Abstract
Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) ALL is the most common genetic subtype of ALL and primarily affects adults. Ph+ ALL is characterized by the constitutively active ABL1 kinase and is resistant to conventional chemotherapy. Thus, Ph+ ALL was historically associated with a dismal prognosis, particularly among patients who did not undergo allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (alloHCT) in first complete remission (CR). Imatinib, the first tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) effective against ABL1, transformed the treatment and prognosis of Ph+ ALL, allowing more patients to achieve CR and become eligible for alloHCT, thereby improving outcomes. In recent years, there has been an improved understanding of the biology of Ph+ ALL, including recognition of distinct subtypes (multilineage and lymphoblast-only Ph+ ALL). There has also been a dramatic expansion of effective therapeutic and diagnostic tools for management of Ph+ ALL, including more potent TKIs, which have activity against ABL kinase–resistance mutations; refinement of the chemotherapy and alloHCT regimens that accompany TKI therapy; introduction of immunotherapy (blinatumomab); and better assays for measurable residual disease monitoring. This article reviews recent advancements and future directions for the initial treatment of Ph+ ALL in adults.
Learning Objectives
Understand the role of TKI therapy in Ph+ ALL
Understand the role of chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant in Ph+ ALL
CLINICAL CASE
A 61-year-old man with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and obesity is diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) after presenting with constitutional symptoms. Karyotype: loss of Y and t(9;22). Reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) reveals the p190 BCR::ABL1 transcript.
Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) ALL
Ph+ ALL is rare in children but frequent in adults, with incidence increasing with age.1 In ALL, the t(9;22) balanced chromosomal translocation occurs via the major breakpoint cluster region in BCR (one-third of cases, resulting in the chimeric 210 kD oncoprotein) or via the minor breakpoint cluster region in BCR (approximately two-thirds of cases, 190 kD oncoprotein). Additional cytogenetic and/or molecular aberrations, including copy number losses of IKZF1 and other genes such as CDKN2A/B and PAX5 (ie, IKZF1 plus), have adverse prognostic implications.2-4 Ph+ ALL is a chemotherapy-resistant disease with durable remissions rarely observed historically, except in patients consolidated with an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (alloHCT) in first complete remission (CR).5 Fortunately, a dramatic expansion of effective therapeutic tools has rapidly improved outcomes and changed standards of clinical care.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Imatinib (IM) transformed the treatment of Ph+ ALL.6 Multiple trials demonstrated that earlier and longer IM exposure results in better disease control.1,7 The efficacy of IM was highlighted by the fact that it could consistently induce a CR accompanied by no or minimal chemotherapy.1,8,9
Following IM, the more potent second-generation (2G) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) dasatinib (DAS) and nilotinib (NIL) were developed. A trial in children with Ph+ ALL prospectively compared DAS (n = 92) with IM (n = 97) plus chemotherapy and demonstrated superior 4-year event-free survival (EFS, 71.0% vs 48.9%, p = 0.005), decreased cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR, 19.8% vs 34.4%, p = 0.01), and improved overall survival (OS, 88.4% vs 69.2%, p = 0.04) without increased toxicity.10 All studies of 2G TKIs in adults with Ph+ ALL are nonrandomized, or the randomization did not involve the choice of TKI (Tables 1 and 2). However, these studies demonstrated improved results when indirectly compared with IM-based studies.
Select studies of second- and third-generation TKIs for Ph+ ALL
| Group (study) . | Low-intensity induction? . | Phase . | Regimen . | N . | Age in years, median (range) . | CMR (%) . | alloHCT, CR1 (%) . | DFS/RFS/ EFS (%) . | OS (%) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIMEMA(Italy) LAL1205 NCT00391989 2006-2008 | Yes | 2 | Ind: DAS, pred Cons: per investigator | 53 | 54 (24-77) | 23 (best) | 34 | 51 (1.7-yr DFS) | 69 (1.7 yr) |
| MDACC(US) NCT00390793 2006-2012 | No | 2 | Ind/cons: DAS + hyper-CVAD | 72 (63a) | 55 (21-80) | 65 (best) | 17 | 42 (5-yr EFS) 44 (5-yr DFS) | 46 (5 yr) |
| EWALL(Europe) Ph01 NCT02888977 2007-2010 | Yes | 2 | Ind: DAS, vinc, dex Cons: DAS, low-int chemo | 71 | 69 (59-83) | 24 (MRD2) | 10 | 27 (5-yr EFS) 28 (5-yr RFS) | 36 (5 yr) |
| SWOG (US) SWOG 0805 NCT00792948 2009-2013 | No | 2 | DAS + hyper-CVAD | 94 (60a) | 44 (20-60) | - | 52 | 55 (3-yr EFS) 62 (3-yr RFS) | 69 (3 yr) |
| CALGB(US) C10701 NCT01256398 2010-2014 | Yes | 2 | Ind: DAS, dex Cons: alloHSCT or autoHSCT; or chemo (>70 yrs) | 65 | 60 (22-87) | 40 (end course IV) | 48 | 37 (5-yr DFS) | 48 (5 yr) |
