Key Points
A patient with BCL11A haploinsufficiency displays >12% fetal hemoglobin; genome-wide analyses indicate otherwise normal erythropoiesis.
The HBG1/2 promoters display increased chromatin accessibility but no loss of DNA methylation.
Abstract
The BCL11A gene encodes a transcriptional repressor with essential functions in multiple tissues during human development. Haploinsufficiency for BCL11A causes Dias-Logan syndrome (OMIM 617101), an intellectual developmental disorder with hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin (HPFH). Due to the severe phenotype, disease-causing variants in BCL11A occur de novo. We describe a patient with a de novo heterozygous variant, c.1453G>T, in the BCL11A gene, resulting in truncation of the BCL11A-XL protein (p.Glu485X). The truncated protein lacks the 3 C-terminal DNA-binding zinc fingers and the nuclear localization signal, rendering it inactive. The patient displayed high fetal hemoglobin (HbF) levels (12.1-18.7% of total hemoglobin), in contrast to the parents who had HbF levels of 0.3%. We used cultures of patient-derived erythroid progenitors to determine changes in gene expression and chromatin accessibility. In addition, we investigated DNA methylation of the promoters of the γ-globin genes HBG1 and HBG2. HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 cells were used as models for fetal and adult human erythropoiesis, respectively. Similar to HUDEP1 cells, the patient’s cells displayed Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin (ATAC) peaks at the HBG1/2 promoters and significant expression of HBG1/2 genes. In contrast, HBG1/2 promoter methylation and genome-wide gene expression profiling were consistent with normal adult erythropoiesis. We conclude that HPFH is the major erythroid phenotype of constitutive BCL11A haploinsufficiency. Given the essential functions of BCL11A in other hematopoietic lineages and the neuronal system, erythroid-specific targeting of the BCL11A gene has been proposed for reactivation of γ-globin expression in β-hemoglobinopathy patients. Our data strongly support this approach.
Introduction
De novo mutations affecting 1 allele of the BCL11A gene are the cause of Dias-Logan syndrome (OMIM 617101), an intellectual developmental disorder with hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin (HPFH).1 A variety of genetic variations, such as deletions, as well as stop codon, frameshift, and missense variants, have been reported in the literature.1-7 BCL11A encodes a transcriptional repressor. Through alternative splicing, a number of isoforms can be produced; the longest is called BCL11A-XL.8 Amplifications and translocations involving the BCL11A gene indicate that the protein is involved in malignancies of diverse cellular origins.8-22 In addition, it has been linked to the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.16,23-29 Remarkably, in the erythroid lineage, BCL11A was identified as a direct repressor of the HBG1/2 genes encoding γ-globin, the fetal β-like globin.30-33 Expression of fetal hemoglobin (HbF; α2γ2) in adults is clinically relevant, because it ameliorates the symptoms of patients with β-hemoglobinopathies. In the case of β-thalassemia, γ-globin chains can functionally replace the missing β-globin chains. In sickle cell anemia, which is caused by a pathological variant of β-globin (p.E6V), increased expression of γ-globin leads to reduced expression of aberrant β-globin. The reduction in sickle hemoglobin (HbSS) decreases the propensity of the cells to change shape as a result of the polymerization of HbSS that occurs under low-oxygen conditions. Hemoglobin switching from HbF to adult hemoglobin (HbA; α2β2) starts perinatally and is completed during the first year of life. Recently, significant progress has been made in understanding the molecular mechanism of hemoglobin switching. A regulatory network involving the transcription factors MYB, KLF1, and BCL11A has been proposed, of which BCL11A acts as a direct repressor of the HBG1/2 genes.34 Additional players in hemoglobin switching are cofactors, such as members of the NuRD35,36 and BAP1/CoREST37,38 complexes; the LRF transcription factor (encoded by ZBTB7A), which is also a direct repressor of the HBG1/2 genes39 ; and factors involved in stress erythropoiesis, such as ATF440 and HKI.41 In addition, LIN28B has been identified as a repressor of BCL11A expression in fetal erythroid cells.42,43 Functional analysis to investigate the role of these proteins in hemoglobin switching has traditionally relied on the use of genetically modified mice and cell lines, such as human K562 and mouse MEL. The emerging power of genome-wide association studies and linkage analysis, followed by application of next-generation sequencing (NGS), has provided strong support for the role of variants of MYB, KLF1, BCL11A, and the HBB locus itself in the regulation of HbF levels in adults.44-46 For BCL11A a number of SNPs associated with an erythroid-specific enhancer are linked to expression levels of the protein in erythroid progenitor cells, with lower-expressing alleles linked to higher HbF levels.30,31,33 Because of its important role in neurological development, pathologic variants of BCL11A affecting the protein occur as de novo events.1 Although the initial reports described patients with microdeletions that included BCL11A and a few genes located nearby,3,4 nonsense, frameshift, and missense variants have been reported more recently in patients with clinical phenotypes characteristic of what is now termed Dias-Logan syndrome (OMIM 617101).1 Here, we describe a patient with a de novo heterozygous variant c.1453G>T in the BCL11A gene, resulting in truncation of the BCL11A-XL protein (p.Glu485X). At the age of 3 years and 10 months, the patient displayed an HbF level of 18.7%, whereas other blood parameters were within normal range. The parents displayed 0.3% HbF, a normal level for adults. To study the effects of BCL11A haploinsufficiency on genome-wide gene expression and chromatin accessibility, we established cultures of primary erythroid progenitors derived from the patient. These data were compared with those obtained from the HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 erythroid progenitor cell lines, which are models for human fetal and adult erythropoiesis, respectively.47 In addition, because methylation of the HBG1/2 promoters has been associated with silencing of the genes,48-50 we studied DNA methylation at cytosine guanine dinucleotide (CpG) residues in the promoters of the HBG1/2 genes.
