Abstract
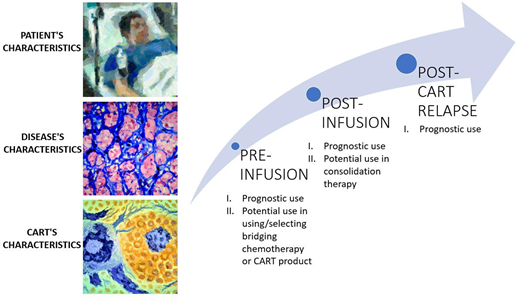
We discuss different pre-infusion, post-infusion and post-CAR T-cell relapse prognostic factors influencing the outcomes of anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas. Despite the overall positive results of anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, a significant percentage of patients relapse. We summarize the efforts made to identify predictive factors for response and durable remissions and survival. In the pre-infusion setting, the patient-related factors discussed include Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, age, and comorbidities. Disease-related factors like tumor burden, histology, and biological features are also considered. In addition, inflammation-related factors and CAR T-cell product-related factors are considered. After CAR T-cell infusion, factors such as disease response assessed by 18FDG-PET/CT scan, liquid biopsy monitoring, and CAR T-cell expansion become crucial in predicting survival outcomes. Response to 18FDG-PET/CT scan is a widely used test for confirming response and predicting survival. Liquid biopsy, in combination with 18FDG-PET/CT scan, has shown potential in predicting outcomes. CAR T-cell expansion and persistence have shown mixed effects on survival, with some studies indicating their association with response. In the setting of post-CAR T-cell relapse, prognostic factors include refractory disease, time of relapse, and elevated lactate dehydrogenase levels at CAR T-cell infusion. Enrollment in clinical trials is crucial for improving outcomes in these patients. Overall, we discuss a comprehensive overview of prognostic factors that can influence the outcomes of anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas, highlighting the need for personalized approaches in treatment decision-making.
Learning Objectives
Identify prognostic factors related to CAR T-cell for lymphoma therapy in the pre-infusion, post-infusion, and post-CART relapse setting
Interpret how the presence of risk factors could have an impact on treatment or a follow-up approach
Introduction
Anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy dramatically changed the clinical scenario of patients affected by B-cell malignancies. In adult patients, the pivotal clinical studies ZUMA-1, JULIET, and TRANSCEND showed the curative potential of such cell therapies in the setting of large B-cell lymphomas beyond second line therapy.1-3 Considering such promising results, anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy was also tested in second-line therapy. The ZUMA-7 and the TRANSFORM trials demonstrated the superiority of CAR T-cell vs autologous stem cell transplant.4,5 Newer CAR T-cell products and their use in first-line therapy and in patients who are not candidates for autologous stem cell transplant are currently being tested.
CLINICAL CASE
In August 2018, a 48-year-old man presented to our department for multiple peripheral enlarged lymph nodes and the presence of B-symptoms. Later, a cervical lymph node biopsy was made with a diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified (NOS), non-germinal center subtype. Molecular analysis detected a TP53 mutation, while fluorescence in situ hybridization studies showed no evidence of MYC, BCL2, or BCL6 rearrangements. The staging positron emission tomography-computed tomography scan (18FDG-PET/CT) revealed multiple hypermetabolic adenopathies with a bulky abdominal lesion infiltrating the pancreas, spleen, left kidney, adrenal gland, and gastroesophageal junction effusion. The revised International Prognostic Index (IPI) was 4; the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) status was 2. The patient received three lines of immunochemotherapy (R-CHOP, R-GDP, and R-ESHAP), with refractoriness to treatment. Therefore, he was a candidate to receive anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy with tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel). After lymphoapheresis, bridging therapy was administrated with one cycle of Rituximab-Bendamustine-Polatuzumab with progression of disease at pre-lymphodepletion 18FDG-PET/CT scan evaluation. A patient-specific circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) analysis was generated using a KMT2D p.Glu4385Gly tumor-specific mutation identified at diagnosis biopsy material. The patient received standard lymphodepletion therapy with fludarabine/cyclophosphamide. Elevated levels of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were detected at the day of infusion.
Pre-infusion prognostic factors
Almost 60% of patients treated with anti-CD19 CAR T-cell will relapse.1-3,6 A prognostic score to predict the outcomes of all patients eligible for anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy is currently missing. However, predictive factors for response and durable remissions have been identified (Table 1).