| GIMEMA(Italy) TOTAL Therapy LAL1509 NCT03318770 2011-2013 | Yes | 2 | Ind: DAS, pred Cons: if CMR → DAS; no CMR → DAS plus HSCT or chemo | 60 | 42 (19-59) | 18 (end ind) | 37 | 47 (5-yr DFS) | 56 (5 yr) |
| DFCI DF/HCC 18-170 2018-2022 | Yes | 1 | Ind: DAS, ASC, pred Cons: DAS, ASC | 22 | 64 (33-85) | - | 33 | 63 (2-yr EFS) | 75 (2 yr) |
| KAALLWP(Korea) NCT00844298 2009-2012 | No | 2 | Ind/cons: NIL + chemo | 90 | 46 (17-71) | 86 (best) | 63 | 72 (2-yr RFS) | 72 (2 yr) |
| EWALL(Europe) Ph02 NCT01528085 2012-2020 | Yes | 2 | Ind: NIL, vinc, pred Cons: NIL, low-int chemo | 72 | 65 (55-85) | 14 (end ind) 58 (end cons) | 33 | 42 (4-yr EFS) | 47 (4 yr) |
| GRAALL(SAKK) GRAAPH-2014 NCT02611492 2015-2019 | Yes | 3 | Ind: NIL, vinc, pred Cons: NIL + high- (A) vs. low- (B) int chemo (1:1) | 156 | 47 (39-54 IQR) | 26 (TP4) | 60 | A: 76 (4-yr RFS) B: 58 (4-yr RFS) p = 0.028 | A: 79 (4 yr) B: 72 (4 yr) p = 0.88 |
| MDACC(US) NCT01424982 2011-2019 | No | 2 | PON + hyper-CVAD | 86 (66a) | 46 (21-80) | 87 (best) | 23 | 65 (6-yr EFS) 80 (6-yr DFS) | 75 (6 yr) |
| GIMEMA(Italy) INCB4344-20/ LAL1811 NCT01641107 2014-2017 | Yes | 2 | PON + pred | 44 | 67 (26-85); 80% ≥ 60 yrs | 41 (week 24) 82% (overall) | 14 | 14.3 mo (med, EFS) | NR (median) |
| PETHEMA(Spain) PONAFIL NCT02776605 2017-2020 | No | 2 | PON + high- int chemo | 30 | 49 (19-59) | 47 (ind) 71% (cons) | 87 | 70 (3-yr EFS) | 96 (3 yr) |
| PhALLCON (Global) NCT03589326 2018-2022 | Yes | 3 | PON vs IM + low-int chemo (2:1) | 245 | 54 | MR4.5 after C9 46 (PON) 26 (IM) | 31 (PON) 37 (IM) | Med EFS 29.0 Med EFS NR (HR 0.65, 95% CI 0.39-1.1) | Med OS NR Med OS NR (HR 0.76, 95% CI 0.38-1.52) |
| Group (study) . | Low-intensity induction? . | Phase . | Regimen . | N . | Age in years, median (range) . | CMR (%) . | alloHCT, CR1 (%) . | DFS/RFS/ EFS (%) . | OS (%) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIMEMA(Italy) LAL1205 NCT00391989 2006-2008 | Yes | 2 | Ind: DAS, pred Cons: per investigator | 53 | 54 (24-77) | 23 (best) | 34 | 51 (1.7-yr DFS) | 69 (1.7 yr) |
| MDACC(US) NCT00390793 2006-2012 | No | 2 | Ind/cons: DAS + hyper-CVAD | 72 (63a) | 55 (21-80) | 65 (best) | 17 | 42 (5-yr EFS) 44 (5-yr DFS) | 46 (5 yr) |
| EWALL(Europe) Ph01 NCT02888977 2007-2010 | Yes | 2 | Ind: DAS, vinc, dex Cons: DAS, low-int chemo | 71 | 69 (59-83) | 24 (MRD2) | 10 | 27 (5-yr EFS) 28 (5-yr RFS) | 36 (5 yr) |
| SWOG (US) SWOG 0805 NCT00792948 2009-2013 | No | 2 | DAS + hyper-CVAD | 94 (60a) | 44 (20-60) | - | 52 | 55 (3-yr EFS) 62 (3-yr RFS) | 69 (3 yr) |
| CALGB(US) C10701 NCT01256398 2010-2014 | Yes | 2 | Ind: DAS, dex Cons: alloHSCT or autoHSCT; or chemo (>70 yrs) | 65 | 60 (22-87) | 40 (end course IV) | 48 | 37 (5-yr DFS) | 48 (5 yr) |
| GIMEMA(Italy) TOTAL Therapy LAL1509 NCT03318770 2011-2013 | Yes | 2 | Ind: DAS, pred Cons: if CMR → DAS; no CMR → DAS plus HSCT or chemo | 60 | 42 (19-59) | 18 (end ind) | 37 | 47 (5-yr DFS) | 56 (5 yr) |
| DFCI DF/HCC 18-170 2018-2022 | Yes | 1 | Ind: DAS, ASC, pred Cons: DAS, ASC | 22 | 64 (33-85) | - | 33 | 63 (2-yr EFS) | 75 (2 yr) |
| KAALLWP(Korea) NCT00844298 2009-2012 | No | 2 | Ind/cons: NIL + chemo | 90 | 46 (17-71) | 86 (best) | 63 | 72 (2-yr RFS) | 72 (2 yr) |
| EWALL(Europe) Ph02 NCT01528085 2012-2020 | Yes | 2 | Ind: NIL, vinc, pred Cons: NIL, low-int chemo | 72 | 65 (55-85) | 14 (end ind) 58 (end cons) | 33 | 42 (4-yr EFS) | 47 (4 yr) |
| GRAALL(SAKK) GRAAPH-2014 NCT02611492 2015-2019 | Yes | 3 | Ind: NIL, vinc, pred Cons: NIL + high- (A) vs. low- (B) int chemo (1:1) | 156 | 47 (39-54 IQR) | 26 (TP4) | 60 | A: 76 (4-yr RFS) B: 58 (4-yr RFS) p = 0.028 | A: 79 (4 yr) B: 72 (4 yr) p = 0.88 |
| MDACC(US) NCT01424982 2011-2019 | No | 2 | PON + hyper-CVAD | 86 (66a) | 46 (21-80) | 87 (best) | 23 | 65 (6-yr EFS) 80 (6-yr DFS) | 75 (6 yr) |
| GIMEMA(Italy) INCB4344-20/ LAL1811 NCT01641107 2014-2017 | Yes | 2 | PON + pred | 44 | 67 (26-85); 80% ≥ 60 yrs | 41 (week 24) 82% (overall) | 14 | 14.3 mo (med, EFS) | NR (median) |
| PETHEMA(Spain) PONAFIL NCT02776605 2017-2020 | No | 2 | PON + high- int chemo | 30 | 49 (19-59) | 47 (ind) 71% (cons) | 87 | 70 (3-yr EFS) | 96 (3 yr) |
| PhALLCON (Global) NCT03589326 2018-2022 | Yes | 3 | PON vs IM + low-int chemo (2:1) | 245 | 54 | MR4.5 after C9 46 (PON) 26 (IM) | 31 (PON) 37 (IM) | Med EFS 29.0 Med EFS NR (HR 0.65, 95% CI 0.39-1.1) | Med OS NR Med OS NR (HR 0.76, 95% CI 0.38-1.52) |
In remission at enrollment.
alloHSCT, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant; Chemo, chemotherapy; CMR, complete molecular remission; cons, consolidation; CR, complete remission; DAS, dasatinib; dex, dexamethasone; DFS, disease-free survival; EFS, event-free survival; HR, hazard ratio; IM, imatinib; ind, induction; int, intensity; IQR, interquartile range; med, median; mo, month; MR, molecular response; MRD, measurable residual disease; NIL, nilotinib; NR, not reached; OS, overall survival; PON, ponatinib; pred, prednisone; SAKK (France, Belgium, and Switzerland); TP, timepoint; US, United States; vinc, vincristine; yr, year.