Materials and methods
Human samples
Clinical exome sequencing was performed as part of a diagnostic work-up, and written informed consent was given for further hematological and molecular studies, according to the requirements of the Institutional Review Board of Erasmus MC’s Medical Ethics Review Committee. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All other materials and methods are described in supplemental Materials and methods.
Results
Patient description and whole-exome sequencing
The female patient is the second child of nonconsanguineous parents with no family history of intellectual disability or congenital abnormalities. She was born after an uneventful pregnancy with a birth weight of 3660 g. At birth, the head circumference was measured as −1 standard deviation [SD]. She was first seen in the pediatric ward at the age of 3 months because of feeding difficulties. Physical examination at that time showed a head circumference of 37 cm (−2 SD) and facial dysmorphism consisting of strabismus, bilateral epicanthi, thin upper lip, and fine hair. She showed no hypotonia, and eye contact was normal. She was treated with a stomach tube at home because of the feeding difficulties. At the age of 10 months her head circumference had declined further compared with healthy children; it was measured as 41.5 cm (−2.7 SD). She developed a significant motor developmental delay. More specifically, she was able to sit unsupported at 16 months; she walked with support at 2 years and independently at 4 years. At the age of 16 months cognitive testing using the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, second version, Dutch language (BSID-II-NL) showed a cognitive delay of 7 months and a developmental index of 55. Head circumference evolved from −2.5 SD up to the age of 3 years to within normal range at 7 years (Figure 1). Her length and weight were always normal. Ophthalmological examination showed hypermetropia (+3.5 oculus dexter and oculus sinister) and amblyopia of the left eye. Brain magnetic resonance imaging at the ages of 1 and 5 years revealed no abnormalities. At the age of 7 years she was evaluated more extensively. She still presented with gait abnormalities and weak motor coordination skills, falling easily. Her build was strikingly muscular, without joint laxity. Behavior showed recurrent hand flapping. Despite speech therapy she was unable to develop meaningful speaking skills, and communication was performed through pictograms. Facial features included strabismus divergens, mild left ptosis, flat midface, flat philtrum, thin upper lip, and protruding ears with thin helixes and attached earlobes (Figure 1).
A patient with BCL11A haploinsufficiency due to de novo p.Glu485X variant. Patient at age 4 months (A) and at age 3 years and 6 months (B). Facial features included strabismus divergens, mild left ptosis, flat midface, flat philtrum, thin upper lip, and protruding ears with thin, flat helixes, and attached earlobes. (C) A muscular build and instable gait present at 3 years and 6 months. (D) Head circumference evolved from −2.5 SD up to the age of 3 years to within normal range at 7 years.
A patient with BCL11A haploinsufficiency due to de novo p.Glu485X variant. Patient at age 4 months (A) and at age 3 years and 6 months (B). Facial features included strabismus divergens, mild left ptosis, flat midface, flat philtrum, thin upper lip, and protruding ears with thin, flat helixes, and attached earlobes. (C) A muscular build and instable gait present at 3 years and 6 months. (D) Head circumference evolved from −2.5 SD up to the age of 3 years to within normal range at 7 years.