Baseline risk factors associated with outcomes for lymphoma patients treated with anti-CD19 CAR T-cell (on multivariate analysis)
| Risk factor . | Hazard ratio HR . |
|---|---|
| • ECOG ≥2 (baseline) | PFS: HR 1.7 (95% CI: 1.1-2.7; p = 0.010) OS: HR 1.8 (95% CI: 1.10-3.00; p = 0.020)9 PFS: HR 2.61 (1.90-3.60) OS: HR 3.27 (2.37-4.52)10 PFS: HR 5.446 (95% CI: 2.354-12.597; p < 0.001) OS: HR 4.306 (95% CI: 1.841-10.071; p = 0.001)11 OS: HR 1.63 (95% CI: 1.06-2.51; p = 0.03), ECOG considered as 1-unit increase8 |
| • Age ≥65 years old • Age >60 years old | ORR: OR 1.39 (95% CI: 1.05–1.83)10 PFS: HR 1.6 (95% CI: 1.1–2.3; p = 0.01)9 |
| • Chemo-resistant disease prior to infusion | PFS: HR 1.48 (95% CI: 1.21–1.79) OS: HR 1.44 (95% CI: 1.15–1.81)10 |
| • Disease status (PD vs other) | PFS: HR 1.804 (95% CI: 1.096-3.507; p = 0.018) OS: HR 2.561 (95% CI: 1.812-3.999; p = 0.018)11 |
| • CIRS ≥7 or CIRS-3+ (baseline) • “Severe4” score (baseline) | OS: HR 2.39 (95% CI: 1.10-5.20; p = 0.03) PFS: HR 2.15 (95% CI: 1.54-2.99; p < 0.001)8 OS: HR 1.94 (95% CI: 1.35-2.78; p < 0.001)13 |
| • aaIPI ≥2 at time of lymphodepletion | PFS: HR 6.76 (95% CI: 2.21–20.69; p = 0.001) OS: HR 7.91 (95% CI: 1.74–35.85; p = 0.007)17 |
| • High LDH at CAR T-cell election | Relapse: HR 2.04 (95% CI: 1.19-3.49; p = 0.009) Early relapse: 9.61 (95% CI: 1.23-75.41; p = 0.031)19 |
| • High LDH at apheresis | PFS: HR 2.181 (95% CI: 1.303-3.651; p = 0.003) OS: HR 1.809 (95% CI: 1.084-3.021; p = 0.023)11 |
| • High LDH before lymphodepletion | PFS: HR 1.9 (95% CI: 1.3-2.9; p = 0.001) OS: HR 3.0 (95% CI: 1.7-5.4; p = 0.0001)9 |
| • Extranodal sites ≥2 at infusion | Relapse: HR 2.50 (95% CI: 1.44-4.35; p = 0.00111) Early relapse: HR 4.67 (95% CI: 1.55-14.11; p = 0.0063) Death: HR 3.61 (95% CI: 1.55-8.38; p = 0.0028319 |
| • High MTV pre-lymphodepletion • Low MTV (baseline) • High MTV (baseline) | Relapse: HR 2.18 (95% CI: 1.23-3.89; p = 0.00794) Early relapse: HR 4.35 (95% CI: 1.32-14.37; p = 0.016) Death: HR 3.41 (95% CI: 1.41-8.26; p = 0.0651)19 PFS: HR 0.40; (95% CI: 0.18-0.89). OS: HR 0.25; (95% CI: 0.10-0.66)18 PFS: HR 3.44 (95% CI: 1.18-10.1; p = 0.02)42 |
| • Use of bridging therapy • Refractory to bridging therapy | OS: HR 1.7 (95% CI: .04–2.70, 0.0300)9 PFS: HR 2.273 (95% CI: 1.484-3.481; p = 0.001) OS: HR 2.273 (95% CI: 1.324-3.901; p = 0.003)21 |
| • Increased CRP at infusion | Relapse: HR 1.12 (95% CI: 1.07-1.17; p = 0.0001) Early relapse: HR 1.15 (95% CI: 1.03-1.29; p = 0.016) Death: HR 1.12 (95% CI: 1.06-1.17; p = .0001)19 |
| • Presence of TP53 gene alterations | CR: OR 3.61 (95% CI: 1.31-10.7; p = 0.016) OS: HR 2.03 (95% CI: 1.02-4.03; p = 0.044)43 |
| • High focal copy number alterations before infusion | PFS: HR 2.11 (95% CI: 1.36-3.275; p = 0.0007) OS: HR 2.10 (95% CI: 1.28-3.43; p = 0.0026)24 |
| • CAR T-cell type Tisa-cel vs axi-cel Axi-cel vs tisa-cel | PFS: HR 1.475 (95% CI: 1.122-1.942; p = 0.005)21 PFS: HR 0.61 (95% CI: 0.46-0.79; p = 0.0003) OS: HR 0.63 (95% CI: 0.45-0.88; p = 0.0072)28 |
| Risk factor . | Hazard ratio HR . |
|---|---|