Patients treated with IM and 2G TKIs commonly relapse via acquisition of T315I, which confers resistance to all TKIs approved for ALL, except ponatinib (PON).11 The development of PON as first-line treatment of Ph+ ALL was pursued to prevent relapse (Tables 1 and 2). In a single-center trial, the MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDACC) combined PON 45 mg daily with hyper-CVAD.12 The dose of PON was decreased after an increased risk of PON- related vascular toxicity was recognized and two grade 5 vascular events were seen on study (modified regimen: PON 45 mg daily for 14 days during cycle 1 followed by continuous PON 30 mg beginning with cycle 2, reduced to 15 mg daily after achievement of a complete molecular remission [CMR]).12-14 The GIMEMA LAL1811 trial (INCB84344-201), which treated older patients (n = 44, ≥60 years) with continuous PON 45 mg without chemotherapy, reported frequent cardiac (29.5%, grade ≥3 18.2%) and vascular (27.3%, grade ≥3 15.9%) treatment-emergent adverse events.13 In contrast, the PETHEMA PONAFIL trial, which treated younger adults (n = 30, 18-60 years) with PON 30 mg plus chemotherapy followed by alloHCT, did not report cardiac or vascular toxicity.15
Regarding efficacy, retrospective studies suggest PON induces deeper, more durable remissions compared with IM.15-17 In the recently reported global phase 3 open-label PhALLCON study, adults (n = 254) were randomized 2:1 to PON (30 mg) versus IM (600 mg) plus reduced-intensity chemotherapy (Tables 1 and 2).18 The study achieved its composite primary endpoint of CR with measurable residual disease (MRD) negativity (BCR::ABL1 MR4) by 3 months (34.4% vs 16.7%, p = 0.002). After 20.1 months median follow-up, EFS trended favorably for the PON arm (hazard ratio [HR] 0.65, 95% CI 0.39-1.10) with no difference in OS.
No studies have prospectively randomized patients to a 2G TKI versus PON. Retrospective propensity score analyses conducted by MDACC have shown improved EFS among patients receiving PON versus DAS plus hyper-CVAD, even when early CMR is achieved.16,19 A novel approach to possibly improve outcomes by limiting mutational resistance is administration of dual TKI therapy with the ATP-competitive inhibitor DAS and the allosteric ABL1 inhibitor asciminib, which is being studied in an ongoing multicenter phase 1 study (Table 1).20 In summary, studies indicate that 2G TKIs and PON are superior to IM, with limited data that PON may be superior to DAS in some contexts.
The tremendous activity of TKIs in Ph+ ALL has permitted safe and effective de-escalation of chemotherapy during remission induction. The randomized GRAAPH-2005 study demonstrated that induction with IM plus vincristine and steroids was as effective as and less toxic than IM plus hyper-CVAD chemotherapy (Table 2).9 The GIMEMA group demonstrated in several phase 2 trials that a TKI plus steroid chemotherapy-free induction reliably and safely induces CR in adults of all ages.1,13 These data have facilitated the design of entirely chemotherapy-free regimens based on a TKI with alloHCT and/or blinatumomab consolidation.21-27
Key phase 3 randomized studies for Ph+ ALL
| Group/study/years . | TKI . | Randomization question . | N . | Age in years, median (range) . | CR (%) . | Early mortality (%) . | Molecular response (%) . | alloHCT, CR1 (%) . | RFS/EFS (%) . | OS (%) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRAALL(SAKK) GRAAPH-2005 NCT00327678 2006-2011 | IM | Induction intensity: low (vincristine, dex) vs high (hyper-CVAD) | 266 135 low (A) 133 high (B) | 47 (18-59) 45 (18-59) 45 (21-59) | 94.8 98.5 91.0 p = 0.006 | 5.6 (day 60) 2.2 9.0 p = 0.017 | 25.8 (MR4, C2) 28.6 22.6 p = 0.35 | 63.3 61.6 65.3 p = 0.53 | 37.1 (5-yr EFS) 42.2 (5-yr EFS) 32.1 (5-yr EFS) p = 0.13 | 45.6 (5 yr) 48.3 (5 yr) 43.0 (5 yr) p = 0.37 |
| GRAALL(SAKK) GRAAPH-2014 NCT02611492 2016-2019 | NIL | Consolidation intensity: low (HD-MTX) vs high (HiDAC, HD-MTX) | 156 79 low (B) 77 high (A) | 47 (IQR 39-54) 47 (IQR 39-54) 49 (IQR 39-54) | 94.2 94.9 93.4 p = 0.74 | 3.2 (day 60) 2.5 3.9 p = 0.68 | 26.4 (MR4, C4) 24.1 28.9 p = 0.59 | 60.0 59.5 60.5 p = 0.97 | - 58.5 (4-yr RFS) 76.2 (4-yr RFS) p = 0.029 | - 73.4 (4 yr) 79.4 (4 yr) p = 0.27 |
| China CCCG-ALL2015 ChiCTR-IPR-14005706 2015-2018 | IM vs DAS | IM vs DAS with chemo | 189 97 IM 92 DAS | 7.8 (IQR 5-11) - - | 96.8 94.8 98.9 p = 0.21 | 1 death (IM arm) | - | None | - 48.9 (4-yr EFS) 71.0 (4-yr EFS) p = 0.005 | - 69.2 (4-yr) 88.4 (4-yr) p = 0.04 |