Whole-exome sequencing (WES), performed in the patients and her parents, revealed a de novo heterozygous variant c.1453G>T (p.Glu485X) in exon 3 of the BCL11A gene (NM_022893 [BCL11A_i001]), resulting in truncation of the BCL11A-XL protein. The c.1453G>T variant is predicted to deleteriously affect isoform L (GenBank: NM_018014.3, Ensembl: ENST00000356842) and isoform XL (NM_022893.3, ENST00000335712) of BCL11A. Thus, the patient was diagnosed with Dias-Logan syndrome (OMIM 617101) due to haploinsufficiency for BCL11A.
Analysis of hematological parameters
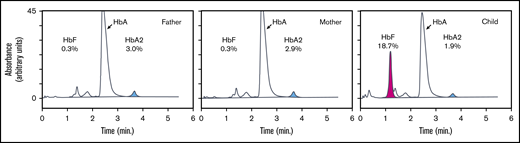
To explore the erythroid phenotype of the patient, we first performed complete blood counts to assess the hematological parameters of the patient and her parents (supplemental Table 1). At the time of blood collection, the patient’s age was 3 years and 10 months. At the age of 7 years and 3 months, HbF was measured again. The complete blood count results were unremarkable; all parameters measured were within normal range expected for the age group. Flow cytometry analysis of CD117 (KIT), CD71 (transferrin receptor), CD44 (Indian blood type), and CD235a (glycophorin A), which are markers for erythroid development, showed that these proteins were expressed at levels similar to those observed in control blood (supplemental Figure 1). We then measured HbF levels by high-performance liquid chromatography, which revealed that both parents had an HbF level of 0.3%, which is within normal range for adults (0-1%). In contrast, the child’s HbF level was 18.7% at the age of 3 years and 10 months and 12.1% at the age of 7 years and 3 months, which is much higher than the normal range for these age groups (0-1%) (Figure 2). Persistent expression of HbF is a hallmark of Dias-Logan syndrome1 and is consistent with the notion that BCL11A is a dose-dependent repressor of the HBG1/2 genes.51
Hemoglobin analysis of peripheral blood. Hemoglobin subtypes of peripheral blood were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography. The percentages of total hemoglobin are indicated for HbA (α2β2), HbA2 (α2δ2; blue), and HbF (α2γ2; pink).
Hemoglobin analysis of peripheral blood. Hemoglobin subtypes of peripheral blood were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography. The percentages of total hemoglobin are indicated for HbA (α2β2), HbA2 (α2δ2; blue), and HbF (α2γ2; pink).
Patient-derived primary erythroid progenitor cultures
We wished to explore the impact of BCL11A haploinsufficiency on erythroid cells in more detail. To this end, we isolated the buffy coat from ∼7 mL of peripheral blood collected from the patient and used these cells to establish cultures of primary human erythroid progenitors (HEPs).52 HEPs can be expanded in defined medium in the presence of stem cell factor, erythropoietin, and the glucocorticoid hormone dexamethasone. At days 14 and 17 of expansion culture, as well as 48 hours after the induction of differentiation (removal of stem cell factor and dexamethasone, increase in erythropoietin, and addition of iron-saturated transferrin), we harvested patient-derived HEPs to isolate RNA and protein for gene expression analysis by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), and western blotting. DNA was isolated to assess methylation of CpG residues in the HBG1/2 promoters by bisulfite sequencing. In addition, 50 000 cells were used to gauge chromatin accessibility with ATAC-seq (Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin with NGS).53 We reasoned that BCL11A haploinsufficiency might confer fetal-like characteristics to the patient’s erythroid cells; therefore, we used HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 cells47 as benchmarks for comparative analyses. These cells are widely used as models to study human fetal and adult erythropoiesis and hemoglobin switching.39,54-56
High HbF levels are maintained in patient-derived HEPs
To characterize the patient-derived HEPs, we investigated the expression levels of the α-like and β-like globin genes, as well as of MYB, KLF1, LIN28B, BCL11A and LRF, because these factors are important regulators of hemoglobin switching. We first used RNA-seq to measure expression of these genes at the messenger RNA (mRNA) level (supplemental Figure 2A; supplemental Table 2). The patterns of differential expression between HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 cells reflected the expected profile for the fetal and adult stages represented by these cells. HUDEP1 cells almost exclusively expressed γ-globin (>90% of total β-like globins) and up to 10% of embryonic ε-globin. HUDEP2 cells predominantly expressed adult β-globin (∼99% of total β-like globin), ∼1% δ-globin, and virtually undetectable levels of fetal and embryonic globins. This was confirmed by RT-qPCR analysis (supplemental Figure 3A).