| • ECOG ≥2 (baseline) | PFS: HR 1.7 (95% CI: 1.1-2.7; p = 0.010) OS: HR 1.8 (95% CI: 1.10-3.00; p = 0.020)9 PFS: HR 2.61 (1.90-3.60) OS: HR 3.27 (2.37-4.52)10 PFS: HR 5.446 (95% CI: 2.354-12.597; p < 0.001) OS: HR 4.306 (95% CI: 1.841-10.071; p = 0.001)11 OS: HR 1.63 (95% CI: 1.06-2.51; p = 0.03), ECOG considered as 1-unit increase8 |
| • Age ≥65 years old • Age >60 years old | ORR: OR 1.39 (95% CI: 1.05–1.83)10 PFS: HR 1.6 (95% CI: 1.1–2.3; p = 0.01)9 |
| • Chemo-resistant disease prior to infusion | PFS: HR 1.48 (95% CI: 1.21–1.79) OS: HR 1.44 (95% CI: 1.15–1.81)10 |
| • Disease status (PD vs other) | PFS: HR 1.804 (95% CI: 1.096-3.507; p = 0.018) OS: HR 2.561 (95% CI: 1.812-3.999; p = 0.018)11 |
| • CIRS ≥7 or CIRS-3+ (baseline) • “Severe4” score (baseline) | OS: HR 2.39 (95% CI: 1.10-5.20; p = 0.03) PFS: HR 2.15 (95% CI: 1.54-2.99; p < 0.001)8 OS: HR 1.94 (95% CI: 1.35-2.78; p < 0.001)13 |
| • aaIPI ≥2 at time of lymphodepletion | PFS: HR 6.76 (95% CI: 2.21–20.69; p = 0.001) OS: HR 7.91 (95% CI: 1.74–35.85; p = 0.007)17 |
| • High LDH at CAR T-cell election | Relapse: HR 2.04 (95% CI: 1.19-3.49; p = 0.009) Early relapse: 9.61 (95% CI: 1.23-75.41; p = 0.031)19 |
| • High LDH at apheresis | PFS: HR 2.181 (95% CI: 1.303-3.651; p = 0.003) OS: HR 1.809 (95% CI: 1.084-3.021; p = 0.023)11 |
| • High LDH before lymphodepletion | PFS: HR 1.9 (95% CI: 1.3-2.9; p = 0.001) OS: HR 3.0 (95% CI: 1.7-5.4; p = 0.0001)9 |
| • Extranodal sites ≥2 at infusion | Relapse: HR 2.50 (95% CI: 1.44-4.35; p = 0.00111) Early relapse: HR 4.67 (95% CI: 1.55-14.11; p = 0.0063) Death: HR 3.61 (95% CI: 1.55-8.38; p = 0.0028319 |
| • High MTV pre-lymphodepletion • Low MTV (baseline) • High MTV (baseline) | Relapse: HR 2.18 (95% CI: 1.23-3.89; p = 0.00794) Early relapse: HR 4.35 (95% CI: 1.32-14.37; p = 0.016) Death: HR 3.41 (95% CI: 1.41-8.26; p = 0.0651)19 PFS: HR 0.40; (95% CI: 0.18-0.89). OS: HR 0.25; (95% CI: 0.10-0.66)18 PFS: HR 3.44 (95% CI: 1.18-10.1; p = 0.02)42 |
| • Use of bridging therapy • Refractory to bridging therapy | OS: HR 1.7 (95% CI: .04–2.70, 0.0300)9 PFS: HR 2.273 (95% CI: 1.484-3.481; p = 0.001) OS: HR 2.273 (95% CI: 1.324-3.901; p = 0.003)21 |
| • Increased CRP at infusion | Relapse: HR 1.12 (95% CI: 1.07-1.17; p = 0.0001) Early relapse: HR 1.15 (95% CI: 1.03-1.29; p = 0.016) Death: HR 1.12 (95% CI: 1.06-1.17; p = .0001)19 |
| • Presence of TP53 gene alterations | CR: OR 3.61 (95% CI: 1.31-10.7; p = 0.016) OS: HR 2.03 (95% CI: 1.02-4.03; p = 0.044)43 |
| • High focal copy number alterations before infusion | PFS: HR 2.11 (95% CI: 1.36-3.275; p = 0.0007) OS: HR 2.10 (95% CI: 1.28-3.43; p = 0.0026)24 |
| • CAR T-cell type Tisa-cel vs axi-cel Axi-cel vs tisa-cel | PFS: HR 1.475 (95% CI: 1.122-1.942; p = 0.005)21 PFS: HR 0.61 (95% CI: 0.46-0.79; p = 0.0003) OS: HR 0.63 (95% CI: 0.45-0.88; p = 0.0072)28 |
aaIPI, age-adjusted International Prognostic Index; CIRS, Cumulative Illness Rating Scale; CRP, C-reactive protein; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; HR, hazard ratio; HR, hazard ration; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MTV, metabolic tumor volume; OS, overall survival; PD, progression of disease; PFS, progression-free survival.
