAAATT CTTGTCATCAACTATAAGTAAAATCACTATGCTT | 0.625 short | 55 | 1 | |
| rs2734440 C>T | NKG2A V5 | Intron 4 (C) | GTTCACATATTTGCAAACATATAAACCTATTC CTACATTAATACAGAGGCACAACAATTCTTC | 1.25 long | 58 | 1 |
| NKG2A V6 | Intron 4 (T) | GTTCACATATTTGCAAACATATAAACCTATTT CTACATTAATACAGAGGCACAACAATTCTTC | 1.25 long | 58 | 1 | |
| rs2734414 A>T | NKG2A V7 | 3' UTR (A) | GACACAAAGTAACGTTCTATCAGTTAAA GTGCATCAGATAAATTGTATATTTCTTAAAATAGAAATATAT | 1.25 long | 58 | 1 |
| NKG2A V8 | 3' UTR (T) | GACACAAAGTAACGTTCTATCAGTTAAT GTGCATCAGATAAATTGTATATTTCTTAAAATAGAAATATAT | 1.25 long | 58 | 1 | |
| rs3216778 AAGTTT> AAGTTTAAGTTT | NKG2A V9 | Intron 3 | GTAACGATAGTTGTTATTCCCTGTAAGTC AAATTTGCATCTAAATCAATCATAATAATTTTAA | 0.833 long | 55 | 1 |
| NKG2A V10 | Intron 3 | GTAACGATAGTTGTTATTCCCTGTAAGTC AAATTTGCATCTAAATCAATCATAATAATTTTTT | 0.833 long | 55 | 1 | |
| rs1967432 T>C | NKG2A V11 | Intron 1 (T) | CAGAGCCCATTGACTAAATGATTTAATTAGA TGGTCTTTTCTTAATGGCTGAAATGTTCT | 1.25 long | 55 | 1 |
| NKG2A V12 | Intron 1 (C) | CAGAGCCCATTGACTAAATGATTTAATTAAG TGGTCTTTTCTTAATGGCTGAAATGTTCT | 0.833 long | 55 | 1 | |
| rs1141715 A>G | NKG2C V1 | Exon 3 (G) | CTATTACAGTCCTGGAGCAGAACAATCC ATCCACTCCTCAGGACAATGGCCACAGT | 0.72 short | 58 | 1 |
| NKG2C V2 | Exon 3 (A) | CTATTACAGTCCTGGAGCAGAACAATAT ATCCACTCCTCAGGACAATGGCCACATT | 0.72 short | 58 | 1 | |
| rs28403159 T>C | NKG2C V3 | Exon 1 (C) | GTATTTCTAAATACAGTATTTTGATTGTTGAC CTCACTTCTGAGAAGGTTCCTCTTTGTTTTC | 0.833 long | 50 | 1 |
| NKG2C V4 | Exon 1 (T) | GTATTTCTAAATACAGTATTTTGATTGTTGAC CTCACTTCTGAGAAGGTTCCTCTTTGTTTTT | 0.833 long | 50 | 1 | |
| N/A | NKG2C Neg | GTAGGATATACTTCGGATTTCTATTTGATGC GCTAAAATTAAATACAAGTGATGTATAAGAAAAAG | 1.25 long | 58 | 1 | |
| rs2246809 A>G | NKG2D V1 | 5' UTR (A) | GCCTGTTTAAATTTATTAATGCACAGGAGATTCT GCAATACAACAAACAGAAATCTGAGTAACCTC | 5 long | 58 | 1 |
| NKG2D V2 | 5' UTR (G) | GCCTGTTTAAATTTATTAATGCACAGGAGATTCC GCAATACAACAAACAGAAATCTGAGTAACCTC | 5 long | 58 | 1 | |
| rs11053781 C>T | NKG2D V3 | Intron 2 (C) | CATAAAATCTTTGCCTAGACTAATGTCCGG ATCACGTTACCTGACTTCAATATATACGA | 1.25 long | 57 | 1 |
| NKG2D V4 | Intron 2 (T) | CATAAAATCTTTGCCTAGACTAATGTCCAA ATCACGTTACCTGACTTCAATATATACGA | 1.25 long | 57 | 1 | |
| rs1049174 G>C | NKG2D V5 | 3' UTR (G) | AGTGAAGGAAGAGAAGGCCAGCAGATCTC ACAAGTACAAATCATAGCAAAGGAAACGTCCTAAGATC | 2.5 long | 60 | 1 |
| NKG2D V6 | 3' UTR (C) | AGTGAAGGAAGAGAAGGCCAGCAGATCCG ACAAGTACAAATCATAGCAAAGGAAACGTCCTAAGATC | 2.5 long | 60 | 1 | |
| rs2302489 A>T | CD94 V1 | Exon 1 (A) | GAACATCATTTAAATACACAATTTTTCATTCTCAA CAATGAAGAATCAGGAAAATATAATGAATGTGG | 1.25 long | 56 | 1 |
| CD94 V2 | Exon 1 (T) | GAACATCATTTAAATACACAATTTTTCATTCTCCT CAATGAAGAATCAGGAAAATATAATGAATGTGG | 2.5 long | 56 | 1 | |
| rs3759272 G>T | CD94 V3 | 5' UTR (G) | ATTACCTGACTTTAGGGCTGAGACTGCAG TTCCATGTACTGTATCTCTCCCACTCAT | 2.5 long | 56 | 1 |
| CD94 V4 | 5' UTR (T) | ATTACCTGACTTTAGGGCTGAGACTGCAT TTCCATGTACTGTATCTCTCCCACTCAT | 5 long | 56 | 1 | |
| rs1264457 G>A | HLA-E 01:01 | Exon 2 (A) | ATGCATGGCTGCGAGCTGGGGCCCGATA GCATGTGTCTTCCAGGTAGGCTCTCTCG | 10 long | 63 | 1 |
| HLA-E 01:03 | Exon 2 (G) | ATGCATGGCTGCGAGCTGGGGCCCGATG GCATGTGTCTTCCAGGTAGGCTCTCTCG | 10 long | 63 | 1 | |
| rs17408553 G>T | HLA-C1 | Exon 2 (G) | TTGGGAGGGAAACGGCCTCTGCGAA TTGGGAGGGAAACGGCCTCTGGGAA GCTCTGGTTGTAGTAGCCGCGCATG | 10 long | 63 | 1 |
| HLA-C2 | Exon 2 (T) | TTGGGAGGGAAACGGCCTCTGCGAA TTGGGAGGGAAACGGCCTCTGGGAA GCTCTGGTTGTAGTAGCCGCGCAAT | 10 long | 63 | 1 | |
| N/A | Long control | CCAAGCCCAACCTTAAGAAGAAAATTGGAG CCAAACCCACGGTACGCATGGGAACACTGC | - | |||
| N/A | Short control | CCCACCTTCCCCTCTCTCCAGGCAAATGGG GGGCCTCAGTCCCAACATGGCTAAGAGGTG | - |
| SNP . | Reaction . | Gene region . | ARMS primer sequence (forward and reverse) . | Control primer conc to use (μM) . | Annealing temperature (°C) . | Elongation time (min) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1983526 G>C | NKG2A V1 | 5' UTR (C) | GATCCTTTTACTAGGGCTTCTAGCAGAC AATCTCCACTCAAACTCCTCTCAACTGT | 1.25 short | 58 | 1 |
| NKG2A V2 | 5' UTR (G) | GATCCTTTTACTAGGGCTTCTAGCAGAG AATCTCCACTCAAACTCCTCTCAACTGT | 1.25 short | 58 | 1 | |
