Abstract
TP53 is mutated in 10 to 15% of cases of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and is associated with a previous exposure to cytotoxic therapy, complex cytogenetic abnormalities, and a poor prognosis. Recent data have established the importance of TP53-mutant allele status, the determination of which requires specific genetic testing. Compared with monoallelic disease, multihit TP53-mutant AML/MDS is associated with chromosomal abnormalities and decreased overall survival. Most TP53 mutations are missense mutations that localize to the DNA binding domain. Hot-spot mutations involving residues R175, Y220, G245, R248, R273, or R282 represent approximately 35% of all TP53 missense mutations in AML/MDS. There is evidence that these hot-spot mutations may have dominant negative or gain-of-function properties. Here we review this evidence and discuss its potential impact on patient outcomes and clinical management.
Learning Objectives
Review the prognostic importance of TP53-mutant allele status in TP53-mutated myeloid malignancies
Understand the proper genetic testing needed to reliably determine TP53-mutant allele status
Review the biological and clinical consequences of hot-spot TP53 mutations in myeloid malignancies
TP53's role as a tumor suppressor
TP53 encodes for p53, a sequence-specific transcription factor that plays a central role in preventing neoplastic transformation. Indeed, it is the most frequently mutated gene in human cancer. The p53 protein includes an N- terminal transactivation motif, a DNA-binding domain, and a tetramerization domain; it is the p53 tetramer that is active and able to bind to p53-response elements in target gene DNA. Although constitutively expressed at the RNA level in most cells, p53 protein is quickly degraded under basal conditions, resulting in it having low steady-state levels. In response to cellular stressors, such as DNA damage, the p53 protein is rapidly stabilized, activating a transcriptional program that induces DNA repair, cell cycle arrest, senescence, or apoptosis, depending on the type and severity of the stress. As part of this program, p53 induces mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2) expression. MDM2 subsequently promotes the ubiquitylation and proteosome-dependent degradation of p53. In this manner, the extent of p53 activation is self-limited.
TP53 mutations in myeloid malignancies
TP53 mutations are present in approximately 10% of de novo acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) cases and approximately 35% of therapy-related myeloid neoplasms.1,2TP53 mutations are associated with complex cytogenetic abnormalities and a very poor prognosis.2 Similar to nonhematologic malignancies, most TP53 mutations are missense mutations. Jambhekar et al recently collected data from 1,117 independent TP53 mutations identified in patients with a myeloid malignancy.3 Missense mutations represented 77.5% of all TP53 mutations, followed by nonsense mutations (7.8%), frameshift indels (7.5%), and splice site mutations (5.7%). The 10 most frequently mutated amino acid residues are shown in Figure 1. The great majority of TP53 missense mutations localize to the DNA-binding domain with hot-spot mutations involving residues R175, Y220, G245, R248, R273, or R282 representing approximately 35% of all missense mutations. Overall, the residues most commonly mutated in myeloid malignancies were comparable to those mutated in solid tumors. Similar data were reported by Tashakori et al, analyzing 442 patients with AML,4 and Bernard et al, analyzing 378 patients with MDS.1 Of note, Jambhekar et al reported that classic loss-of-function TP53 mutations (nonsense, frameshift, or splice site mutations) are more common in AML with myelodysplastic changes compared to MDS. This result is consistent with the observation that deletion of the second TP53 allele is a frequent occurrence in TP53-mutated AML.1,2,5
Diagram representing the 10 most common TP53 mutations identified in AML/MDS.3 Mutations highlighted in red are also among the 5 most commonly mutated residues in overall malignancies. CTD, C-terminal domain; DBD, DNA-binding domain; HD, hinge domain; OD, oligomerization domain; PRR, proline-rich region; TAD, transactivation domain.
Diagram representing the 10 most common TP53 mutations identified in AML/MDS.3 Mutations highlighted in red are also among the 5 most commonly mutated residues in overall malignancies. CTD, C-terminal domain; DBD, DNA-binding domain; HD, hinge domain; OD, oligomerization domain; PRR, proline-rich region; TAD, transactivation domain.
CLINICAL CASE 1
A 55-year-old woman with a history of non–small cell lung cancer was treated with surgery, adjuvant chemotherapy, and mediastinal radiotherapy. She presents 2 years later with progressive anemia and thrombocytopenia, 60% bone marrow cellularity, 15% blasts, and more than 15% ringed sideroblasts, leading to a diagnosis of therapy-related MDS. Cytogenetics revealed a complex monosomal karyotype with loss of chromosomes 5, 7, and 20. Sequencing identified an R196X TP53 mutation with a variant allele frequency (VAF) of 48.9%. Based on the lack of a chromosomal 17p abnormality, she was categorized as monoallelic TP53-mutated with a Molecular International Prognostic Scoring System for Myelodysplastic Syndromes risk stratification of moderately high. Are further studies needed to investigate her TP53 mutation allele status?