Patient-related
ECOG performance status ≥2 was independently associated with an inferior overall response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).7-9 These findings were further validated in the largest real-word prospective study by Jacobson et al and in a recent comparison study between tisa-cel and axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel).10,11
Age is not considered a strict determinant for eligibility to receive anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy. In a large study conducted by the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research for axi-cel, patients age ≥65 were associated with higher ORR than younger patients.12 The superior efficacy observed may be attributed to a selection bias, but further studies are needed to deepen the disease biology features in this setting. Age and performance status are part of the International Prognostic Index score. As described later, this score has a prognostic significance in this setting.
Comorbidities have a prognostic impact also in this setting. In a first evaluation of the impact of the Cumulative Illness Rating Scale (CIRS) on survival, the high comorbidity burden (defined as CIRS ≥7 or CIRS 3/4 in one system) was significantly associated with inferior OS and PFS.8 In a recent multicenter retrospective real-world evidence analysis, a simplified CIRS-based index called “Severe4” was developed that included CIRS >2 at the respiratory, hepatic, renal, and upper gastrointestinal levels. This index was independently associated with inferior PFS, OS, and relapse-related mortality in DLBCL patients eligible for CAR T-cell therapy.13
Considering the crucial role of the gut microbiota in the antitumor immune-response to therapy, two recent retrospective and prospective studies showed that lower diversity and a specific microbiota composition are associated with survival outcomes after anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in patients with B-cell malignancies.14 Nevertheless, further studies are needed to deepen our understanding in this area.
Disease-related
In the context of R/R DLBCL with anti-CD19 CAR T-cell, conventional tumor-related predictive features that have prognostic significance in newly diagnosed DLBCL, such as activated B-cell-like phenotype, cell of origin, and double-hit rearrangements, have no prognostic value.2,7,9 Nevertheless, several tumor intrinsic factors contribute to CAR T-cell failure, including tumor burden, histology, and biological features.
Intrinsic anti-CD19 CAR T-cell resistance was observed in a small cohort of 9 patients with T-cell/histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma who were treated with axi-cel or tisa-cel, with all patients progressing by day +90.15 Although the sample size was limited, an explanation was the unique immune environment that defines this disease. However, no clear reduction in the effectiveness of anti-CD19 CAR T-cell in pivotal and real-world studies involving high-grade B cell lymphoma patients was observed.16
IPI and age-adjusted-IPI (aaIPI) are two simple and widely used tools in the management of patients with DLBCL. A retrospective study evidenced the strong correlation between aaIPI ≥2 at the time of lymphodepletion with inferior PFS and OS in patients treated with commercial anti-CD19 CAR T-cell products.17 LDH is part of IPI score and is independently associated with clinical outcomes. A real-world report of the Lymphoma CAR T-cell Consortium, by Nastoupil et al, found that elevated LDH before lymphodepleting chemotherapy, as a surrogate of metabolic tumor burden, was significantly associated with inferior PFS and OS.9 Further analysis supported the negative prognostic influence of elevated LDH at CAR T-cell therapy election, at apheresis, and at pre-infusion.9,16,17
The total metabolic tumor volume (TMTV) measured on 18FDG-PET/CT is a cumulative volume measure of lesions. When the volume of the tumor was calculated before CAR T-cell infusion, patients in the low baseline TMTV group exhibited significantly improved OS and PFS compared to those in the high TMTV group.18 The negative prognostic significance of a high TMTV was confirmed even after the bridging treatment in a French real-world analysis of 116 patients treated with axi-cel or tisa-cel.19 Notably, the presence of two or more extranodal sites, when combined with high pre-infusion TMTV, showed the highest hazard ratio and was identified as an independent prognostic factor for relapse and early progression in multivariate analyses.