Compared with HUDEP1 cells, expression of MYB was approximately eightfold higher and expression of BCL11A was approximately twofold higher in HUDEP2 cells, whereas there was no change for KLF1 and even a small reduction for LRF (∼0.87-fold). Most notably, expression of LIN28B was downregulated >150-fold in HUDEP2 cells compared with HUDEP1 cells (supplemental Figure 2; supplemental Table 2). LIN28B represses BCL11A protein expression in human fetal erythroid progenitors, and forced expression of LIN28B causes adult human erythroblasts to differentiate with a more fetal-like phenotype.42,43 Collectively, these data show that these distinctive features of human fetal and adult erythropoiesis are faithfully reproduced by the HUDEP1/HUDEP2 model system.
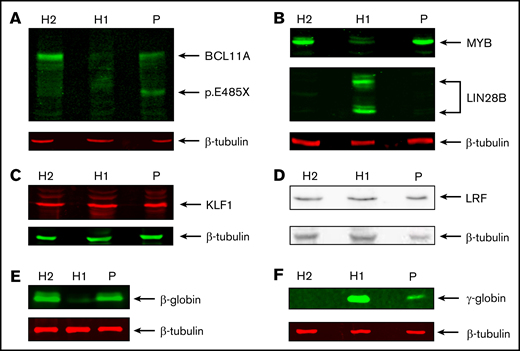
We then compared expression of these genes in patient-derived HEPs. We observed much higher γ-globin mRNA levels (∼17% of total β-like globin) compared with HUDEP2 cells, establishing that the HPFH phenotype is sustained throughout the culture period (supplemental Figure 2; supplemental Table 2). This was confirmed by RT-qPCR analysis (∼11% γ-globin of total β-like globin in patient RNA samples; supplemental Figure 3A). In contrast, expression levels of MYB, KLF1, BCL11A, and LRF were similar to those observed in HUDEP2 cells. This could be expected for MYB, KLF1 and LRF, because these factors are not thought to be regulated by BCL11A.31 Of note, we observed that LIN28B was not expressed in patient-derived HEPs. Thus, LIN28B has no role in the HPFH phenotype of the patient, and its absence sets the patient-derived HEPs apart as adult erythroid progenitors. This is further supported by the low level of embryonic ζ-globin expression in patient-derived HEPs, whereas it was expressed at substantial levels in HUDEP1 cells (supplemental Figure 2; supplemental Table 2; ∼15% ζ-globin of α-like globin in differentiated HUDEP1 cells). RNA-seq data indicated that the BCL11A p.Glu485X variant may not trigger nonsense-mediated RNA decay, because wild-type and mutant allele mRNA were detected in the RNA-seq data. Therefore, it was important to assess the impact of BCL11A haploinsufficiency on protein expression levels. We performed western blots on whole-cell extracts of HUDEP1, HUDEP2, and patient-derived HEP cells (Figure 3). We observed a clear reduction in the expression of the BCL11A-XL isoform in patient-derived HEPs compared with HUDEP2 cells. Furthermore, a protein with the expected molecular weight of p.Glu485X BCL11A was detected in the patient sample only (Figure 3A).55 Of note, domain mapping of BCL11A-XL indicates that the BCL11A p.Glu485X variant is unable to repress HBG1/2 genes.55 MYB was expressed at similar levels in patient-derived HEPs and HUDEP2 cells but at much lower levels in HUDEP1 cells (Figure 3B, top panel). In contrast, expression of LIN28B was only detectable in HUDEP1 cells (Figure 3B, middle panel). The transcriptional regulators KLF1 and LRF were expressed at apparently similar levels in all 3 cell types (Figure 3C-D). These results are all consistent with the RNA-seq data. Finally, western blot analysis of β- and γ-globin expression (Figure 3E-F) was in agreement with the RNA-seq and RT-qPCR data (supplemental Figures 2 and 3A). Collectively, our results strongly support the notion that the HPFH phenotype of the patient is caused by reduced expression of the BCL11A-XL isoform.
Protein expression analysis of transcription factors, LIN28B, and globins. Western blots showing expression of BCL11A (XL isoform and p.Glu485X) (A), MYB and LIN28B (B), KLF1 (C), LRF (D), β-globin (E), and γ-globin (F). β-tubulin was used as loading control. Protein extracts were derived from HUDEP1 cells (H1), HUDEP2 cells (H2), and patient HEPs (P).
Protein expression analysis of transcription factors, LIN28B, and globins. Western blots showing expression of BCL11A (XL isoform and p.Glu485X) (A), MYB and LIN28B (B), KLF1 (C), LRF (D), β-globin (E), and γ-globin (F). β-tubulin was used as loading control. Protein extracts were derived from HUDEP1 cells (H1), HUDEP2 cells (H2), and patient HEPs (P).