| Global PhALLCON NCT03589326 2018-2022 | IM vs PON | IM vs PON with low-intensity chemo | 245 81 IM 163 PON | 54 (19-82) 52 (19-75) 54 (19-82) | - | 0 | (MR4, C9) 44.9 62.1 | 32.7 37.0 30.5 | - Med EFS 29 mos Med EFS NR (HR 0.65, 95% CI 0.39-1.1) | - Med OS NR Med OS NR (HR 0.76, 95% CI 0.38-1.5) |
| Group/study/years . | TKI . | Randomization question . | N . | Age in years, median (range) . | CR (%) . | Early mortality (%) . | Molecular response (%) . | alloHCT, CR1 (%) . | RFS/EFS (%) . | OS (%) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRAALL(SAKK) GRAAPH-2005 NCT00327678 2006-2011 | IM | Induction intensity: low (vincristine, dex) vs high (hyper-CVAD) | 266 135 low (A) 133 high (B) | 47 (18-59) 45 (18-59) 45 (21-59) | 94.8 98.5 91.0 p = 0.006 | 5.6 (day 60) 2.2 9.0 p = 0.017 | 25.8 (MR4, C2) 28.6 22.6 p = 0.35 | 63.3 61.6 65.3 p = 0.53 | 37.1 (5-yr EFS) 42.2 (5-yr EFS) 32.1 (5-yr EFS) p = 0.13 | 45.6 (5 yr) 48.3 (5 yr) 43.0 (5 yr) p = 0.37 |
| GRAALL(SAKK) GRAAPH-2014 NCT02611492 2016-2019 | NIL | Consolidation intensity: low (HD-MTX) vs high (HiDAC, HD-MTX) | 156 79 low (B) 77 high (A) | 47 (IQR 39-54) 47 (IQR 39-54) 49 (IQR 39-54) | 94.2 94.9 93.4 p = 0.74 | 3.2 (day 60) 2.5 3.9 p = 0.68 | 26.4 (MR4, C4) 24.1 28.9 p = 0.59 | 60.0 59.5 60.5 p = 0.97 | - 58.5 (4-yr RFS) 76.2 (4-yr RFS) p = 0.029 | - 73.4 (4 yr) 79.4 (4 yr) p = 0.27 |
| China CCCG-ALL2015 ChiCTR-IPR-14005706 2015-2018 | IM vs DAS | IM vs DAS with chemo | 189 97 IM 92 DAS | 7.8 (IQR 5-11) - - | 96.8 94.8 98.9 p = 0.21 | 1 death (IM arm) | - | None | - 48.9 (4-yr EFS) 71.0 (4-yr EFS) p = 0.005 | - 69.2 (4-yr) 88.4 (4-yr) p = 0.04 |
| Global PhALLCON NCT03589326 2018-2022 | IM vs PON | IM vs PON with low-intensity chemo | 245 81 IM 163 PON | 54 (19-82) 52 (19-75) 54 (19-82) | - | 0 | (MR4, C9) 44.9 62.1 | 32.7 37.0 30.5 | - Med EFS 29 mos Med EFS NR (HR 0.65, 95% CI 0.39-1.1) | - Med OS NR Med OS NR (HR 0.76, 95% CI 0.38-1.5) |
Chemo, chemotherapy; CR, complete remission; CMR, complete molecular remission; DAS, dasatinib; dex, dexamethasone; EFS, event-free survival; GRAALL, Group for Research on Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia; HD-MTX, high-dose methotrexate; HiDAC, high-dose ara-c; HR, hazard ratio; IM, imatinib; med, median; mos, months; MR, molecular response; NIL, nilotinib; NR, not reached; OS, overall survival; PON, ponatinib; RFS, relapse-free survival; SAKK (France, Belgium, and Switzerland); TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; yr, year.
CLINICAL CASE (continued)
The patient was recommended to receive a chemotherapy- free induction with DAS or PON plus corticosteroids. He enrolled in an investigational study combining DAS and asciminib. Further molecular analysis revealed deletion of IKZF1, CDKN2A, and CDKN2B. Additionally, a next-generation sequencing (NGS) MRD assay identified 3 clones (defined by B-cell receptor gene rearrangement) appropriate for MRD tracking. After 1 month of dual TKI therapy and prednisone, the patient achieved a CR, MRD-negative by multiparameter flow cytometry (<10−4). Molecular sequencing revealed a CMR by NGS (0 transcripts, sensitivity <10−6) and a BCR::ABL1 RT-PCR of 0.0474% (MR3).
Consolidation: role of chemotherapy
The GRAAPH-2014 study investigated whether chemotherapy could be reduced during consolidation.28 The study randomized patients (receiving NIL) to receive or not receive high-dose cytarabine consolidation and demonstrated no difference in the primary endpoint (post-consolidation MR3) but excess relapse in the low-intensity consolidation arm. Notably, increased relapse was restricted to patients not receiving alloHCT, suggesting that the need for chemotherapy intensification is restricted to non- allografted patients (Table 3). A single-center Dana-Farber analysis has similarly shown no difference in outcomes by intensity of pre-alloHCT chemotherapy.24
Select studies evaluating role of alloHCT in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission
| Study . | Pre-alloHCT regimen . | Population (# in CR1, age, transplant allocation) . | Outcomes (alloHCT vs no) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRAALL(SAKK) GRAAPH-20059 NCT00327678 | IM, chemotherapy | n = 254; 18-59 yrs Transplant allocation: 161 allo, 35 auto, 58 no transplant | OS HR 0.64, p = 0.02 RFS HR 0.69, p = 0.04 In MR4 at MRD2: RFS HR 1.02, p = 0.96 Not in MR4 at MRD2: RFS HR 0.62, p = 0.03 |