Prognostic importance of mutant TP53 allele status
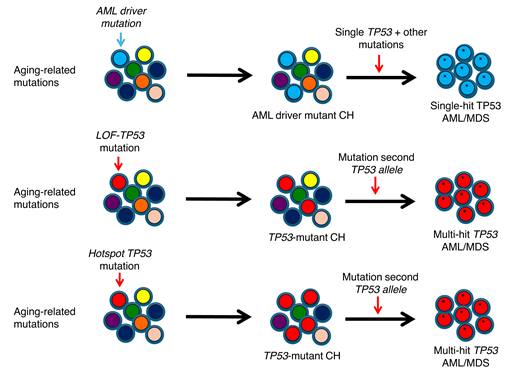
TP53 is a classic tumor suppressor gene working through a 2-hit mechanism. Current evidence suggests that the first hit is usually a missense TP53 mutation.6 Loss of the remaining wild-type allele may arise through various mechanisms: deletion of the allele (eg, via loss of the chromosomal arm on which TP53 resides, del(17p)), replacement of the allele with its mutant counterpart (termed copy neutral loss of heterozygosity, or CN-LOH), or the emergence of a second TP53 mutation in the allele. Whole-genome sequencing of 42 cases of TP53-mutated myeloid malignancies showed that deletion of the second copy of TP53 is the most common second hit, occurring in 51% of cases (Figure 2).5 CN-LOH was the second hit in 27% of cases, and 2 different missense mutations were identified in only 12% of cases.
Loss of the remaining wild-type TP53 allele is a common event in TP53-mutant AML/MDS. Shown are the identified mechanisms for loss of this allele in 42 cases of AML/MDS. SNV, single-nucleotide variant. Adapted from Abel et al5 with permission.
Loss of the remaining wild-type TP53 allele is a common event in TP53-mutant AML/MDS. Shown are the identified mechanisms for loss of this allele in 42 cases of AML/MDS. SNV, single-nucleotide variant. Adapted from Abel et al5 with permission.
Recent data have shown that TP53-mutant allele status is a major determinant of outcomes in MDS. In 1 large study of MDS, patients judged to have a single TP53 mutation (monoallelic) had a 3-year overall survival of approximately 40%, similar to that of non–TP53 mutated MDS.1 In contrast, in patients with MDS and multiple TP53 mutations (multihit), the 3-year overall survival was markedly reduced, at approximately 10%. Of note, the VAFs for many of the patients with single-hit MDS were less than 10%; thus, it is likely that some of these cases represent non–TP53 mutated MDS coexisting with TP53-mutated clonal hematopoiesis. Tashakori et al observed a similar phenotype in AML, with 186 of 248 (75%) AML cases harboring a single TP53 mutation with evidence of TP53 copy number loss, and this subset of patients having a significantly worse overall survival when compared to those with monoallelic loss (odds ratio = 1.65).4 In both of these studies, complex cytogenetic abnormalities were more common in multihit TP53-mutated cases. The importance of multihit TP53 mutations as indicators of a dismal prognosis in AML/MDS has been recently included in the International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemias.7
Accurately determining mutant TP53 allele status
The definition of multihit TP53-mutation status has recently undergone significant debate. Per the International Consensus Classification, criteria include the presence of 2 or more distinct mutations (each with a VAF of 10% or more) or a single mutation with a VAF greater than 50% and/or a VAF greater than or equal to 10% with evidence of LOH.8 If a single TP53 mutation with a VAF of 10 to 49% is present without available LOH data, a complex karyotype (3 or more independent cytogenetic abnormalities excluding loss of the Y chromosome) or del(17p) is required. In contrast, the World Health Organization considers the presence of 2 or more TP53 mutations or 1 TP53 mutation with evidence of copy number loss or CN-LOH to indicate multihit status regardless of VAF; a single TP53 mutation having a VAF of greater than or equal to 50% is considered to be presumptive evidence of loss of the wild-type allele or CN-LOH.9
However, standard molecular testing of myeloid malignancies using next-generation gene panel sequencing and cytogenetics may miss some TP53 mutations, especially CN-LOH. Moreover, a VAF cutoff of 50% is not sufficient to reliably determine TP53- mutant allele status. For example, a recent study showed that 25% of patients with MDS and a TP53 mutation VAF below 50% were misclassified as monoallelic due to CN-LOH.1 In our study of TP53-mutated AML or MDS, multihit involvement of TP53 was identified in 40 of 41 cases (91%) by whole-genome sequencing, including 5 cases (12%) upgraded from single hit to multihit status by the detection of CN-LOH or complex chromosomal rearrangements that were missed with cytogenetics. Thus, specific approaches that reliably detect CN-LOH are needed to accurately determine TP53-mutant allele status, such as expanded gene panels designed to detect TP53 LOH, single-nucleotide variant arrays, or whole-genome/exome sequencing. We previously showed that whole-genome sequencing can be used as a clinical diagnostic test for AML, providing rapid, accurate, comprehensive, and cost-efficient genomic profiling.10 Alternatively, a lower TP53-mutant VAF cutoff would be expected to identify more patients with multihit AML/MDS, albeit with a risk of misclassifying some single-hit cases. Of note, Short et al showed that a TP53-mutant VAF cutoff of 40% was predictive of response to a cytarabine-based regimen.11