Furthermore, the need for a bridging therapy aligns closely with the escalating tumor burden and was associated with worse OS as well.9 However, when effective bridging chemotherapy is able to reduce the burden of disease pre-infusion, its negative impact disappear.20,21
Analysis of TP53 alterations through next-generation sequencing has shown a predictive role in this setting. Shouval et al observed a notable independent association between TP53 alterations and inferior complete response (CR) and OS in a multivariable Cox regression model, especially with CAR T-cell product with 4-1 co-stimulation domain compared to CD28 (1-year PFS 10% vs 34% and 1-year OS 36% vs 51%).22 Also, the pretreatment presence of complex structural variants, APOBEC mutational signatures, and genomic damage from reactive oxygen species predict anti-CD19 CAR T-cell resistance.23 A retrospective analysis conducted by Cherng et al found that a high focal copy number alteration score detected with low-pass whole-genome sequencing of cell-free DNA at time of leukapheresis, as a surrogate of genomic instability, was correlated with inferior +3 months CR (p = 0.0029), PFS, and OS.24
Inflammation-related
The inflammatory state, directly related to tumor burden, appears to be inversely correlated with in vivo CAR T-cell cell expansion and durable response. In a real-world analysis, day 0 CRP <30 mg/L correlated with improved duration of response (median not reached [NR] vs 3.6 months; p = 0.0030), PFS (median NR v 2,5 months; p = 0.001), and OS (median NR v 6,5 months; p = 0.001).7 Moreover, a reduced peak ferritin was associated to an improved PFS (median 6.8 vs 2.2; p = 0.020) and OS (median NR vs 2.2; p = 0.001). Locke et al analyzed samples from ZUMA-1 patients and found that systemic inflammation markers (LDH, IL6, ferritin) were the most significant risk factors for durable response along with CAR T-cell phenotype.25 An elevated CRP at infusion level was confirmed as a predictive factor of relapse, early relapse, and death in multivariate analysis.19
CAR T-cell product-related
The heterogeneity in T-cell composition in the peripheral blood, including the proportion of T “naive” (TN), T central memory (TCM), and T effector memory (TEM) cells along with their exhaustion phenotype related to age and chemotherapy regimens administered, can significantly influence the quality of lymphocyte apheresis product and subsequent CAR T-cell production. A strong correlation between the infusion of poorly differentiated memory anti-CD19 CAR T-cell and their enhanced expansion and prolonged persistence have been demonstrated. Notably, in the ZUMA-1 trial, a CAR T-cell product with a higher proportion of CD8 TN/stem cell memory T cells (TSCM) was associated with an objective (p = 0.0327) and durable response (p = 0.0301).25 Finally, Monfrini et al. found that an enrichment of CD8 TCM CAR T-cell products was associated with increased CAR T-cell expansion in vivo, which correlated with higher efficacy (odds ratio = 5.6, 95% CI (confidence interval), 1.681-18.65, p < 0.005) and PFS (median PFS NR vs 3.7 months, respectively; p < 0.05).26 In patients treated with axi-cel, a higher number of CD8+ CAR T-cells expressing memory signatures was associated with better responses at +3 months, while the presence of CD8+ CAR T-cells with an exhaustion profile was associated with poorer clinical response.27
Back to the CLINICAL CASE
The post-infusion course was complicated by cytokine release syndrome (CRS) grade 3 and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome grade 1 at day +4 treated with tocilizumab. At day +6, CRS worsened, requiring the administration of high doses of dexamethasone with progressive resolution. The patient was discharged on day +45. The 18FDG-PET/CT scan performed at +1 month showed a partial response (PR), and concomitant levels of ctDNA at +1 month and +2 months progressively decreased and became undetectable. Unfortunately, the 18FDG-PET/CT at +3 months and a concurrent liquid biopsy showed a radiological and serological disease relapse. In the absence of salvage therapies, palliative care was initiated, and the patient died 4 months after anti-CD19 CAR T-cell infusion.