| GRAALL(SAKK) GRAAPH-201428 NCT02611492 | NIL, chemotherapy | n = 155; 18-59 yrs Transplant allocation: 93 allo, 40 auto, 22 no transplant | alloHCT associated with longer RFS (4-yr 79.4%) vs auto (57.2%; HR 0.46, p = 0.018) and vs no transplant (32.0%, HR 0.17, p < 0.0001) By randomization: Similar results in arm B (low-intensity consolidation), but improved RFS after alloHCT not seen in arm A (high-intensity consolidation) |
| KAALLWP(Korea) NCT0084429830 | NIL, chemotherapy | n = 82; 17-71 yrs Transplant allocation: allo 57, no allo 25 | OS 80% vs 72%, p = 0.23 RFS 78% vs 49%, p = 0.045 CIR 19% vs 41%, p = not reported NRM 19% vs 20%, p = not significant In MR5: RFS 65% vs 53%, p = 0.78 Multivariable analysis: alloHCT (HR 3.3, p = 0.048) and achievement of MR3 (HR 12.3, p = 0.038) associated with 2-yr RFS |
| SWOG (US) SWOG 080531 NCT00792948 | DAS, hyper-CVAD | n = 85; 20-60 yrs Transplant allocation: 41 protocol- specified allo; 44 no protocol-specified allo (8 nonprotocol allo) | Received protocol-specified: RFS 83% (12 mo); 76% (3 yr) Landmark analysis (175 days): protocol allo associated with improved RFS (HR 0.42, p = 0.038 and OS HR 0.35, p = 0.037) |
| Retrospective US (5 transplant centers)32 | IM, DAS, PON, chemo (mostly IM/DAS plus hyper-CVAD) | n = 230 all in MR4 by 3 months; 19-73 yrs Transplant allocation: 98 allo; 132 non-allo | OS (5 yr): 58% vs 61% (p = 0.63) RFS (5 yr): 63% vs 52% (p = 0.42) CIR (5 yr): 15% vs 36% (p = 0.001) NRM (5 yr): 21% vs 11% (p = 0.06) GRFS (5 yr): 25% vs 52% (p = 0.0001) |
| JALSG(Japan)33 Ph+ALL202, Ph+ALL208, Ph+ALL213 | IM, DAS plus chemo | n = 147 all in MR5 by 3 mos; 15-64 yrs Transplant allocation: 101 allo; 46 non-allo | OS (5 yr): 73% vs 50% (aHR 0.54, p = 0.04) RFS (5 yr): 70% vs 20% (aHR 0.21, p < 0.001) CIR (5 yr): 14% vs 73% (aHR 0.10, p < 0.001) NRM (5 yr): 17% vs 5% (aHR 3.49, p = 0.03) GRFS (5 yr): 50% vs 20% (p = NS) |
| Study . | Pre-alloHCT regimen . | Population (# in CR1, age, transplant allocation) . | Outcomes (alloHCT vs no) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRAALL(SAKK) GRAAPH-20059 NCT00327678 | IM, chemotherapy | n = 254; 18-59 yrs Transplant allocation: 161 allo, 35 auto, 58 no transplant | OS HR 0.64, p = 0.02 RFS HR 0.69, p = 0.04 In MR4 at MRD2: RFS HR 1.02, p = 0.96 Not in MR4 at MRD2: RFS HR 0.62, p = 0.03 |
| GRAALL(SAKK) GRAAPH-201428 NCT02611492 | NIL, chemotherapy | n = 155; 18-59 yrs Transplant allocation: 93 allo, 40 auto, 22 no transplant | alloHCT associated with longer RFS (4-yr 79.4%) vs auto (57.2%; HR 0.46, p = 0.018) and vs no transplant (32.0%, HR 0.17, p < 0.0001) By randomization: Similar results in arm B (low-intensity consolidation), but improved RFS after alloHCT not seen in arm A (high-intensity consolidation) |
| KAALLWP(Korea) NCT0084429830 | NIL, chemotherapy | n = 82; 17-71 yrs Transplant allocation: allo 57, no allo 25 | OS 80% vs 72%, p = 0.23 RFS 78% vs 49%, p = 0.045 CIR 19% vs 41%, p = not reported NRM 19% vs 20%, p = not significant In MR5: RFS 65% vs 53%, p = 0.78 Multivariable analysis: alloHCT (HR 3.3, p = 0.048) and achievement of MR3 (HR 12.3, p = 0.038) associated with 2-yr RFS |
| SWOG (US) SWOG 080531 NCT00792948 | DAS, hyper-CVAD | n = 85; 20-60 yrs Transplant allocation: 41 protocol- specified allo; 44 no protocol-specified allo (8 nonprotocol allo) | Received protocol-specified: RFS 83% (12 mo); 76% (3 yr) Landmark analysis (175 days): protocol allo associated with improved RFS (HR 0.42, p = 0.038 and OS HR 0.35, p = 0.037) |
| Retrospective US (5 transplant centers)32 | IM, DAS, PON, chemo (mostly IM/DAS plus hyper-CVAD) | n = 230 all in MR4 by 3 months; 19-73 yrs Transplant allocation: 98 allo; 132 non-allo | OS (5 yr): 58% vs 61% (p = 0.63) RFS (5 yr): 63% vs 52% (p = 0.42) CIR (5 yr): 15% vs 36% (p = 0.001) NRM (5 yr): 21% vs 11% (p = 0.06) GRFS (5 yr): 25% vs 52% (p = 0.0001) |
| JALSG(Japan)33 Ph+ALL202, Ph+ALL208, Ph+ALL213 | IM, DAS plus chemo | n = 147 all in MR5 by 3 mos; 15-64 yrs Transplant allocation: 101 allo; 46 non-allo | OS (5 yr): 73% vs 50% (aHR 0.54, p = 0.04) RFS (5 yr): 70% vs 20% (aHR 0.21, p < 0.001) CIR (5 yr): 14% vs 73% (aHR 0.10, p < 0.001) NRM (5 yr): 17% vs 5% (aHR 3.49, p = 0.03) GRFS (5 yr): 50% vs 20% (p = NS) |
aHR, adjusted hazard ratio; allo, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant; chemo, chemotherapy; CIR, cumulative incidence of relapse; CMR, complete molecular remission; CR, complete remission; DAS, dasatinib; GRFS, GVHD relapse-free survival; HR, hazard ratio; IM, imatinib; mo, month; NIL, nilotinib; NRM, nonrelapse mortality; OS, overall survival; PON, ponatinib; RFS, relapse-free survival; SAKK (France, Belgium, and Switzerland); US, United States; year, yr.