| rs7301582 C>T | NKG2A V3 | Intron 5 (C) | TCAAAAGTACATTAGCAGTATATGAATTTTAAACC CTTGTCATCAACTATAAGTAAAATCACTATGCTT | 0.625 short | 58 | 1 |
| NKG2A V4 | Intron 5 (T) | TCAAAAGTACATTAGCAGTATATGAATTTTAAATT CTTGTCATCAACTATAAGTAAAATCACTATGCTT | 0.625 short | 55 | 1 | |
| rs2734440 C>T | NKG2A V5 | Intron 4 (C) | GTTCACATATTTGCAAACATATAAACCTATTC CTACATTAATACAGAGGCACAACAATTCTTC | 1.25 long | 58 | 1 |
| NKG2A V6 | Intron 4 (T) | GTTCACATATTTGCAAACATATAAACCTATTT CTACATTAATACAGAGGCACAACAATTCTTC | 1.25 long | 58 | 1 | |
| rs2734414 A>T | NKG2A V7 | 3' UTR (A) | GACACAAAGTAACGTTCTATCAGTTAAA GTGCATCAGATAAATTGTATATTTCTTAAAATAGAAATATAT | 1.25 long | 58 | 1 |
| NKG2A V8 | 3' UTR (T) | GACACAAAGTAACGTTCTATCAGTTAAT GTGCATCAGATAAATTGTATATTTCTTAAAATAGAAATATAT | 1.25 long | 58 | 1 | |
| rs3216778 AAGTTT> AAGTTTAAGTTT | NKG2A V9 | Intron 3 | GTAACGATAGTTGTTATTCCCTGTAAGTC AAATTTGCATCTAAATCAATCATAATAATTTTAA | 0.833 long | 55 | 1 |
| NKG2A V10 | Intron 3 | GTAACGATAGTTGTTATTCCCTGTAAGTC AAATTTGCATCTAAATCAATCATAATAATTTTTT | 0.833 long | 55 | 1 | |
| rs1967432 T>C | NKG2A V11 | Intron 1 (T) | CAGAGCCCATTGACTAAATGATTTAATTAGA TGGTCTTTTCTTAATGGCTGAAATGTTCT | 1.25 long | 55 | 1 |
| NKG2A V12 | Intron 1 (C) | CAGAGCCCATTGACTAAATGATTTAATTAAG TGGTCTTTTCTTAATGGCTGAAATGTTCT | 0.833 long | 55 | 1 | |
| rs1141715 A>G | NKG2C V1 | Exon 3 (G) | CTATTACAGTCCTGGAGCAGAACAATCC ATCCACTCCTCAGGACAATGGCCACAGT | 0.72 short | 58 | 1 |
| NKG2C V2 | Exon 3 (A) | CTATTACAGTCCTGGAGCAGAACAATAT ATCCACTCCTCAGGACAATGGCCACATT | 0.72 short | 58 | 1 | |
| rs28403159 T>C | NKG2C V3 | Exon 1 (C) | GTATTTCTAAATACAGTATTTTGATTGTTGAC CTCACTTCTGAGAAGGTTCCTCTTTGTTTTC | 0.833 long | 50 | 1 |
| NKG2C V4 | Exon 1 (T) | GTATTTCTAAATACAGTATTTTGATTGTTGAC CTCACTTCTGAGAAGGTTCCTCTTTGTTTTT | 0.833 long | 50 | 1 | |
| N/A | NKG2C Neg | GTAGGATATACTTCGGATTTCTATTTGATGC GCTAAAATTAAATACAAGTGATGTATAAGAAAAAG | 1.25 long | 58 | 1 | |
| rs2246809 A>G | NKG2D V1 | 5' UTR (A) | GCCTGTTTAAATTTATTAATGCACAGGAGATTCT GCAATACAACAAACAGAAATCTGAGTAACCTC | 5 long | 58 | 1 |
| NKG2D V2 | 5' UTR (G) | GCCTGTTTAAATTTATTAATGCACAGGAGATTCC GCAATACAACAAACAGAAATCTGAGTAACCTC | 5 long | 58 | 1 | |
| rs11053781 C>T | NKG2D V3 | Intron 2 (C) | CATAAAATCTTTGCCTAGACTAATGTCCGG ATCACGTTACCTGACTTCAATATATACGA | 1.25 long | 57 | 1 |
| NKG2D V4 | Intron 2 (T) | CATAAAATCTTTGCCTAGACTAATGTCCAA ATCACGTTACCTGACTTCAATATATACGA | 1.25 long | 57 | 1 | |
| rs1049174 G>C | NKG2D V5 | 3' UTR (G) | AGTGAAGGAAGAGAAGGCCAGCAGATCTC ACAAGTACAAATCATAGCAAAGGAAACGTCCTAAGATC | 2.5 long | 60 | 1 |
| NKG2D V6 | 3' UTR (C) | AGTGAAGGAAGAGAAGGCCAGCAGATCCG ACAAGTACAAATCATAGCAAAGGAAACGTCCTAAGATC | 2.5 long | 60 | 1 | |
| rs2302489 A>T | CD94 V1 | Exon 1 (A) | GAACATCATTTAAATACACAATTTTTCATTCTCAA CAATGAAGAATCAGGAAAATATAATGAATGTGG | 1.25 long | 56 | 1 |
| CD94 V2 | Exon 1 (T) | GAACATCATTTAAATACACAATTTTTCATTCTCCT CAATGAAGAATCAGGAAAATATAATGAATGTGG | 2.5 long | 56 | 1 | |
| rs3759272 G>T | CD94 V3 | 5' UTR (G) | ATTACCTGACTTTAGGGCTGAGACTGCAG TTCCATGTACTGTATCTCTCCCACTCAT | 2.5 long | 56 | 1 |
| CD94 V4 | 5' UTR (T) | ATTACCTGACTTTAGGGCTGAGACTGCAT TTCCATGTACTGTATCTCTCCCACTCAT | 5 long | 56 | 1 | |
| rs1264457 G>A | HLA-E 01:01 | Exon 2 (A) | ATGCATGGCTGCGAGCTGGGGCCCGATA GCATGTGTCTTCCAGGTAGGCTCTCTCG | 10 long | 63 | 1 |
| HLA-E 01:03 | Exon 2 (G) | ATGCATGGCTGCGAGCTGGGGCCCGATG GCATGTGTCTTCCAGGTAGGCTCTCTCG | 10 long | 63 | 1 | |
| rs17408553 G>T | HLA-C1 | Exon 2 (G) | TTGGGAGGGAAACGGCCTCTGCGAA TTGGGAGGGAAACGGCCTCTGGGAA GCTCTGGTTGTAGTAGCCGCGCATG | 10 long | 63 | 1 |
| HLA-C2 | Exon 2 (T) | TTGGGAGGGAAACGGCCTCTGCGAA TTGGGAGGGAAACGGCCTCTGGGAA GCTCTGGTTGTAGTAGCCGCGCAAT | 10 long | 63 | 1 | |
| N/A | Long control | CCAAGCCCAACCTTAAGAAGAAAATTGGAG CCAAACCCACGGTACGCATGGGAACACTGC | - | |||
| N/A | Short control | CCCACCTTCCCCTCTCTCCAGGCAAATGGG GGGCCTCAGTCCCAACATGGCTAAGAGGTG | - |
Each is listed with the SNP, its associated reaction name or variant (referred to throughout this study), targeted gene region, primer sequences, control primer concentration, annealing temperature, and elongation time.