Returning to our case presentation, whole-genome sequencing identified CN-LOH of 17p, resulting in the reclassification of this patient as having multihit TP53-mutated MDS and increasing the Molecular International Prognostic Scoring System for Myelodysplastic Syndromes stratification from moderately high to very high. Interestingly, TP53 mutations have been recurrently identified in MDS with ringed sideroblasts and are associated with the lack of an SF3B1 mutation, excess blasts, complex cytogenetics, and poor survival.12
CLINICAL CASE 2
A 69-year-old man with a history of Crohn's disease presents with newly diagnosed MDS. Bone marrow cellularity was 75% with 2% blasts and frequent ring sideroblasts, consistent with MDS with multilineage dysplasia and refractory cytopenias. Cytogenetics showed del(7q) and del(20). Gene-panel sequencing revealed a TP53 R248Q mutation with a VAF of 55%. Whole-genome sequencing demonstrated CN-LOH of 17p. TP53 R248Q is a hot-spot mutation in myeloid malignancies. Does the type of TP53 mutation contribute to the pathogenesis of AML/MDS or its response to treatment?
Evidence that TP53 mutations primarily function by inducing loss of TP53 function
Several well-controlled studies suggest that hot-spot TP53 mutations act primarily through a dominant-negative or loss-of-function fashion. Giacomelli et al studied the function of 8258 mutant TP53 alleles in the absence or presence of wild-type TP53, assessing their retention of p53 function and their ability to dominantly-negatively suppress p53 activity.13 Using a phenotypic score derived from these 2 activities and the observed rate at which somatic mutations occur in human cancer, they were able to recapitulate the observed prevalence of TP53 mutations in human cancer, suggesting that much of the biologic effect of mutant TP53 alleles lies in their ability to suppress p53 function. Boettcher et al introduced TP53 hot-spot mutations into 2 human AML cell lines.14 They showed that hot-spot TP53 mutations showed strong dominant-negative activity and induced similar gene-expression changes as the simple loss of TP53. Moreover, the fitness of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) expressing only hot-spot TP53 mutations was similar to TP53NULL HSCs. Aubrey et al showed that the enforced expression of 5 Trp53 missense alleles had no impact on lymphoma development in a Trp53-null background.15 However, these same alleles synergized with c-myc overexpression to promote lymphomagenesis in a Trp53 wild-type background with evidence of a dominant-negative downregulation of a subset of TP53 target genes. Finally, Wang et al recently used CRISPR gene editing to delete TP53 hot-spot mutations in multiple cell lines.16 In each case they observed that the conversion from a TP53 hot-spot mutant to a null mutant had no or minimal impact on cell proliferation in vitro or in vivo, response to chemotherapy, or gene expression. Collectively, these studies suggest that loss-of-function is the major mechanism by which TP53 mutations contribute to leukemogenesis, with TP53 hot-spot mutations causing a greater decrease in p53 activity through a dominant-negative mechanism (Figure 3).
Reduction of p53 activity with TP53 hot-spot mutations. Simple loss-of-function (eg, nonsense) mutations are depicted as “-” and hot-spot mutations as “mut.” HSCs carrying heterozygous TP53 hot-spot mutations have reduced p53 activity compared with heterozygous TP53 null cells.
Reduction of p53 activity with TP53 hot-spot mutations. Simple loss-of-function (eg, nonsense) mutations are depicted as “-” and hot-spot mutations as “mut.” HSCs carrying heterozygous TP53 hot-spot mutations have reduced p53 activity compared with heterozygous TP53 null cells.