Consolidation: role of blinatumomab
Blinatumomab, a bi-specific CD19-CD3 T-cell engager, is particularly effective in the setting of low disease burden, making it suited to consolidate TKI-induced remissions (Table 4). A SWOG trial treated 24 patients ≥65 years with DAS plus prednisone induction followed by DAS plus blinatumomab (3 cycles) consolidation.27 After 2.7 years of median follow-up, 3-year OS and disease-free survival (DFS) were 87% and 77%, respectively. The GIMEMA LAL2116 study treated 63 adults with a 3-month DAS plus prednisone induction followed by up to 5 cycles of DAS plus blinatumomab consolidation.23 In LAL2116, 29% of patients achieved a molecular response (MR, undetectable or positive nonquantifiable BCR::ABL1 transcript) after induction, which increased to 60% after 2 blinatumomab cycles and 80% after 4 blinatumomab cycles. With a 53-month median follow-up, 4-year DFS and OS were 76% and 81%, respectively.22 The investigators hypothesize that the ability of DAS plus blinatumomab to induce progressively deeper and durable remissions may be in part due to host immune system modulation.29 Impressively, none of the 17 patients who achieved an MR after induction (prior to blinatumomab) have relapsed, highlighting a group with exceptional outcomes. The 9 relapses reported on study were enriched for IKZF1 deletion, T315I, and central nervous system (CNS) involvement.
Studies of blinatumomab in initial treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia
| Group (study) . | Phase . | Regimen . | Years . | N . | Age in years, median (range) . | CMR (%) . | alloHCT, CR1 (%) . | RFS/EFS (%) . | OS (%) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWOG(US) SWOG 1318 NCT02143414 | 2 | Ind: DAS, pred × 84 days Cons: DAS, blina x 3C CNS: 8 IT chemo | 2015-2021 | 24 | 73 (65-87) | 63 (12/19, anytime) | 3.8 | 77 (3-yr DFS) | 87 (3-yr) |
| GIMEMA(Italy) LAL2116 D-ALBA NCT02744768 | 2 | Ind: DAS, pred × 85 days Cons: DAS, blina x 5C CNS: 12 IT chemo | 2017-2019 | 63 | 54 (24-82) | 60 (blina C2) 82 (blina C4) | 38.1 | 75 (4-yr EFS) | 81 (4-yr) |
| MDACC(US) NCT03263572 | 2a | Ind/cons: PON + blina (C1-C5) CNS: 12 IT chemo | 2018- | 60 (39b) to date | 55 (20-83) | 83 (98 by NGS) | 3.3 | 77 (3-yr EFS) | 91 (3-yr) |
| DFCI(US) DF/HCC 18-170 NCT03595917 | 1a | Ind: DAS, ASC, pred x 1C Cons: DAS, ASC, blina x 5C CNS: 12 IT chemo | 2022- (blina cohort) | 15a | Eligibility: ≥18 | - | Per treating physician | - | - |
| ECOG-ACRIN(US) EA9181 NCT04530565 | 3a | Ind: DAS or PON + pred Cons: DAS or PON + hyper-CVAD vs blina (1:1) CNS: IT chemo + HD-MTX intensification x 1C | 2020- | 348a | Eligibility: 18-75 | - | Per treating physician | - | - |
| GIMEMA(Italy) ALL2820 NCT04722848 | 3a | Ind/cons: PON + blina vs IM + chemo (2:1) CNS: 15 IT chemo | 2021- | 236a | Eligibility: ≥18 | - | Based on IKZF1 plus and MRD | - | - |
| GRAALL(SAKK) GRAAPH-2024 | 3a | Ind: PON, blina, chemo Cons: alloHCT vs chemo/blina CNS: IT and systemic chemo | - | - | - | - | Randomize if in CMR (NGS) | - | - |
| Group (study) . | Phase . | Regimen . | Years . | N . | Age in years, median (range) . | CMR (%) . | alloHCT, CR1 (%) . | RFS/EFS (%) . | OS (%) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWOG(US) SWOG 1318 NCT02143414 | 2 | Ind: DAS, pred × 84 days Cons: DAS, blina x 3C CNS: 8 IT chemo | 2015-2021 | 24 | 73 (65-87) | 63 (12/19, anytime) | 3.8 | 77 (3-yr DFS) | 87 (3-yr) |
| GIMEMA(Italy) LAL2116 D-ALBA NCT02744768 | 2 | Ind: DAS, pred × 85 days Cons: DAS, blina x 5C CNS: 12 IT chemo | 2017-2019 | 63 | 54 (24-82) | 60 (blina C2) 82 (blina C4) | 38.1 | 75 (4-yr EFS) | 81 (4-yr) |
| MDACC(US) NCT03263572 | 2a | Ind/cons: PON + blina (C1-C5) CNS: 12 IT chemo | 2018- | 60 (39b) to date | 55 (20-83) | 83 (98 by NGS) | 3.3 | 77 (3-yr EFS) | 91 (3-yr) |
| DFCI(US) DF/HCC 18-170 NCT03595917 | 1a | Ind: DAS, ASC, pred x 1C Cons: DAS, ASC, blina x 5C CNS: 12 IT chemo | 2022- (blina cohort) | 15a | Eligibility: ≥18 | - | Per treating physician | - | - |
| ECOG-ACRIN(US) EA9181 NCT04530565 | 3a | Ind: DAS or PON + pred Cons: DAS or PON + hyper-CVAD vs blina (1:1) CNS: IT chemo + HD-MTX intensification x 1C | 2020- | 348a | Eligibility: 18-75 | - | Per treating physician | - | - |
| GIMEMA(Italy) ALL2820 NCT04722848 | 3a | Ind/cons: PON + blina vs IM + chemo (2:1) CNS: 15 IT chemo | 2021- | 236a | Eligibility: ≥18 | - | Based on IKZF1 plus and MRD | - | - |
| GRAALL(SAKK) GRAAPH-2024 | 3a | Ind: PON, blina, chemo Cons: alloHCT vs chemo/blina CNS: IT and systemic chemo | - | - | - | - | Randomize if in CMR (NGS) | - | - |
ongoing/planned.
previously untreated.
ara-C, cytarabine; ASC, asciminib; blina, blinatumomab; C, cycle; chemo, chemotherapy; CNS, central nervous system; cons, consolidation; DAS, dasatinib; EFS, event-free survival; HD-MTX; high-dose methotrexate; ind, induction; IT, intrathecal; NGS, next-generation sequencing; OS, overall survival; PON, ponatinib; pred, prednisone; RFS, relapse-free survival; SAKK (France, Belgium, and Switzerland); US, United States.