Methylation of the HBG1/HBG2 promoters
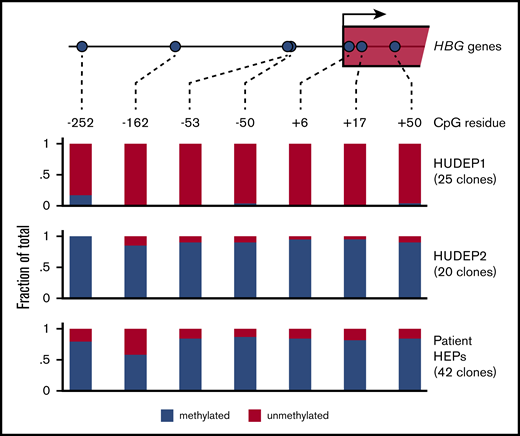
The promoters of the HBG1/2 genes contain a number of CpGs that become methylated during human development.50 Of note, treatment of a small number of β-hemoglobinopathy patients with the DNA demethylating agent 5-azacytidine led to increased HbF levels.48,49 This experimental treatment has seen a recent revival, as reflected by a randomized phase 1 study in which the 5-azacytidine derivative decitabine was used.57 To this day it remains controversial whether demethylation of the HBG1/2 promoters is the direct cause of the therapeutic effect of 5-azacytidine.58 Therefore, it is of interest to investigate the methylation status of the HBG1/2 promoters in the setting of BCL11A haploinsufficiency. We performed bisulfite sequencing to assess methylation of 7 CpGs, located between positions −252 and +50 of the HBG1/2 promoters (Figure 4). We observed that these 7 CpGs are virtually unmethylated in HUDEP1 cells, as expected in cells representing human fetal erythropoiesis.50 In contrast, they are almost fully methylated in HUDEP2 cells (Figure 4). We then investigated the methylation status of the HBG1/2 promoters in HEPs derived from the patient with BCL11A haploinsufficiency. We observed that, despite the considerable level of γ-globin expression, DNA methylation was present at a high level for most CpGs. Of note, the methylation level of the −162 CpG was between that of HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 cells, indicating that methylation of this residue might serve as a biomarker for activity of the HBG1/2 promoters. We conclude that the fetal methylation profile of the HBG1/2 promoters is not maintained in adult erythroid cells with BCL11A haploinsufficiency.
DNA methylation of the HBG1/2 promoters. Genomic DNA was isolated from HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 cells and patient-derived HEPs. DNA methylation of the HBG1/2 promoters was analyzed by bisulfite sequencing. The number of clones sequenced for each bisulfite-converted DNA sample is indicated.
DNA methylation of the HBG1/2 promoters. Genomic DNA was isolated from HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 cells and patient-derived HEPs. DNA methylation of the HBG1/2 promoters was analyzed by bisulfite sequencing. The number of clones sequenced for each bisulfite-converted DNA sample is indicated.
Genome-wide gene expression analysis
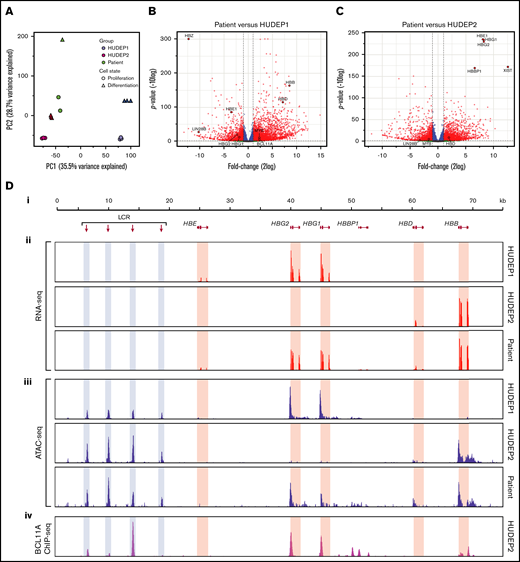
Having validated the HEP culture system as a tool to study the impact of BCL11A haploinsufficiency on human erythropoiesis, we were interested in further exploring gene expression using RNA-seq data. Principal component analysis of the RNA-seq profiles showed that the adult/fetal erythropoiesis state was the main source of variation between the samples. Principal component 1 (PC1) separated fetal HUDEP1 samples from adult HUDEP2 and patient samples, whereas PC2 separated the samples according to their state of differentiation (Figure 5A). Thus, the global gene expression profile of the patient’s cells was much more similar to that of HUDEP2 cells than to HUDEP1 cells. This was also reflected in the number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs): 3812 in patient cells vs HUDEP2 cells and 4930 in patient cells vs HUDEP1 cells (2log fold change > |1| and adjusted P value < .01; Figure 5B-C; supplemental Figure 4; supplemental Table 2). Considering that 1849 DEGs were shared between HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 cells (supplemental Figure 4), we could narrow this down to 1963 DEGs in patient cells vs HUDEP2 cells and 3081 DEGs in patient cells vs HUDEP1 cells. We used volcano plots of all expressed genes (15 488; supplemental Table 2) to highlight the differences in number and magnitude of DEGs in the patient cells vs HUDEP1 cells (Figure 5B) or HUDEP2 cells (Figure 5C). These plots also illustrate the differential expression of several globin genes and key regulators that were discussed earlier (Figures 2 and 3; supplemental Figures 2 and 3; supplemental Table 2). Compared with HUDEP2 cells, we observed high expression of XIST in the cells from our patient (Figure 5C). This is consistent with the fact that HUDEP2 cells were derived from a male donor, whereas HUDEP1 cells were derived from a female donor (R.K. and Y.N., unpublished data, 30 October 2020).