Post-infusion prognostic factors
After CAR T-cell infusion, other prognostic factors become fundamental in predicting survival outcomes (Table 2). Response to the 18FDG-PET/CT scan is, at present, the most standardized and commonly used test to confirm a response and predict survival outcomes. In the long-term analysis of the ZUMA-1 trial, the estimated proportion of patients with PFS at +24 months was 72.0% (95% CI: 56.0-83.0) among those with CR at +3 months, 75.0% (95% CI: 31.5-93.1) among those with PR at +3 months, and 22.2% (95% CI: 3.4-51.3) among those with stable disease (SD) at +3 months from infusion.6 In the JULIET trial, the estimated probability of survival at +12 months was 49% (95% CI: 39-59) among all patients and 90% (95% CI: 74-96) among patients with a CR.2 In the TRANSCEND trial, patients who achieved CR at +1 year had OS of 86% (95% CI: 78.2-90.5) vs 58% (95% CI: 51.3-63.8) of the whole study cohort.3 PFS at +1 year was 44% (95% CI: 37.3-50.7) for the total population and 65% (95% CI:56.1-72.7) among patients who had CR. The role of 18FDG-PET/CT response has been studied also in the real-life setting. Kuhnl et al. described the prognostic role of 18FDG-PET/CT at +1 month post-infusion, measured by the Deauville score (DS), in terms of response and survival outcomes.29 Of 171 patients infused with commercial anti-CD19 CAR T-cell (axi-cel, tisa-cel), the risk of early progression was 15% for DS1 to 2, 32% for DS3, 37% for DS4, and 100% for DS5. Moreover, survival outcomes were associated with different scores. PFS at +1 year was 77.1% (DS1-2), 63.5% (DS3), 43.5% (DS4), and 0% (DS5). OS at +1 year was 87.1% (DS1-2), 86.2% (DS3), 62.7% (DS4), and 38.1% (DS5). Al Zaki et al found that the only factor associated with disease progression was having an SUV max ≥10 at day +30 post-infusion.30 Finally, Guidetti et al combined DS at day +30 with SUV variation from pre-infusion to day +30.31 Patients with DS4-5 and decreased SUV have +1 year PFS of 61%, which is similar to those with DS1-3. Patients with DS4-5 and increased SUV had a worse PFS at +1 year of 33% (p = 0.04).
Risk factors associated with survival outcomes for lymphoma patients after anti-CD19 CAR T-cell infusion
| Risk factor . | Prognostic role . |
|---|---|
| • Higher CAR T-cell product expansion | ORR: OR 1.268 (95% CI: 1.062-1.676; p < 0.05)26 |
| • +1 month 18FDG-PET/CT disease evaluation | • Prognostic role on relapse and PFS (Deauville score)29 • SUV max useful in predicting progression for patients in PR/SD30 • Deauville score combined with SUV variation allowed better stratification of patients at day +30 DS4-531 |
| • Tumor burden measured by liquid biopsy (VDJ ctDNA) | • Prognostic role after infusion at +1 week, +1 month, and +3 months; also, useful in stratifying patients with radiological SD/PR at +1 month32 |
| Risk factor . | Prognostic role . |
|---|---|
| • Higher CAR T-cell product expansion | ORR: OR 1.268 (95% CI: 1.062-1.676; p < 0.05)26 |
| • +1 month 18FDG-PET/CT disease evaluation | • Prognostic role on relapse and PFS (Deauville score)29 • SUV max useful in predicting progression for patients in PR/SD30 • Deauville score combined with SUV variation allowed better stratification of patients at day +30 DS4-531 |
| • Tumor burden measured by liquid biopsy (VDJ ctDNA) | • Prognostic role after infusion at +1 week, +1 month, and +3 months; also, useful in stratifying patients with radiological SD/PR at +1 month32 |
ctDNA, circulating tumor DNA; OR, odds ratio; ORR, overall response rate; PFS, progression-free survival; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease; VDJ, variable, diversity, and joining gene segments.