ARMS, amplification-refractory mutation system; conc, concentration.
Phenotypic analysis by flow cytometry
PBMCs (2 × 105 cells per well) were surface-stained for 30 minutes at room temperature with the indicated antibodies (supplemental Table 1) in phosphate-buffered saline with 0.5% bovine serum albumin and 2 mM EDTA for 30 minutes. Dead cells were excluded by staining with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Invitrogen) or live/dead (Invitrogen), and NK cells were defined by CD3−CD56+ gating. All fluorescence-activated cell sorting analyses were performed on an LSR Fortessa (BD Biosciences) and analyzed using the FlowJo software (10.6.2, Treestar).
Cell lines
HLA-ABC–deficient B-cell leukemia 721.221 and K562 were knocked out for the endogenous HLA-E gene through the lentiCRISPR system; lentivirus was generated as described previously29 using a plasmid encoding an single-guide RNA targeting HLA-E and Cas9 with puromycin resistance from GenScript, and the viral supernatant was used to transduce the 721.221 and K562 cells. HLA-E–negative clones were selected after puromycin selection.
For the generation of K562 HLA-E, fusion genes containing the leader sequences (amino acids, 1-24) of HLA-A∗02 (MAVMAPRTLVLLLSGALALTQTWA) combined with the mature protein of HLA-E, the cell line was generated as described previously.29 Cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 with 10% fetal calf serum and penicillin plus streptomycin.
These cell lines were used for CD107a mobilization and interferon gamma (IFN-γ) production to quantify NK cell activation, as previously described29 (supplemental Methods).
Cell culture condition and activation assays
CD107a mobilization and IFN-γ production were used to quantify the NK cell activation. Frozen PBMCs were thawed and rested overnight in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and 200 U/mL interleukin-2 (Proleukin, Prometheus Laboratories) and incubated at 37°C with 5% CO2. The following day, PBMCs (5 × 105 cells per well) were plated in V-bottom 96-well plates and incubated with HLA class I–negative K562 (ATCC), K562 transduced with HLA-E, or 721.221 cell lines (kindly provided by Peter Parham, Stanford University, Stanford, CA) at a 5:1 ratio in the presence of an anti-CD107a antibody (BD Biosciences). After 1 hour of coculture, Brefeldin A (MP Biomedicals) and Golgi stop (BD) were added to each well and incubated for an additional 3 hours. The cells were then washed with phosphate-buffered saline and stained with LIVE/DEAD (Invitrogen) for 20 minutes at room temperature (RT), followed by surface staining: cells were stained with anti-CD56, anti-CD3, anti-CD158a/h, anti-CD158b1/b2/j, anti-CD158e1, anti-NKG2A, and anti-NKG2C for 30 minutes at RT. The cells were fixed and permeabilized using the FIX & PERM Kit (Invitrogen), according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. The intracellular IFN-γ was stained with an antibody for 25 minutes at RT. NK cells exclusively expressing NKG2A (NKG2A-SP) were evaluated, excluding cells coexpressing other inhibitory receptors that might contribute to NK education (KIR2DL1, KIR2DL2, KIR2DL3, and KIR3DL1), as well as cells expressing activating receptors (NKG2C, KIR2DS1, and KIR2DS2).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using unpaired parametric or nonparametric tests to compare independent groups. Before this, a normality test was used to assess whether the groups followed a Gaussian distribution. Depending on the outcome of the normality test, either t tests or Mann-Whitney tests were used to determine the statistical significance among different groups, and the mean ± standard error of the mean or median ± interquartile ranges were represented. Correlations were assessed using the Pearson correlation coefficient. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) was assessed using the χ2 test. All tests are indicated in individual figure legends. The significance levels are denoted as follows: ∗P ≤ .05, ∗∗P ≤ .01, ∗∗∗ P ≤ .001, and ∗∗∗∗P ≤ .0001. All analyses and graphical representations were generated using the Prism software (GraphPad).
Results
Common NKG2A noncoding SNPs are in positive LD and associate with NKG2A expression
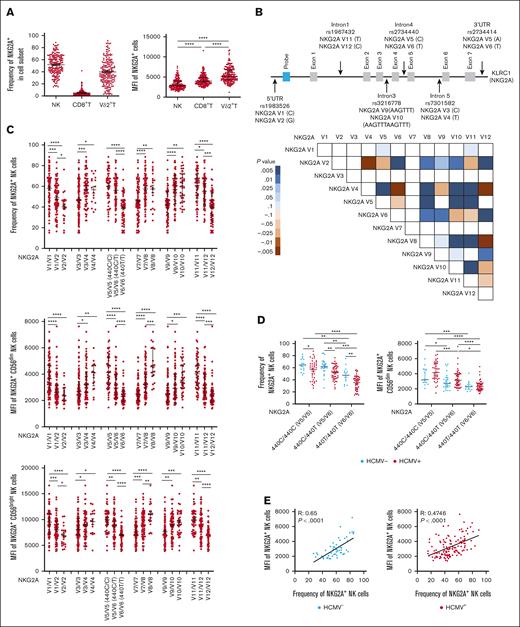
We measured by flow cytometry the frequency and cell surface density of NKG2A on lymphocytes from 204 PBMC samples from healthy individuals. Consistent with previously published findings, we observed NKG2A expression on NK and T cells.1-3 Among T cells, NKG2A was found in CD8+ T cells and Vδ2+ T cells. Between individuals, the frequency of NKG2A expression in NK and Vδ2+ T-cell populations was highly variable, with mean values of 51.84% and 39.70%, respectively. In comparison, the frequency of NKG2A expression on CD8+ T cells was universally low, with a mean value of 5.12% (Figure 1A). NKG2A surface density, as measured by mean fluorescence intensity (MFI), varied between individuals, but in general, expression was lower on NK cells, intermediate on CD8+ T cells, and higher on Vδ2+ T cells (Figure 1A).
Common NKG2A noncoding SNPs are in positive LD and associate with NKG2A expression independent of HCMV serostatus. (A) NKG2A frequency and MFI in NK cells, CD8+ T cells, and Vδ2+ T cells from phenotyping of 204 healthy blood donors. (B) Common noncoding KLRC1 SNPs and LD analysis from genotyping of 204 donors. Positive LD shaded blue; negative LD shaded red. (C) NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and MFI stratified by NKG2A variant. (D) NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and MFI stratified by HCMV serostatus and SNP rs2734440 (440C refers to SNP rs2734440 C and 440T refers to rs2734440 T). (E) Correlation between NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and MFI in HCMV– and HCMV+ individuals. (F) Distribution of rs2734440 alleles among different ethnic groups. For panels C-D, t tests were performed, and the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) was presented to analyze NKG2A frequencies. For panels A,C-D, Mann-Whitney tests were performed, and median ± interquartile range (IQR) is presented to analyze NKG2A MFI. Correlations were assessed using the Pearson correlation coefficient for panel E. LD was assessed using the χ2 test for panel B. The symbols represent individual samples. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
Common NKG2A noncoding SNPs are in positive LD and associate with NKG2A expression independent of HCMV serostatus. (A) NKG2A frequency and MFI in NK cells, CD8+ T cells, and Vδ2+ T cells from phenotyping of 204 healthy blood donors. (B) Common noncoding KLRC1 SNPs and LD analysis from genotyping of 204 donors. Positive LD shaded blue; negative LD shaded red. (C) NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and MFI stratified by NKG2A variant. (D) NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and MFI stratified by HCMV serostatus and SNP rs2734440 (440C refers to SNP rs2734440 C and 440T refers to rs2734440 T). (E) Correlation between NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and MFI in HCMV– and HCMV+ individuals. (F) Distribution of rs2734440 alleles among different ethnic groups. For panels C-D, t tests were performed, and the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) was presented to analyze NKG2A frequencies. For panels A,C-D, Mann-Whitney tests were performed, and median ± interquartile range (IQR) is presented to analyze NKG2A MFI. Correlations were assessed using the Pearson correlation coefficient for panel E. LD was assessed using the χ2 test for panel B. The symbols represent individual samples. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
We sought to identify the genetic determinants of NKG2A expression. Although the coding sequence of KLRC1 does not have common SNPs, SNPs are common in noncoding regions. We developed a PCR-based methodology to genotype 6 SNPs (Table 1) (rs1983526 G>C, rs7301582 C>T, rs2734440 C>T, rs2734414 A>T, rs3216778 AAGTTT>AAGTTTAAGTTT, and rs1967432 T>C) in noncoding regions (5′ untranslated region; Introns 1, 3, 4, and 5; and 3′ untranslated region, respectively) of KLRC1 (Figure 1B). SNP typing of 204 healthy donors permitted the analysis of LD and identification of several positive and negative associations between SNPs (Figure 1B).