RNA expression and chromatin accessibility at the HBB locus. (A) Principal component analysis of RNA-seq data. PC1 separates fetal cells (HUDEP1) from adult cells (HUDEP2 and patient). PC2 separates cells according to differentiation status. (B) Volcano plot of HUDEP1 cells vs patient RNA-seq data. (C) Volcano plot of HUDEP2 cells vs RNA-seq data. (D) An overview of the HBB locus (Di) with RNA expression (RNA-seq; red) (Dii) and chromatin accessibility (ATAC-seq; blue) (Diii) assays on HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 cells and patient HEPs. (Div) Binding of BCL11A to the HBB locus in HUDEP2 cells, as assessed by chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by NGS (ChIP-seq); data are from Martyn et al.64 HBB, β-globin gene; HBBP1, β-globin pseudogene 1; HBD, δ-globin gene; HBE, ε-globin gene; HBG1, Aγ-globin gene; HBG2, Gγ-globin gene; LCR, a series of enhancers marked by hypersensitive sites.
RNA expression and chromatin accessibility at the HBB locus. (A) Principal component analysis of RNA-seq data. PC1 separates fetal cells (HUDEP1) from adult cells (HUDEP2 and patient). PC2 separates cells according to differentiation status. (B) Volcano plot of HUDEP1 cells vs patient RNA-seq data. (C) Volcano plot of HUDEP2 cells vs RNA-seq data. (D) An overview of the HBB locus (Di) with RNA expression (RNA-seq; red) (Dii) and chromatin accessibility (ATAC-seq; blue) (Diii) assays on HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 cells and patient HEPs. (Div) Binding of BCL11A to the HBB locus in HUDEP2 cells, as assessed by chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by NGS (ChIP-seq); data are from Martyn et al.64 HBB, β-globin gene; HBBP1, β-globin pseudogene 1; HBD, δ-globin gene; HBE, ε-globin gene; HBG1, Aγ-globin gene; HBG2, Gγ-globin gene; LCR, a series of enhancers marked by hypersensitive sites.