Despite being considered experimental still, liquid biopsy proved to be an extremely powerful tool, when used in combination with 18FDG-PET/CT scan, in predicting survival outcomes. Frank et al reported the results of 69 patients treated with commercial axi-cel for whom liquid biopsy was available before CAR T-cell infusion and at different timepoints after infusion.32 Patients with detectable day +28 ctDNA had a median PFS of 3 months vs NR (p < 0.0001) and a median OS of 19 months vs NR (p = 0.0080) for those without ctDNA. Moreover, of the patients with radiologically SD/PR at day +28, only 1/10 with concurrently undetectable ctDNA relapsed vs 15/17 with concurrently detectable ctDNA (p = 0.0001). Finally, all patients with durable responses had undetectable ctDNA at or before +3 months from infusion. It should be considered that this study used clonoseq assay using VDJ gene rearrangement as liquid biopsy technique, which is possibly not the best method. Other techniques such as PhasED-Seq or CAPP-seq have more potential in this setting.33,34
Finally, expansion and persistence of anti-CD19 CAR T-cell showed a mixed effect on survival. In the JULIET study, no effect on outcomes were observed in terms of CAR T-cell expansion and persistence.2 On the contrary, in the ZUMA-1 study, CAR T-cell expansion during the first 28 days was associated with response (p < 0.001) with an area under the curve 5.4 times higher between responders and no responders.1 Also, in the TRANSCEND study, expansion of lisocabtagene maraleucel was associated with response. In fact, patients who reached a PR/CR had a higher Cmax (3.55-fold, p < 0.0001) and area under the curve during the first 28 days (2.72-fold, p < 0.0001).3 Monfrini et al showed that CAR T-cell expansion has a prognostic role also in the real-life setting (only axi-cel and tisa-cel).26 In their study, patients in PR/CR within +3 months of infusion had a superior CAR T-cell expansion compared to non-responders measured by CAR T-cell concentration at day +7 and +10, with maximum concentration and area under the curve during the first 30 days. When CAR T-cell are used as second-line therapy, no prognostic role of expansions has been observed for axi-cel in terms of overall survival or for tisa-cel in terms of event-free survival.34,35 The role of anti-CD19 CAR T-cell persistence did not show any prognostic significance in the lymphoma setting.
Post-CAR T-cell relapse prognostic factors
In the setting of relapse after anti-CD19 CAR T-cell was used after 2 or more lines of therapy, there are a few studies that identified prognostic factors able to predict survival outcomes (Table 3). No data are currently available for relapse after anti-CD19 CAR T-cell is used as second-line therapy. When patients relapse after anti-CD19 CAR T-cell is used beyond second-line therapy, median PFS and OS are 3 and 6 months, respectively.35-40 The treatment landscape in such a scenario is rapidly changing, considering the emergence of newer therapeutic strategies in this setting. One of the first prognostic risk factors identified was having a refractory disease (progression of disease <30 days from infusion). Chow et al showed that the progression of disease within 30 days of infusion has a median OS of 3.75 months vs 9.29 months (p = 0.042).41 The same results were demonstrated by Zurko et al, who recorded a OS of 2.9 months vs 8.0 months (p < 0.01) for patients with SD or progression of disease at day +30.36 An elevated LDH at CAR T-cell infusion was confirmed as one of the most important factors in the post-CAR T-cell relapse setting. No prospective clinical trials defined which is the best therapeutic approach in this setting. Data on the use of newer therapies (eg, lenalidomide; Rituximab-polatuzumab-bendamustine) should not be viewed as definitive because of known biases in the selection of patients fit for additional therapy. Enrollment into clinical trials should be always encouraged, considering the dismal outcomes of such patients.