Evidence for gain-of-function induced by TP53 hot-spot mutations
Several early studies showed that transgenic mice expressing mutations corresponding to the human TP53 hot-spot mutations R175H, R273H, R248W, or R248Q develop an altered tumor spectrum with more metastases compared to Trp53−/− mice.17-22 Here, we focus on studies providing evidence that TP53 hot-spot mutations activate a distinct set of target genes that may contribute to leukemogenesis. Loizou et al showed that mice transplanted with Trp53R172H (corresponding to human TP53 R175H) bone marrow cells developed AML with a shorter latency than mice transplanted with Trp53−/− cells.23 Moreover, they provided evidence that expression of Trp53R172H promotes the self-renewal of hematopoietic progenitor cells in vitro through increased expression of the transcription factor Foxh1. Rajagopalan et al studied Trp53R172H/+ mice in combination with the NrasG12D/+ allele.24 Mice with a complete loss of Trp53 in the setting of NrasG12D develop a mixed AML/T-cell leukemia/lymphoma, which is transcriptionally characterized by Trp53 loss. In contrast, Trp53R172H/+ NrasG12D mice develop a rapid-onset AML, which is transcriptionally characterized by Gata2 downregulation and NF-κB–mediated inflammatory signaling. Finally, although performed using a colorectal cancer cell line, it is worth reviewing the study by Kotler et al in which the fitness of 9833 TP53 variants was assessed.25 They showed that certain TP53 hot-spot mutations, while having a similar effect as many non−hot-spot mutations on cell proliferation in vitro, had a modestly increased impact on fitness in vivo. Thus, any gain-of-function provided by a hot-spot TP53 mutation may be context dependent and vary depending on the cell of origin, genetic background, and other genetic/epigenetic features.
Clinical relevance of hot-spot TP53 mutations
Multiple studies have examined the impact of TP53 mutation type, including hot-spot mutations, on clinical outcomes. In Li Fraumeni patients, individuals carrying germline TP53 mutations with dominant-negative activity develop tumors at an earlier age than individuals carrying loss-of-function nonsense or frameshift mutations or genomic rearrangements.26 In solid tumors, the impact of the class of TP53 mutation on prognosis is less clear-cut and differs depending on the tumor type.27 There are data suggesting that specific TP53 hot-spot mutations may be associated with overall survival in certain malignancies. For example, TP53 R273 mutations have been associated with increased metastases and decreased survival in colon cancer.28 In AML, several studies have failed to find an association between the type of TP53 mutation (missense vs truncating) and the overall prognosis.4,14 Several scoring systems for TP53 mutations have been developed. Poeta et al classified TP53 mutations as disruptive or nondisruptive based on their location and predicted amino acid alteration.29 Nesky et al used an evolutionary trace approach to assign an evolutionary action (EAp53) score to TP53 missense mutations.30 Both scoring systems were validated in head and neck cancers. Finally, Kotler et al used saturation mutagenesis to systematically assess the function of variants in the TP53 DNA-binding domain, deriving a relative fitness score (RFS) from this data.25 Dutta et al assessed the impact of the EAp53 and RFS scores on the outcomes of 98 patients with TP53-mutated AML.31 Although the EAp53 score did not correlate with survival, patients with a high-risk RFS score had reduced overall (12.9 vs 5.5 months; P = .017) and event-free (7.3 vs 5.2 months; P = .054) survival. Although provocative, this study needs to be validated in a larger cohort of TP53-mutated myeloid malignancies, controlling for the impact of TP53-mutant allele status.
Conclusion
TP53-mutated myeloid malignancies remain a therapeutic challenge. Recent data have established the importance of accurately determining TP53-mutant allele status, which requires genetic testing able to detect CN-LOH of 17p. Multihit TP53-mutant AML/MDS is associated with complex cytogenetic abnormalities and a very poor prognosis, whereas single-hit TP53-mutated AML/MDS behaves more like non–TP53-mutated AML/MDS. In our current model of the pathogenesis and clonal evolution of TP53-mutated myeloid malignancies, HSCs that acquire a TP53 loss-of-function mutation gain a fitness advantage. This results in the selective expansion of single-hit TP53-mutant HSCs, especially under conditions of genotoxic stress or other cellular stressors such as ribosomal stress.6,14,32TP53 hot-spot mutations, through their dominant-negative activity, provide HSCs with a further enhanced fitness when compared with simple loss-of-function TP53 mutations (eg, nonsense mutations). In some cases, TP53 hot-spot mutations may also have gain-of-function properties that contribute to enhanced fitness. Together, these fitness-enhancing properties of TP53 hot-spot mutations help explain their frequency in cancer. The loss of the remaining wild-type TP53 allele is likely an early progression event that contributes to genomic instability and the development of complex chromosomal abnormalities. Current evidence does not support the routine use of TP53 mutation identity in the selection of therapy. However, areas of active investigation include the development of drugs designed to restore certain mutant p53 proteins to their wild-type conformations and the assessment of whether certain TP53 mutations may generate neoantigen targets for immunotherapy.33-35
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
Terrence N. Wong: no competing financial interests to declare.
Daniel C. Link: no competing financial interests to declare.
Off-label drug use
Terrence N. Wong: Nothing to disclose.
Daniel C. Link: Nothing to disclose.