MDACC recently updated results of the first 60 patients treated on their single-center phase 2 study of PON plus blinatumomab (Table 4).25 Patients were induced with PON 30 mg and blinatumomab followed by PON plus blinatumomab consolidation, with PON reduced to 15 mg after achievement of CMR. Responses are rapid (CMR achieved by 83%, 67% at the end of course 1; of note, 21 patients entered the study in CR after previous treatment). With a median follow-up of 24 months, the estimated 3-year EFS and OS were 77% and 91%, respectively, with only 2 patients transplanted in CR1.
Consolidation: role of alloHCT
The ability of alloHCT to cure patients with ALL is established, but indications for transplantation in Ph+ ALL are evolving. In the pre-TKI era, “donor versus no-donor” analyses established the benefit of alloHCT.5 Subsequently, studies treating patients with IM or a 2G TKI continued to demonstrate reduced relapse and improved OS with alloHCT (Table 3).9,21,30,31
It is uncertain whether patients who achieve an early, deep MRD response after TKI plus chemotherapy induction still benefit from alloHCT. In the GRAAPH-2005 trial, the benefit of alloHCT could not be confirmed in IM-treated patients who achieved MR3 at an early time point.9 In a Korean study of NIL plus chemotherapy, among patients who achieved an MR5 response there was no difference in relapse based on receipt of alloHCT, although alloHCT was associated with superior survival in multivariable analysis.30
A retrospective multicenter study of 230 patients treated primarily with DAS plus hyper-CVAD showed that among patients who achieved an MR4 response by day 90, there was no improvement in OS (aHR 0.86, p = 0.63) or relapse-free survival (RFS, HR 0.80, p = 0.42) with alloHCT, although cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) was lower (aHR 0.37, p = 0.01) while nonrelapse mortality was higher (aHR 2.29, p = 0.06).32 In contrast, a Japanese study reported that alloHCT was associated with superior RFS and OS among 147 patients who achieved MR5 after 3 months of IM or DAS plus chemotherapy, confirmed by multivariable analysis (OS aHR 0.54, p = 0.04; RFS aHR 0.21, p < 0.001; nonrelapse mortality [NRM], aHR 3.49, p = 0.03; relapse risk aHR 0.10, p < 0.001).33
There are limited data on the benefit of alloHCT in PON-treated patients. MDACC has reported no benefit to alloHCT in the context of PON plus hyper-CVAD, but in their study, alloHCT assignment was at physician discretion, was performed rarely (23%), and occurred late (median of 8 months from diagnosis).14 In contrast, the PONAFIL trial, where PON was combined with chemotherapy followed by alloHCT, has reported excellent outcomes among the 30 enrolled patients, of whom 26 were transplanted (median follow-up 4.1 years, treatment-related mortality 7.6%, 4-year EFS and OS 66% and 92%, respectively).34 The GRAAPH-2024 study will randomize PON-treated patients in CMR to alloHCT or no transplant.
The role of alloHCT in the setting of blinatumomab is also not defined. In the GIMEMA LAL2116 study, approximately one-third of patients (24/63) received alloHCT in CR1, enriched in poor molecular responders. On the other hand, half of patients are in ongoing CR without alloHCT (or chemotherapy).22 In the MDACC ponatinib plus blinatumomab study, only 2 of 60 patients were transplanted.25
In the future, alloHCT is likely to be deployed strategically. For instance, the GRAAPH-2014 trial suggested that alloHCT benefited high-risk patients as defined by high white blood cell (WBC) at diagnosis and poor early MRD response.28
Special concerns: CNS disease, IKZF1 plus, and MRD
Ph+ ALL has a predilection to invade the CNS. Intrathecal (IT) chemotherapy and high-dose chemotherapy (methotrexate and cytarabine) effectively prevent CNS relapse, as highlighted by the very low rate of CNS relapse GRAAPH-2014.28 Relapses among patients treated with chemotherapy-free blinatumomab regimens appear to involve the CNS disproportionately, prompting efforts to intensify CNS prophylaxis in this context (via more IT chemo, and/or integration of chemotherapy, Table 4).35
Ph+ ALL with “IKZF1 plus” genetics is at increased risk for relapse, including in the context of alloHCT,3 PON with chemotherapy,4 and DAS plus blinatumomab.22,23 Clinical outcomes for this group treated with PON plus blinatumomab are not yet known. The ability of alloHCT to decrease risk of relapse is also not known.
A significant minority (up to 40%) of de novo Ph+ ALL (both p190 and p210) is now recognized to have BCR::ABL1 multilineage involvement (“CML-like”), with BCR::ABL1 detected in myeloid cells and mature B and T cells in addition to lymphoblasts.36-39 Patients with multilineage Ph+ ALL do not have inferior outcomes compared with patients with lymphoblast-only Ph+ ALL, but they do have discordant MRD response kinetics (ie, molecular remission by lymphoblast-specific clonal tracking but persistence of BCR::ABL1 MRD).36-38,40 It is now established that MRD response based on clonal tracking of unique B-cell/T-cell receptors (via NGS or quantitative PCR) more accurately predicts risk of relapse.38,40 The long-term malignant potential of persistent BCR::ABL1-positive non-lymphoblast hematopoietic lineages is not known.
Optimizing and answering remaining questions
Ongoing and planned trials are anticipated to help answer remaining questions regarding the role of blinatumomab and alloHCT in Ph+ ALL (Table 4). The ECOG 9181 study allows investigator choice of TKI (DAS or PON) and randomizes patients to blinatumomab or hyper-CVAD after a chemotherapy-free induction; alloHCT is permitted. The GIMEMA LAL2820 study randomizes patients to IM plus chemotherapy versus PON plus blinatumomab, with intensified CNS treatment (15 “triple” IT chemotherapy instillations) and allocates patients to alloHCT based on risk (IKZF1 plus and MRD-based). The GRAAPH-2024 study will treat all patients with PON in combination with blinatumomab alternating with chemotherapy and then randomize patients achieving MRD-negative CR (as assessed by quantitative Ig/TR PCR) to alloHCT or nontransplant therapy.
CLINICAL CASE (continued)
After induction, the patient was consolidated with 2 cycles of DAS, asciminib, and blinatumomab on protocol. After shared decision-making, the patient elected to pursue alloHCT in CR1 given high-risk genetic features. CNS prophylaxis included 12 IT chemotherapy treatments prior to alloHCT.