We then determined whether the selected KLRC1 SNPs are associated with NKG2A expression. The 6 SNPs were associated with different frequencies of NKG2A expression among the total NK population and by cell surface density on individual CD56dim and CD56bright NK cells (Figure 1C), with CD56bright cells having higher NKG2A expression overall than CD56dim NK cells. Several SNPs were associated with similar patterns of NKG2A expression in CD8+ T cells (supplemental Figure 1A) and Vδ2+ T cells (supplemental Figure 1B).
The dimorphic SNP rs2734440 was characterized by either cytosine (440C) or thymine (440T) and appeared to be a suitable marker for our study, stratifying groups hierarchically (440C/C > 440C/T > 440T/T) in all 3 cell populations with a relatively even distribution of individuals between groups (Figure 1C). We assessed the impact of HCMV exposure on NKG2A expression and found a lower NKG2A+ NK cell frequency but higher MFI in individual NK cells from HCMV+ individuals compared with those from HCMV– individuals (Figure 1D), no impact on NKG2A expression in CD8+ T cells (supplemental Figure 1C), and a lower frequency of NKG2A+ Vδ2+ T cells in HCMV+ individuals (supplemental Figure 1E). A clear correlation between NKG2A+ frequency and surface density was evident in NK cells (Figure 1E). The correlation was stronger in HCMV– (R = 0.65, P < .0001) individuals than in HCMV+ individuals (R = 0.4746; P < .0001). Similar observations were made for CD8+ T cells and Vδ2+ T cells (supplemental Figure 1D,F).
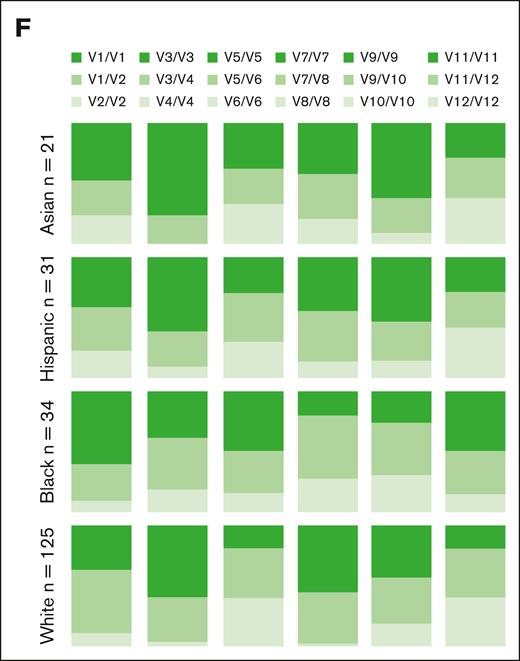
SNP frequencies differed between the ethnic groups (Figure 1F). In comparison with other ethnic groups, African-American individuals displayed a higher frequency of rs2734440 C/C (440C/C) vs rs2734440 T/T (440T/T). Although our cohort size is limited, our observations are consistent with those from larger data sets available in the National Center for Biotechnology Information SNP database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/), in which the allele rs2734440 T is present at an average of 51.92% in a cohort of 9912 European individuals and 16.96% in a cohort of 2848 African-American individuals.
SNPs among KLR gene family members are in LD and associate with NKG2A expression
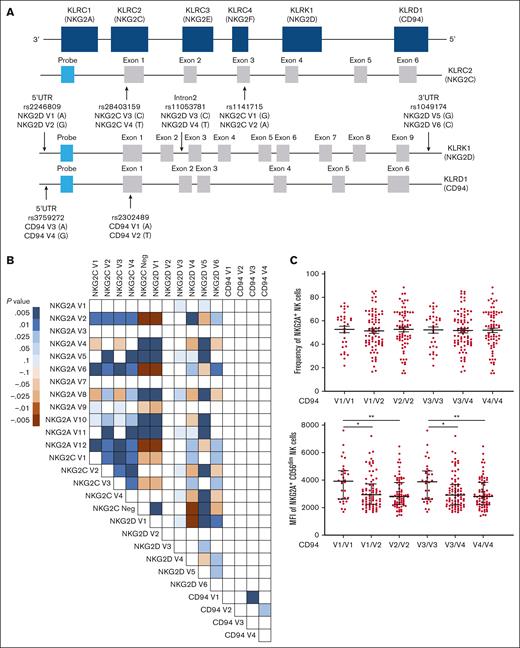
Members of the KLR gene family are located in close proximity on chromosome 12 and encode the proteins CD94 (KLRD1), NKG2D (KLRK1), NKG2A (KLRC1), NKG2C (KLRC2), NKG2E (KLRC3), and NKG2F (KLRC4) (Figure 2A). We developed a PCR-based methodology to detect SNPs for NKG2D, CD94, and NKG2C genes (Figure 2A; Table 1), as well as gene copy number for NKG2C.30 Typing of 204 healthy donors permitted the evaluation of LD between each SNP, identifying a strong LD between NKG2A, NKG2D, and NKG2C variants (Figure 2B). NKG2C allele typing results obtained using the 2 SNPs for NKG2C (rs1141715 and rs28403159) revealed an almost identical LD (Figure 2B). The overwhelming majority of individuals exhibited only NKG2C∗01 or NKG2C∗02, with only 1 individual exhibiting the NKG2C∗03 allele.31,32 Interestingly, the CD94 SNPs were not significantly linked with any other selected variants (Figure 2B). In light of the strong LD in the KLR gene region, we assessed various polymorphisms as potential proxies for predicting NKG2A expression.