RNA-seq analysis of the HBB locus
To visualize expression of the β-like globin genes in HUDEP1 cells, HUDEP2 cells, and the patient’s cells, RNA-seq data were displayed on the HBB locus (Figure 5D). From these tracks, we inferred the expression ratios of the HBG1 (encoding Aγ-globin) and HBG2 (encoding Gγ-globin) genes. In Aγ-globin mRNA, codon 136 reads GCA encoding alanine, whereas in Gγ-globin mRNA it reads GGA encoding glycine. During hemoglobin switching there is a gradual increase in the Aγ-globin/Gγ-globin mRNA ratio. In HUDEP1 cell cultures this ratio was 0.24/0.76. HUDEP2 cells express too little γ-globin mRNA to determine the Aγ/Gγ ratio reliably. Therefore, we used RNA-seq data obtained from control adult HEP cultures (Steven Heshusius, Laura Grech, N.G., R.W.W.B., Xander T. den Dekker, W.F.J.v.IJ., Benjamin Nota, Alex E. Felice, T.B.v.D., Marieke von Lindern, Joseph Borg, Emile van den Akker, and S.P., manuscript submitted March 2021). We found that these cells displayed an Aγ/Gγ ratio of 0.34:0.66, whereas this ratio was 0.30:0.70 in the patient’s cells. Thus, our data indicate that, in addition to increasing γ-globin expression, BCL11A haploinsufficiency yields an Aγ-globin/Gγ-globin mRNA ratio close to the one that is characteristic of the adult stage of human erythropoiesis. Of note, expression of the HBBP1 pseudogene was much higher in patient-derived HEPs than in HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 cells (supplemental Figures 2 and 3B; supplemental Table 2). We also observed an increase in HBBP1 expression in BCL11A-null HUDEP2 cells (supplemental Figure 3D). HBBP1 has been implicated in HbF expression,59-61 chromatin architecture of the HBB locus,62 and erythropoiesis.63
Chromatin accessibility of the HBB locus
First, we used our ATAC-seq data to assess chromatin accessibility at the HBB locus in HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 cells. In HUDEP1 cells, the distal regulatory elements of the locus control region (LCR) and the HBG1/2 promoters displayed strong ATAC peaks, whereas the promoter of the HBB gene was inaccessible (Figure 5Diii; HUDEP1 cells). In HUDEP2 cells, strong ATAC peaks were observed at the LCR and the HBB gene promoter but not at the HBG1/2 promoters (Figure 5Diii; HUDEP2 cells). This is consistent with the notion that BCL11A binds to the promoters of the HBG1/2 genes in adult erythroid cells64 (Figure 5Div), thus precluding promoter activation and rendering the local chromatin in a closed and inaccessible structure.55,64 Remarkably, in patient-derived HEPs we observed, in addition to the LCR peaks, strong ATAC peaks at the promoters of the HBG1/2 genes and at the promoter of the HBB gene. We conclude that reduced levels of BCL11A (Figure 3A) profoundly affect chromatin accessibility at the HBG1/2 promoters, even in the presence of apparently normal levels of 2 other key regulators of hemoglobin switching,39,65 LRF and KLF1 (Figure 3B-C), and high DNA methylation levels (Figure 4).
Discussion
We analyzed the erythroid phenotype of a patient with BCL11A haploinsufficiency. This patient carries a de novo variant, c.1453G>T, resulting in an inactivating truncation of the BCL11A-XL protein (p.Glu485X). Previous work identified BCL11A as a direct repressor of the HBG1/2 genes in adult erythropoiesis.55,64 In mice, the complete absence of BCL11A results in neonatal lethality, accompanied by hematopoietic and neuronal abnormalities.66,67 In the hematopoietic system, the stem cell and lymphoid compartments are particularly affected.68 In the neuronal system, BCL11A is required for neuronal differentiation and the formation of sensory circuits.66 Using conditional knockout alleles in combination with hematopoietic-specific Cre recombinase lines, such as Mx1-Cre and EpoR-Cre, BCL11A was established as a dose-dependent repressor of the embryonic and fetal hemoglobin genes.39,51,69,70 In the patient, we found that all blood parameters were within normal range, with the exception of high HbF levels (12.1-18.7% of total hemoglobin). RNA-seq and RT-qPCR revealed high expression of the HBG1/2 genes in cultured primary erythroid progenitors derived from peripheral blood of the patient. This was paralleled by the results of chromatin accessibility mapping by ATAC-seq, which established that promoters of the HBG1/2 genes displayed an open chromatin conformation. Because expression of KLF1 and LRF, 2 other key regulators of hemoglobin switching,39,65 was not affected at the RNA or protein level, our data indicate that activity of the HBG1/2 promoters in BCL11A haploinsufficiency is maintained via a direct mechanism involving reduced levels of BCL11A protein. This is consistent with the western blot analysis of BCL11A expression in the patient-derived HEP cells. The high level of HBBP1 expression in patient-derived HEPs and BCL11A-null HUDEP2 cells is an intriguing observation. HBBP1, a β-like globin pseudogene, is expressed in human erythroid cells as a long noncoding RNA.63 Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in HBBP1 have been associated with HbF levels59-61 ; deletion of HBBP1 increases HBG1/2 expression and affects the 3-dimensional chromatin architecture of the HBB locus.62 Because BCL11A binds to the HBBP1 region,54,64 our data support the notion that BCL11A is directly involved in the function of the HBBP1 region.62 In addition, the HBBP1 transcript may stabilize TAL1 mRNA, boosting expression of this essential transcription factor in erythroid cells.63 Whether HBBP1 expression has a role in the erythroid phenotype of BCL11A deficiency is an interesting topic for follow-up research.