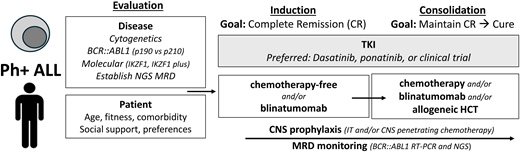
How I treat
My approach to a newly diagnosed patient with Ph+ ALL is summarized in Table 5. Initial evaluation includes assessment of patient comorbidities, values, and social context. Disease assessment includes establishing transcript type (p190 versus p210), interrogating for additional chromosomal and molecular abnormalities (copy number loss of IKZF1, CDKN2A/ CDKN2B, and PAX5), and determining baseline clonal Ig/TCR sequence(s) for NGS MRD monitoring. Whenever possible, I offer a clinical trial.
How I treat newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia
| Diagnostics/evaluation | Patient: Age, fitness/frailty, cardiovascular risk factors, support Disease: Genetic risk: cytogenetic, molecular (IKZF1; IKZF1 plus) MRD monitoring: RT-PCR p190 vs p210; NGS or PCR for clonal tracking |
| When possible, (a) enroll on clinical trial, (b) follow published regimen | |
| Phase: Induction Goal: Complete remission (CR) | TKI: DAS or PON or clinical trial PLUS: Low intensity (steroids, steroids + vincristine, steroids + blinatumomab) |
| Phase: Consolidation Goal: Prolong CR (indefinitely) | TKI: DAS or PON or clinical trial -If DAS, consider change to PON if inadequate response -If PON, dose reduce to 15 mg after achievement of CMR PLUS: 1. TKI alone (if alloHCT planned or palliative goal) 2. Chemotherapy (age adjusted) 3. Blinatumomab (within 3 months) 4. AlloHCT |
| AlloHCT, in CR1 | Favoring yes 1. High-risk genetic features (chromosomes: complex, “double” Ph; IKZF1 plus) 2. No achievement of CMR by 3 months (with TKI+/- chemotherapy) 3. Fit, appropriate donor 4. No blinatumomab available or not tolerated Favoring no 1. No high-risk genetic features 2. Achievement of CMR by 3 months (with TKI+/- chemotherapy) 3. Blinatumomab Unknown 1. Poor response to TKI+/- chemo but CMR with blinatumomab 2. High-risk genetics but optimal MRD response |
| CNS prophylaxis | IT chemotherapy (12-15) High-dose methotrexate and/or cytarabine |
| Monitoring | BCR::ABL1 RT-PCR NGS, to establish presence of CML-like biology, and if present to supplement BCR::ABL1 transcript monitoring |
| Diagnostics/evaluation | Patient: Age, fitness/frailty, cardiovascular risk factors, support Disease: Genetic risk: cytogenetic, molecular (IKZF1; IKZF1 plus) MRD monitoring: RT-PCR p190 vs p210; NGS or PCR for clonal tracking |
| When possible, (a) enroll on clinical trial, (b) follow published regimen | |
| Phase: Induction Goal: Complete remission (CR) | TKI: DAS or PON or clinical trial PLUS: Low intensity (steroids, steroids + vincristine, steroids + blinatumomab) |
| Phase: Consolidation Goal: Prolong CR (indefinitely) | TKI: DAS or PON or clinical trial -If DAS, consider change to PON if inadequate response -If PON, dose reduce to 15 mg after achievement of CMR PLUS: 1. TKI alone (if alloHCT planned or palliative goal) 2. Chemotherapy (age adjusted) 3. Blinatumomab (within 3 months) 4. AlloHCT |
| AlloHCT, in CR1 | Favoring yes 1. High-risk genetic features (chromosomes: complex, “double” Ph; IKZF1 plus) 2. No achievement of CMR by 3 months (with TKI+/- chemotherapy) 3. Fit, appropriate donor 4. No blinatumomab available or not tolerated Favoring no 1. No high-risk genetic features 2. Achievement of CMR by 3 months (with TKI+/- chemotherapy) 3. Blinatumomab Unknown 1. Poor response to TKI+/- chemo but CMR with blinatumomab 2. High-risk genetics but optimal MRD response |
| CNS prophylaxis | IT chemotherapy (12-15) High-dose methotrexate and/or cytarabine |
| Monitoring | BCR::ABL1 RT-PCR NGS, to establish presence of CML-like biology, and if present to supplement BCR::ABL1 transcript monitoring |
The first goal is achieving CR without early toxicity. I recommend a DAS- or PON-based induction without chemotherapy. In choosing a TKI, I consider patient age and comorbidities as well as financial aspects. I initially assess response monthly. For DAS-treated patients who do not achieve a CR after 1 month or a deep MR after approximately 3 months, I escalate to PON. In PON-treated patients, the dose is reduced to 15 mg after achieving CMR.
The second goal is securing a durable remission. I discuss consolidation approaches including conventional chemotherapy, blinatumomab, and/or alloHCT. Treatment with TKI alone is recommended only in the palliative setting. My preferred approach is to introduce blinatumomab after CR and consider alloHCT based on individual characteristics (age, comorbidities, and social circumstances) and disease risk (leukocyte count at presentation, MRD response, and genetic profile). As blinatumomab availability varies by geography and payer mix, it is important to note that excellent outcomes may also be achieved with chemotherapy and alloHCT consolidation. CNS prophylaxis includes IT chemotherapy, with a target of at least 12 treatments.
AlloHCT is a reasonable consolidation option for any fit Ph+ ALL patient but is particularly considered for younger and fit patients with high-risk genetic features, high diagnostic WBC, slow MRD clearance, and/or those who do not tolerate or do not have access to blinatumomab. Patients without high-risk features who achieve a CMR by BCR::ABL1 RT-PCR or NGS after TKI +/- chemotherapy within 3 months of treatment have excellent outcomes, and alloHCT can be reasonably deferred.4,16,22,32 The possibility of multilineage Ph+ ALL should be considered in making transplant decisions based on persistence of BCR::ABL1-determined MRD. The best approach for patients who have a poor response to TKI +/- chemotherapy but achieve CMR with blinatumomab as well as patients who have high-risk features but achieve optimal MRD milestones is less certain, and alloHCT may be considered after individualized discussion.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
Marlise R. Luskin: research funding: AbbVie, Novartis; honoraria: Novartis, Pfizer, Jazz, KITE.
Off-label drug use
Marlise R. Luskin: Nothing to disclose.