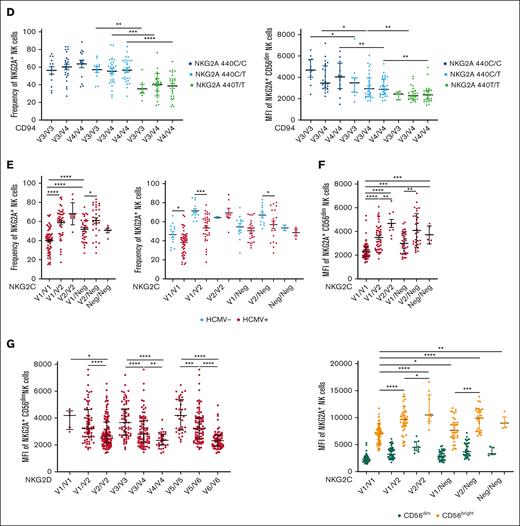
SNPs among KLR gene family members are in LD and associate with NKG2A expression. (A) KLR gene complex and SNPs targeted. (B) LD between selected NKG2C, NKG2D, and CD94 SNPs based on the genotyping of 204 healthy donors. Positive LD shaded blue; negative LD shaded red. (C) NKG2A frequency and MFI stratified by CD94 SNPs. (D) NKG2A MFI stratified by CD94 SNPs, in conjunction with NKG2A variants. (E) NKG2A+ NK cells frequency stratified by NKG2C SNPs and HCMV serostatus. (F) NKG2A MFI stratified by NKG2C SNPs and CD56 cell surface expression levels. (G) NKG2A MFI on CD56dim NK cells stratified using NKG2D SNPs. For panels C-E, t tests were performed, and mean ± SEM is presented to analyze NKG2A frequencies. For panels C-D,F-G, Mann-Whitney tests were performed, and median ± IQRs are presented to analyze NKG2A MFI. LD was assessed using the χ2 test for panel B. Symbols represent individual samples. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
SNPs among KLR gene family members are in LD and associate with NKG2A expression. (A) KLR gene complex and SNPs targeted. (B) LD between selected NKG2C, NKG2D, and CD94 SNPs based on the genotyping of 204 healthy donors. Positive LD shaded blue; negative LD shaded red. (C) NKG2A frequency and MFI stratified by CD94 SNPs. (D) NKG2A MFI stratified by CD94 SNPs, in conjunction with NKG2A variants. (E) NKG2A+ NK cells frequency stratified by NKG2C SNPs and HCMV serostatus. (F) NKG2A MFI stratified by NKG2C SNPs and CD56 cell surface expression levels. (G) NKG2A MFI on CD56dim NK cells stratified using NKG2D SNPs. For panels C-E, t tests were performed, and mean ± SEM is presented to analyze NKG2A frequencies. For panels C-D,F-G, Mann-Whitney tests were performed, and median ± IQRs are presented to analyze NKG2A MFI. LD was assessed using the χ2 test for panel B. Symbols represent individual samples. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
NKG2A covalently associates with CD94 on the cell surface to form a heterodimeric receptor.1 We therefore hypothesized that the availability of CD94 might be a limiting factor for the cell surface expression of NKG2A. Although we did not observe an impact of CD94 polymorphisms on the frequency of NKG2A+ NK cells (Figure 2C) or NKG2A+ CD8+ T cells (supplemental Figure 2A), we observed significant differences in the cell surface density of NKG2A on NK cells (Figure 2C) and CD8+ T cells (supplemental Figure 2A), depending on CD94 SNP typing of the individual. Interestingly, the opposite was observed in Vδ2+ T cells: CD94 polymorphisms were associated with significant differences in NKG2A+ Vδ2+ frequency but not cell surface expression of NKG2A (supplemental Figure 2C).
To confirm that CD94 and NKG2A variants independently contributed to NKG2A MFI, we performed an analysis of SNPs from both loci and found a cumulative impact of CD94 and NKG2A SNPs on NKG2A surface expression in CD8+ T cells (supplemental Figure 2B) and on the frequency of Vδ2+ T cells (supplemental Figure 2D) but not on NKG2A+ NK cell frequency or NKG2A surface expression (Figure 2D). In an extended analysis involving 40 donors, we explored the relationship between NKG2A, NKG2C, and CD94 cell surface expression. We observed that CD94 expression was predominantly influenced by NKG2A and NKG2C (supplemental Figure 2E-G). Additionally, our findings revealed a low level of CD94 cell surface expression on NKG2A– NKG2C– (double negative) NK cells compared with NKG2A+ or NKG2C+ NK cells (supplemental Figure 2F-H), suggesting that NKG2A or NKG2C regulates the cell surface expression of the heterodimeric complex.
Due to the strong LD observed between NKG2A and NKG2C polymorphisms, we found that the NKG2C polymorphism rs1141715, which distinguishes NKG2C V1(NKG2C∗01 + NKG2C∗03) and V2 (NKG2C∗02), and copy number associated with NKG2A expression in a distinct hierarchy for both frequency (Figure 2E) and cell surface expression (Figure 2F). The NKG2C SNP-associated hierarchy of NKG2A+ NK frequencies remained consistent between HCMV– and HCMV+ donors (Figure 2E). Similarly, the hierarchy of NKG2A+ surface density among CD56dim and CD56bright NK cells was also associated with NKG2C typing (Figure 2F). Similar patterns were observed in CD8+ T cells (supplemental Figure 3A-B) and Vδ2+ T cells (supplemental Figure 3C; Figure 3D).
Finally, we investigated the impact of NKG2D SNPs on NKG2D and NKG2A expression. Three NKG2D SNPs were associated with NKG2D surface expression (supplemental Figure 3E). Cell surface expression of NKG2D and NKG2A was correlated with both CD56dim and CD56bright NK cells (supplemental Figure 3F). As for CD94 and NKG2C, NKG2D SNP typing–associated donors into different groups of NKG2A expression (Figure 2G). In summary, due to the high LD between SNPs in the KLR genetic region, we identified numerous polymorphisms associated with NKG2A expression.
NKG2A surface density and frequency impact NK cell responsiveness
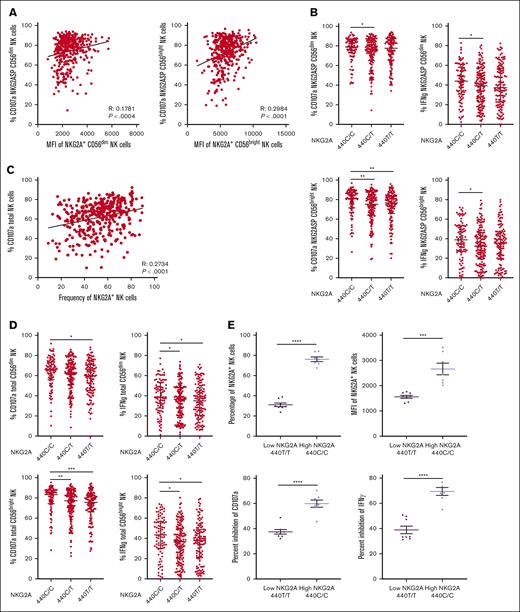
Because NK receptor–ligand expression and interaction are integral to NK function at the level of the single cell and global NK repertoire, we investigated how variations in the expression of NKG2A impact NK cell function. Examining NKG2A-single positive NK cells (lacking coexpression of NKG2C and all KIR, NKG2A-SP) in a cohort of 400 individuals, we found a significant correlation between NKG2A surface expression and effector response, as measured by CD107a mobilization to the K562 HLA class I–negative target cell line, in which we also knocked out HLA-E (K562 HLA-E KO). This correlation was seen within both the CD56dim (R = 0.1781; P < .0004) and CD56bright populations (R = 0.2984; P < .0001; Figure 3A). We found that the NKG2A polymorphism rs2734440 C vs T (440C/C, 440C/T, and 440T/T) was associated with NK cell education, as evidenced by CD107a mobilization and IFN-γ accumulation in both CD56dim and CD56bright NK cells (Figure 3B). These findings collectively suggest that the education of NKG2A+ NK cells is influenced by the surface density of NKG2A.