We used the HUDEP1 and HUDEP2 erythroid progenitor cell lines as benchmarks for human fetal and adult erythropoiesis, respectively.47 Our comparative analysis strongly supports the notion that BCL11A haploinsufficiency does not involve maintenance of the fetal phenotype of the erythroid compartment. Notably, the LIN28B gene, which is highly expressed in human fetal erythropoiesis,42,43 is not expressed in HUDEP2 cells and patient-derived HEPs. Furthermore, the methylation pattern of the HBG1/2 promoters closely resembles the hypermethylated state found in adult erythroid cells, rather than the hypomethylated state typical of fetal erythroid cells.50 Principal component analysis of the RNA-seq data also places the patient-derived HEPs more closely to adult erythroid progenitors than to fetal erythroid progenitors. The erythroid phenotype of BCL11A haploinsufficiency is different from that observed for KLF1 haploinsufficiency, which is also associated with HPFH.46,65 KLF1 is an activator of the BCL11A and ZBTB7A genes; therefore, its effects on HBG1/2 expression are indirect.56,65 Moreover, in contrast to BCL11A, KLF1 orchestrates the entire terminal erythroid differentiation program; consequently, KLF1 haploinsufficiency has a much broader impact on the erythroid transcriptome.46 For instance, KLF1 haploinsufficiency is associated with the In(Lu) blood type46 that is characterized by reduced expression of BCAM and CD44, which is not the case in our patient.
Because BCL11A deficiency does not impede steady-state or stress erythropoiesis, it is a very attractive molecular target for reactivation of γ-globin expression in β-hemoglobinopathy patients. Given the essential functions of BCL11A in other hematopoietic lineages and the neuronal system, erythroid-specific targeting of the BCL11A gene has been proposed as a strategy for reactivation of γ-globin expression.54,71-75 Deletion of the erythroid-specific enhancer located in intron 2 of the gene in hematopoietic stem cells, using genome editing tools such as zinc finger nucleases (NCT03432364, NCT03653247) and CRISPR/Cas9 (NCT03655678, NCT03745287),76 is being explored in clinical trials. In addition, erythroid-specific knockdown of BCL11A mRNA is being tested using a lentiviral gene transfer approach (NCT03282656).77 In this context, it is relevant to study the impact of constitutive BCL11A haploinsufficiency, as occurs in patients with Dias-Logan syndrome, on human erythropoiesis. Reassuringly, our data show that constitutive BCL11A haploinsufficiency is associated with maintenance of high HbF expression without generally affecting the adult characteristics of erythropoiesis. Collectively, our results extend the observations from previous studies on cellular and mouse models of BCL11A deficiency and fully support the approach to reduce BCL11A activity in erythroid cells as a means to reactivate HbF expression in β-hemoglobinopathy patients.
All next-generation sequencing data reported in this article have been deposited in the European Nucleotide Archive (accession number PRJEB31728).
Data sharing requests should be sent to Sjaak Philipsen (j.philipsen@erasmusmc.nl).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patient and her parents for participation in this study. They also thank Tom de Vries Lentsch for assistance with the illustrations.
Work in the laboratory of S.P. was funded by the Landsteiner Foundation for Blood Transfusion Research (LSBR 1627), the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (ZonMw TOP 40-00812-98-12128), and EU FP7 Specific Cooperation Research Project THALAMOSS (306201) (S.P.). D.E.B. was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (DP2HL137300 and P01HL032262) and the Burroughs Wellcome Fund. S.C. was supported by National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases award F31DK122637-02.
Authorship
Contribution: M.W.W., D.E.B., M.C.G.N.v.d.H., W.F.J.v.IJ., and S.P. designed research; M.W.W., T.B.v.D., N.G., K.L.J.S., K.v.L., D.S.V., S.C., S.A.d.M., R.P., Z.A., R.W.W.B., and M.C.G.N.v.d.H. performed research; M.W.W., M.H.C., D.S.V., S.C., R.K., Y.N., R.W.W.B., D.E.B., and M.C.G.N.v.d.H. contributed vital new reagents, patient data, or analytical tools; M.W.W., M.H.C., T.B.v.D., K.v.L., D.S.V., R.P., D.E.B., M.C.G.N.v.d.H., W.F.J.v.IJ., and S.P. analyzed data; and M.W.W., M.H.C., D.S.V., D.E.B., M.C.G.N.v.d.H., W.F.J.v.IJ., and S.P. wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Sjaak Philipsen, Erasmus MC, Department of Cell Biology, Room Ee1071b, P.O. Box 2040, 3000 CA Rotterdam, The Netherlands; e-mail: j.philipsen@erasmusmc.nl.
References
Author notes
The full-text version of this article contains a data supplement.