Risk factors associated with survival outcomes for lymphoma patients with relapse after anti-CD19 CAR T-cell infusion
| Risk factor . | Hazard ratio HR (95% CI) . |
|---|---|
| • Response to axi-cel | OS: HR 0.45 (95% CI: 0.29-0.71; p = 0.0005)40 |
| • Progression <30 day | OS: HR 2.93 (95% CI: 1.56-5.50; p = 0.0009)37 |
| • CAR T-cell refractoriness | OS: HR 2.33 (95% CI: 1.02-5.29)38 |
| • Grade 3-4 CRS | OS: HR 5.39 (95% CI: 2.48-11.7; p = 2.2. × 10−5)40 |
| • Bridging chemotherapy | OS: HR 2.11 (95% CI: 1.32-3.39; p = 0.002)40 |
| • >2 lines of therapy before CAR T-cell infusion | PFS: HR 1.89 (95% CI: 1.1-3.5; p = 0.03)36 |
| • No double hit or double expressor lymphoma subtype | PFS: HR 0.42 (95% CI: 0.18-0.89; p = 0.03)36 |
| • Polatuzumab-bendamustine-rituximab after CAR T-cell failure as salvage treatment | PFS: HR 0.097 (95% CI: 0.013-0.57; p = 0.01)36 |
| • Lenalidomide-based after CAR T-cell failure as salvage treatment | PFS: HR 0.15, (95% CI: 0.026-0.76; p = 0.03)36 OS: HR 0.42 (95% CI: 0.21.0.82; p = 0.01)37 |
| • High LDH at infusion | PFS: HR 3.42 (95% CI: 1.93-6.05; p < 0.0001) OS: HR 2.10 (95% CI: 1.16-3.78; p = 0.01)37 OS: HR 2.95 (95% CI: 1.61-5.38)38 |
| • High ferritin at infusion | PFS: HR 1.02 (95% CI: 1.00-1.03; p = 0.01)37 |
| • High CRP at infusion | OS: HR 1.11 (95% CI: 1.04-1.19; p = 0.003)37 |
| • Bulky disease at apheresis | OS: HR 2.27 (95% CI: 1.10-4.72)38 |
| • Older age | OS: HR 2.65 (95% CI 1.49-4.73)38 |
| Risk factor . | Hazard ratio HR (95% CI) . |
|---|---|
| • Response to axi-cel | OS: HR 0.45 (95% CI: 0.29-0.71; p = 0.0005)40 |
| • Progression <30 day | OS: HR 2.93 (95% CI: 1.56-5.50; p = 0.0009)37 |
| • CAR T-cell refractoriness | OS: HR 2.33 (95% CI: 1.02-5.29)38 |
| • Grade 3-4 CRS | OS: HR 5.39 (95% CI: 2.48-11.7; p = 2.2. × 10−5)40 |
| • Bridging chemotherapy | OS: HR 2.11 (95% CI: 1.32-3.39; p = 0.002)40 |
| • >2 lines of therapy before CAR T-cell infusion | PFS: HR 1.89 (95% CI: 1.1-3.5; p = 0.03)36 |
| • No double hit or double expressor lymphoma subtype | PFS: HR 0.42 (95% CI: 0.18-0.89; p = 0.03)36 |
| • Polatuzumab-bendamustine-rituximab after CAR T-cell failure as salvage treatment | PFS: HR 0.097 (95% CI: 0.013-0.57; p = 0.01)36 |
| • Lenalidomide-based after CAR T-cell failure as salvage treatment | PFS: HR 0.15, (95% CI: 0.026-0.76; p = 0.03)36 OS: HR 0.42 (95% CI: 0.21.0.82; p = 0.01)37 |
| • High LDH at infusion | PFS: HR 3.42 (95% CI: 1.93-6.05; p < 0.0001) OS: HR 2.10 (95% CI: 1.16-3.78; p = 0.01)37 OS: HR 2.95 (95% CI: 1.61-5.38)38 |
| • High ferritin at infusion | PFS: HR 1.02 (95% CI: 1.00-1.03; p = 0.01)37 |
| • High CRP at infusion | OS: HR 1.11 (95% CI: 1.04-1.19; p = 0.003)37 |
| • Bulky disease at apheresis | OS: HR 2.27 (95% CI: 1.10-4.72)38 |
| • Older age | OS: HR 2.65 (95% CI 1.49-4.73)38 |
CRP, C-reactive protein; CRS, cytokine release syndrome; HR, hazard ratio; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival.
Conclusions
Factors related to patients, anti-CD19 CAR T-cell product, and disease characteristics can be identified before or after infusion or at relapse post-CAR T-cell product infusion. Currently, there is not a personalized risk score with high accuracy that can be used in clinical practice to detect high-risk patients. Moreover, disease progression may depend on factors that are not apparent pre-infusion but emerge after therapy, making the risk stratification process more dynamic than static as a means of evaluation. In the future, better pre-infusion risk factor identification could possibly guide therapeutic decisions, such as the use of bridging chemotherapy. The same consideration can be made for the post-infusion setting, where high-risk patients could be considered for consolidation/maintenance therapy.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
Alberto Mussetti: BMS: consultancy; Takeda: honoraria; Gilead: research funding; Jazz Pharaceuticals: consultancy.
Nicole Fabbri: no competing financial interests to declare.
Anna Sureda: consultancy for BMS, Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Sanofi, Takeda, and GSK; speakers bureau for Takeda; travel grants from BMS, Celgene, Janssen, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda; research support from Takeda and BMS.
Off-label drug use
Alberto Mussetti: no conflict to disclose.
Nicole Fabbri: no conflict to disclose.
Anna Sureda: no conflict to disclose.