NKG2A surface density and frequency impact NK cell responsiveness. (A) Correlation between NKG2A MFI and degranulation of NKG2A+ CD56dim and CD56bright NK cells in a CD107a. (B) NKG2A-SP CD56dim or CD56bright NK cell degranulation and IFN-γ frequency stratified by SNP rs2734440 (440C represents rs2734440 T). (C) Correlation between NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and global NK cell degranulation. (D) Total NK cell degranulation and IFN-γ frequency in CD56dim or CD56bright NK cell stratified by SNP rs2734440. (E) Total NK cell inhibitability, measured by inhibition of CD107a and IFN-γ response in a killing assay against K562 HLA-E KO or K562 transduced with HLA-E in NKG2A high (440 C/C, n = 7) and low (440 T/T, n = 8) expression groups, as defined by the NKG2A genotype. Correlations were assessed using the Pearson correlation coefficient for panels A,C. Mann-Whitney tests were performed and median ± IQRs are presented in panels B,D. For panel E, t tests were performed, and mean ± SEM is presented. Symbols represent individual samples. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
NKG2A surface density and frequency impact NK cell responsiveness. (A) Correlation between NKG2A MFI and degranulation of NKG2A+ CD56dim and CD56bright NK cells in a CD107a. (B) NKG2A-SP CD56dim or CD56bright NK cell degranulation and IFN-γ frequency stratified by SNP rs2734440 (440C represents rs2734440 T). (C) Correlation between NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and global NK cell degranulation. (D) Total NK cell degranulation and IFN-γ frequency in CD56dim or CD56bright NK cell stratified by SNP rs2734440. (E) Total NK cell inhibitability, measured by inhibition of CD107a and IFN-γ response in a killing assay against K562 HLA-E KO or K562 transduced with HLA-E in NKG2A high (440 C/C, n = 7) and low (440 T/T, n = 8) expression groups, as defined by the NKG2A genotype. Correlations were assessed using the Pearson correlation coefficient for panels A,C. Mann-Whitney tests were performed and median ± IQRs are presented in panels B,D. For panel E, t tests were performed, and mean ± SEM is presented. Symbols represent individual samples. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
We then sought to investigate the influence of HLA-E expression on the education of NKG2A-SP NK cells, by first examining published models linking HLA class I with NKG2A+ NK function. These models include the HLA-E polymorphism, HLA-B leader peptide, z score of HLA-A expression, and HLA class I signal peptide variants.25-27 For each of these genetic models, we found no significant association with NKG2A+ NK education, as assessed by CD107a mobilization in primary NK cells against K562 HLA-E KO target cells (supplemental Figure 4A-D). Furthermore, we found no correlation between CD107a response and overall HLA-E cell surface expression (supplemental Figure 4E). We conclude that despite reports linking specific HLA class I signal peptides to higher HLA-E expression and NKG2A binding,25,26 we find these signal peptide-based methodologies are not necessarily predictive of NKG2A-associated NK education.
We identified a direct correlation between the frequency of NKG2A+ NK cells and the overall CD107a response (R = 0.2782; P < .0001; Figure 3C). Analyzing the data based on NKG2A polymorphism at rs2734440 (440C vs 440T), we observed a significant association of this polymorphism with the global NK effector response (Figure 3D).
Because NK education impacts inhibition, as well as the capacity for effector response, we assessed the impact of NKG2A frequency on inhibition of the NK repertoire, comparing the global NK response against the NK-sensitive K562 HLA-E KO cell line and K562 transduced with the inhibitory ligand HLA-E loaded with HLA-E A∗02 peptide. Individuals with genotyping indicating high NKG2A (440C/C) frequency and surface expression exhibited a significantly greater frequency of inhibited NK cells (P < .0001) when compared with those with genotyping indicative of a low NKG2A expression (440T/T) (Figure 3E).
HLA-E expression depends on the quantity of HLA class I signal peptide available and associates with HLA-C epitope
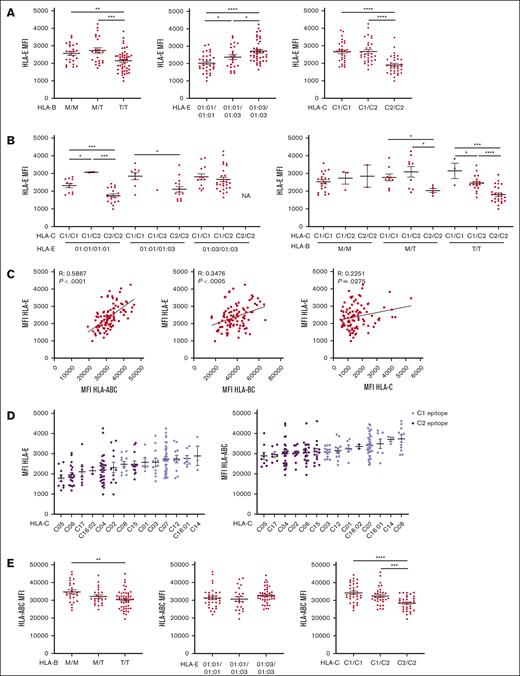
HLA-E expression is dependent on HLA class I signal peptide binding and previous studies have shown that HLA-B leader peptide dimorphism (−21T vs M)26 and HLA-E allele (∗01:01 vs ∗01:03)26,33-35 can influence HLA-E cell surface expression. In a cohort of 100 individuals tested, the HLA-E polymorphism was associated with HLA-E cell surface expression, independent of the HLA-B leader peptide (Figure 4A; supplemental Figure 5A). Because of the high level of LD observed between HLA class I genes,36,37 we tested other HLA class I polymorphisms as proxies for HLA-E expression. Interestingly, we found that the polymorphism coding for the HLA-C2 KIR epitope was associated with low expression of HLA-E (Figure 4A). A comprehensive analysis combining HLA-C epitopes with HLA-E alleles or HLA-B leader peptide demonstrated an influence of HLA-C epitope, independent of HLA-E allele and HLA-B leader peptide, on HLA-E expression despite the existence of LD between HLA-C and HLA-B26 (Figure 4B). In addition, expression of HLA-E was higher in HCMV-seropositive individuals (P < .05; supplemental Figure 5B), suggesting the presence of a viral peptide modulating HLA-E expression. Although the HLA-C2 epitope is associated with the −21T HLA-B leader peptide, the finding that HLA-C2 further segregates HLA-E expression within individuals with HLA-B leader T/T indicates an influence on HLA-E distinct from HLA-B leader dimorphism.
HLA-E expression depends on the quantity of HLA class I signal peptide available and associates with HLA-C epitopes. All HLA MFI were measured on CD3+ CD56– T cells. (A) HLA-E MFI segregated by HLA-B leader peptide, HLA-E allele, or HLA-C epitope. (B) HLA-E MFI is segregated by HLA-E and HLA-C epitopes or by HLA-B leader peptide and HLA-C epitopes. (C) Correlation between HLA-E MFI and HLA class I expression, as measured by anti-HLA-ABC, anti-HLA-BC, and anti-HLA-C. (D) HLA-ABC and -E MFI grouped by HLA-C alleles, color-coded by HLA-C KIR ligand epitope, and ranked in ascending order. (E) HLA-ABC MFI segregated by HLA-B leader peptide, HLA-E allele, and HLA-C epitope. For panels A-B,E, t tests were performed, and mean ± SEM is presented. Correlations were assessed using the Pearson correlation coefficient for panel C. Symbols represent individual samples. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
HLA-E expression depends on the quantity of HLA class I signal peptide available and associates with HLA-C epitopes. All HLA MFI were measured on CD3+ CD56– T cells. (A) HLA-E MFI segregated by HLA-B leader peptide, HLA-E allele, or HLA-C epitope. (B) HLA-E MFI is segregated by HLA-E and HLA-C epitopes or by HLA-B leader peptide and HLA-C epitopes. (C) Correlation between HLA-E MFI and HLA class I expression, as measured by anti-HLA-ABC, anti-HLA-BC, and anti-HLA-C. (D) HLA-ABC and -E MFI grouped by HLA-C alleles, color-coded by HLA-C KIR ligand epitope, and ranked in ascending order. (E) HLA-ABC MFI segregated by HLA-B leader peptide, HLA-E allele, and HLA-C epitope. For panels A-B,E, t tests were performed, and mean ± SEM is presented. Correlations were assessed using the Pearson correlation coefficient for panel C. Symbols represent individual samples. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
In healthy donors, peptides that stabilize HLA-E on the cell surface are self-HLA class I derived.38 A major difficulty in establishing a hierarchy of HLA class I expression is the limited availability of antibodies that allow for a direct comparison between the protein expression of different HLA class I molecules. To establish a relationship between cell surface expression of classical HLA class I and HLA-E, we first compared HLA-ABC expression with HLA-E expression (Figure 4C), finding a strong correlation (R = 0.4746; P < .0001). In efforts to refine this relationship to the relevant HLA class I molecule, we compared the cell surface expression of HLA-BC to HLA-E using a monoclonal antibody that recognizes all HLA-B and HLA-C alleles but does not recognize the most common HLA-A alleles.39 We separately compared the cell surface expression of HLA-C to that of HLA-E (R = 0.3476; P < .0005 and R = 0.2251; P < .05, respectively) (Figure 4C). The global expression of HLA-ABC correlated better than HLA-BC or HLA-C with HLA-E expression, indicating the contribution of HLA-A, -B, and -C to HLA-E expression. As no pan-HLA-A antibodies were available, we were unable to investigate any direct relationship between cell surface expression of HLA-A and HLA-E. Using previously established z scores,27 we did not find a significant correlation between HLA-A expression and either HLA-ABC or HLA-E expression (supplemental Figure 5C). Moreover, using the degree of HLA-E expression to rank HLA-A alleles did not reproduce the previously published rankings27 (supplemental Figure 5D).
Finding no apparent dominance among HLA-A, -B, and -C, but observing a strong association between HLA-C KIR ligand epitope and HLA-E expression, we assessed LD between HLA-A and -B alleles and HLA-C epitopes on 293 donors to determine whether LD between these genes might explain the association of HLA-E expression with the HLA-C epitope (supplemental Figure 5E). As expected, we found in our cohort that the HLA-C epitope was linked strongly with HLA-B alleles and to a lesser extent with HLA-A and HLA-E alleles. Looking at HLA class I cell surface expression grouped by HLA-C antigen and by epitope, we found that HLA-C epitope was associated with HLA-ABC and HLA-E expression (Figure 4D). Individuals with HLA-C alleles within the HLA-C2 epitope group exhibited low expression of HLA-ABC and HLA-E, whereas HLA-C1 was associated with a high expression of HLA-ABC and HLA-E (Figure 4D). The separation of HLA-E expression by HLA-C epitopes persisted when grouped by HLA-B alleles assigned to either −21M or −21T, indicating that the association between HLA-C epitope and HLA-E expression is independent of HLA-B leader dimorphism (supplemental Figure 5E). HLA-B leader peptide did not exhibit a strong association with HLA-ABC expression as an HLA-C epitope (supplemental Figure 5F). In summary, the polymorphism coding for the HLA-C epitope associates with HLA-ABC expression level independent of and better than all other HLA class I genotype markers tested (Figure 4E) and can be used as a proxy for HLA-E expression.
HLA-C epitopes impact NKG2A expression and function
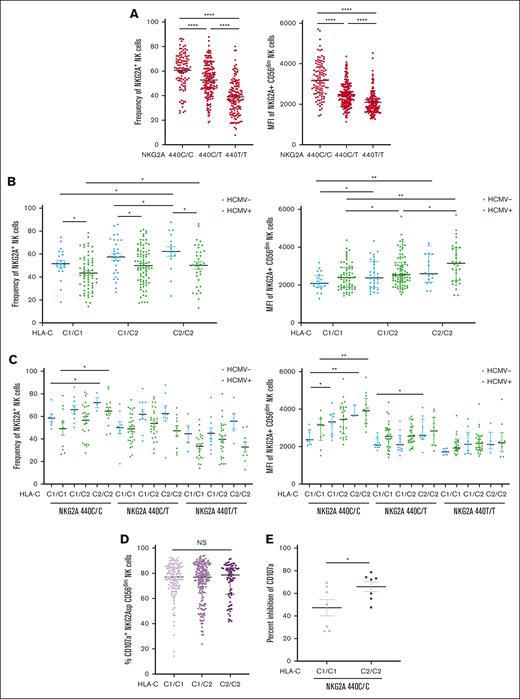
We previously reported the impact of the HLA-C2 epitope on the expression of its cognate receptor KIR2DL1.8 We therefore investigated whether the HLA-C epitope, a genetic marker associated with HLA-E expression, also influences NKG2A expression. In a cohort of 400 healthy individuals, we recapitulated the impact of rs2734440 on NKG2A frequency and cell surface expression (Figure 5A). In HCMV– and HCMV+ individuals, the HLA-C epitope was significantly associated with NKG2A surface density and frequency within the NK repertoire, with the C2/C2 genotype associated with the highest levels of NKG2A (Figure 5B). Combining these parameters with NKG2A SNP typing, we found a strong impact of the HLA-C epitope on frequency and cell surface density in the high NKG2A expression group (440C/C), but not in the low expression group (440T/T) (Figure 5C). Although there was no significant association between the HLA-B leader peptide or HLA-E allele and NKG2A frequency, there were isolated associations with NKG2A cell surface density (supplemental Figure 6A-D).
HLA-C epitopes impact NKG2A expression and NK cell function. (A) NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and MFI stratified by the SNP rs2734440 in 400 healthy blood donors. (B) NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and NKG2A MFI stratified by the HLA-C KIR ligand epitope and HCMV serostatus. (C) NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and MFI stratified by HLA-C epitope, NKG2A SNP genotype, and HCMV serostatus. (D) Degranulation response of NKG2A-SP CD56dim NK cells to K562 HLA-E KO segregated by HLA-C KIR ligand epitope. (E) Global NK inhibition in C1/C1 and C2/C2 in HCMV+ individuals with the NKG2A 440C/C (high) genotype, as measured by change in CD107a response to K562 HLA-E KO vs K562 transduced with HLA-E. For panels, A-C,E, t tests were performed, and mean ± SEM is presented to analyze NKG2A frequencies. Mann-Whitney tests were performed and median ± IQRs are presented to analyze NKG2A MFI for panels A-C. Symbols represent individual samples. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
HLA-C epitopes impact NKG2A expression and NK cell function. (A) NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and MFI stratified by the SNP rs2734440 in 400 healthy blood donors. (B) NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and NKG2A MFI stratified by the HLA-C KIR ligand epitope and HCMV serostatus. (C) NKG2A+ NK cell frequency and MFI stratified by HLA-C epitope, NKG2A SNP genotype, and HCMV serostatus. (D) Degranulation response of NKG2A-SP CD56dim NK cells to K562 HLA-E KO segregated by HLA-C KIR ligand epitope. (E) Global NK inhibition in C1/C1 and C2/C2 in HCMV+ individuals with the NKG2A 440C/C (high) genotype, as measured by change in CD107a response to K562 HLA-E KO vs K562 transduced with HLA-E. For panels, A-C,E, t tests were performed, and mean ± SEM is presented to analyze NKG2A frequencies. Mann-Whitney tests were performed and median ± IQRs are presented to analyze NKG2A MFI for panels A-C. Symbols represent individual samples. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
Because the HLA-E expression level did not correlate with NKG2A-mediated education (supplemental Figure 4E), we were not surprised that HLA-C epitopes also did not associate with the education of NKG2A-SP NK cells (Figure 5D). In contrast, we found that NK cells from HLA-C2/C2 donors were more easily inhibited by target cells expressing HLA-E (Figure 5E). Together, the combination of the HLA-C epitope and genetic markers of NKG2A expression demonstrated the best association with the magnitude of the NKG2A+ NK cell population and overall sensitivity to HLA-E inhibition.
Discussion
Although NKG2A polymorphism has been studied in the context of some immune diseases23,24 very little is known about its impact on lymphocyte biology. In this study, we reported 6 SNPs associated with NKG2A+ cell frequency and cell surface expression. All of these SNPs are located in the noncoding regions of KLRC1 and have no impact on protein isoforms. Other NK receptor genes, such as those encoding KIRs, promoters, and other noncoding intronic regulatory regions, can regulate gene expression through methylation and microRNA.40-43 A positive LD between polymorphisms makes it difficult to identify exactly which has a direct impact on transcription but all NKG2A SNPs we targeted were associated with significant transcriptional expression variation in blood mononuclear cells (https://www.gtexportal.org/home/). We therefore used NKG2A polymorphisms as proxies for protein expression and function, rather than determining the direct functional effect of each noncoding SNP.
The SNP rs2734440 was a major focus of this study, because of its relative frequency in our cohort and its ability to separate individuals into groups with high and low NKG2A expression. NKG2A has an established role in NK cell education17,18 and inhibition,15,16 but recent publications have shown that NKG2A is also functional in CD8+ T cells3,6,20,44 and Vδ2+ T cells,3,7 underscoring the relevance of our results among different lymphocyte populations. We report an association between NKG2A SNPs and NKG2A expression on CD8+ T cells and Vδ2+ T cells, a finding that may have clinical relevance as adoptive lymphocyte therapies gain use.
We observed a lower NKG2A frequency among HCMV-seropositive individuals, which is consistent with the combination of increased NKG2C frequency driven by HCMV infection45,46 and the typically mutually exclusive expression of the 2 receptors.47 The distribution of NKG2A SNPs varies significantly among different racial and ethnic groups. Homozygosity for rs2734440 T, associated with the lowest NKG2A expression, is most frequent among self-identified White individuals, whereas rs2734440 C/C, associated with high NKG2A expression, is most common in self-identified Black/African-American individuals.
Because of the LD between KLR SNPs, we considered whether there is a stronger association between other receptor polymorphisms and NKG2A expression, identifying the combination of an NKG2C SNP and gene copy number as a strong expression marker. Because the NKG2C genotype is associated with both NKG2A and NKG2C expression (data not shown), both of which are known to mediate NK cell functionality, it is a potentially interesting marker to investigate further in data sets of tumors or infectious diseases in which HLA-E expression is known to be modulated.48-60
Given that NKG2A plays a role in NK cell education, we considered whether there was an association between any related NKG2A polymorphism and education. We observed that NKG2A education correlated with NKG2A MFI, but interestingly, not with the MFI of its ligand, HLA-E. NKG2A frequency correlates with total NK cell responsiveness, highlighting the importance of NKG2A in the global response of the NK repertoire. Individuals with a high NKG2A frequency exhibit a higher global NK response to HLA class I–negative targets, coupled with higher inhibitability when challenged with HLA-E–expressing target cells. These results mirror the findings for KIR2DL1 and KIR3DL1, in which allelic diversity influences receptor density, education, and NK cell inhibitability.11,61 The use of NKG2A and NKG2C SNPs will enable genetic association studies that may reveal the importance of NKG2A+ lymphocyte populations in disease.
As a ligand partner for NKG2A, HLA-E plays an important role in NK cell inhibition. Identifying the contribution of HLA class I peptides could provide a more robust model for predicting HLA-E expression. We found evidence that HLA-ABC peptide availability drives the cell surface expression of HLA-E, although HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C alone were the dominant contributors. Although the HLA-E allele and HLA-B leader peptide were significantly associated with HLA-E cell surface expression levels, the HLA-C KIR ligand epitope segregated HLA-E expression better, likely due to its association with HLA-ABC expression.
Although the frequency of NKG2A appears to be predominantly influenced by KLR polymorphisms and impacts global NK cell responsiveness and inhibitability, the magnitude of education and inhibition of NKG2A at the level of a single cell is certainly affected by HLA class I peptide. NKG2A education and inhibitability are highly complex and appear to be influenced by numerous factors, including NKG2A expression, HLA class I peptide, and overall HLA class I expression. The upregulation of HLA-E in HCMV-seropositive adds further complexity to the model. Developing a robust mathematical model predictive of NKG2A education will likely necessitate the integration and careful weighting of these variables.
By cumulative analysis, we identified that the NKG2A variant, HLA-C epitope, and HCMV serostatus all have distinct impacts on NKG2A expression and that NKG2A rs2734440 C/C and HLA-C2/C2 genotypes are associated with greater frequency and stronger inhibition of NKG2A+ NK cells. These results provide potential insights into the higher risk of posttransplant relapse observed in HLA-C2 homozygous patients with acute myelogenous leukemia, an NK-sensitive disease.62,63
Loss of classical HLA class I expression is a well-known evasion mechanism for T cell–mediated immunity in infected and malignant cells64,65; however, increased HLA-E expression has been observed in various viral diseases51,52,55-58 and malignancies.48-50,53,54,59,60 Even when HLA-E is downregulated in malignant cells, as in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, residual expression of HLA-E can still inhibit NKG2A.66 Altogether, the data we presented here show that different immunogenetic polymorphisms influence NKG2A expression, impacting NK function at the level of the single cell and global repertoire. Therefore, genetic markers predictive of NKG2A expression are likely to be informative, especially among patients with diseases marked by high HLA-E expression.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Deutsche Knochenmarkspenderdatei Life Science Lab for the HLA allele sequencing of their cohort.
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases grant U01 A1069197. Support was also provided by NIH core grant P30 CA008748 (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center).
Authorship
Contribution: J.-B.L.L. conceived the study; J.-B.L.L., T.K., and K.C.H. designed the study and wrote and edited the manuscript; J.-B.L.L., T.K., H.L., and R.S. performed experiments; M.K.P. provided knocked out HLA-E and K562 with HLA-E cell lines; G.S., C.M., and V.L. performed HLA class I allelic typing; J.-B.L.L., T.K., M.K.P., and K.C.H. analyzed and interpreted the data; and all authors reviewed and revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.K.P. and K.C.H. are listed as inventors on a provisional patent for the design and use of HLA-E:peptide chimeric molecules (US provisional patent application number, 63/173,966). The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Jean-Benoît Le Luduec, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, Zuckerman 745-D, 408 East 69th St, New York, NY 10021; email: leluduej@mskcc.org.
References
Author notes
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article, its supplemental information files, and/or are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author, Jean-Benoît Le Luduec (leluduej@mskcc.org).
The full-text version of this article contains a data supplement.