Abstract
The role of the hematologist in the management of vascular anomalies is evolving. Several vascular tumors and malformations are associated with complex coagulation derangements. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma or tufted angiomas may present with a consumptive coagulopathy known as the Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon (KMP). The management of KMP is essential to reduce morbidity and mortality from this condition. Slow-flow vascular malformations (SFVM) are also frequently complicated by a coagulopathy requiring anticoagulation, especially during and after surgical procedures, and some of these conditions pose a high risk of venous thromboembolism. Pain in SFVM is also frequently responsive to anticoagulation as well. It is essential for a hematologist with expertise in vascular anomalies to assist in the management of these complex conditions as part of a multidisciplinary team to reduce morbidity and mortality. Through case-based discussions, we attempt to highlight the critical role of the hematologist in managing these anomalies.
Learning Objectives
Diagnose and manage consumptive coagulopathy in the context of vascular anomalies
Manage perioperative care in slow-flow vascular malformations, focusing on anticoagulation to prevent bleeding and VTE
Introduction
The International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies classifies vascular anomalies into 2 broad categories: vascular malformations and vascular tumors. Vascular malformations include both simple and complex malformations of the venous, lymphatic, or arterial vasculature or a combination of these. Vascular tumors include the common infantile hemangiomas as well as more aggressive vascular tumors, such as kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (KHE) and tufted angioma (TA). The full classification system can be found online at https://www.issva.org/UserFiles/file/ISSVA-Classification-2018.pdf.1 Hematologists are often consulted when patients with certain vascular anomalies present with hematologic aberrations or thrombotic or bleeding complications. (Table 1).2 Although almost all are considered congenital lesions, these complications can present early in life in the case of KHE or other congenital hemangiomas or even later in childhood or early adulthood in some cases of vascular malformations. Understanding the underlying anomaly as well as the involved vasculature is very important in risk assessment as well as management of these complex patients.
Simplistic overview of classification schema of vascular anomalies
| Vascular tumors . | Vascular malformations . | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemangioma . | Slow flow . | Fast flow . | Other/unclassified . |
| Infantile Congenital Rapidly involutinga Noninvoluting KHEa TAa | CM VMa LM Macro- or microcystic LM GLA KLAa Combined malformation CVMa CLMa CLVMa VLMa PROSa KTSa CLOVESa | Arteriovenous Arteriovenous fistula | Malformation MLTa |
| Vascular tumors . | Vascular malformations . | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemangioma . | Slow flow . | Fast flow . | Other/unclassified . |
| Infantile Congenital Rapidly involutinga Noninvoluting KHEa TAa | CM VMa LM Macro- or microcystic LM GLA KLAa Combined malformation CVMa CLMa CLVMa VLMa PROSa KTSa CLOVESa | Arteriovenous Arteriovenous fistula | Malformation MLTa |
These conditions can be associated with various types of coagulation derangements.
CLM, capillary-lymphatic malformation; CLOVES, congenital lipomatous (fatty) overgrowth, vascular malformations, epidermal nevi, and scoliosis/ skeletal/spinal anomalies; CLVM, capillary-lymphatic-venous malformation; CM, capillary malformation; CVM, capillary-venous malformation; GLA, generalized lymphatic anomaly; KHE, kaposiform hemangioendothelioma; KLA, kaposiform lymphangiomatosis; KTS, Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome; LM, lymphatic malformation; MLT, multifocal lymphangiomatosis with thrombocytopenia; PROS, PIK3CA-related overgrowth syndrome; TA, tufted angioma; VLM, venous-lymphatic malformation; VM, venous malformation.
Adapted and reprinted from Crary and Mack2 with permission.
CLINICAL CASE 1
A newborn term infant presents at birth with a large, violaceous, firm mass covering most of his right lower thigh. The mass seems to get larger and firmer over the first day of life. On day 2 of life, the baby has some oozing from the heel-stick site and petechiae on his chest. A complete blood count and coagulation studies are obtained and the white blood cell count and hemoglobin level are normal, but the platelet count is 19 000/mm3. D-dimer is elevated to 63.4 mg/L fibrinogen equivalent units (FEU), and fibrinogen is 82 mg/dL. Magnetic resonance imaging is obtained and shows a 4.4 × 6.4 × 6.3 cm ill-defined, vascular, T1 isointense, heterogeneously T2 hyperintense mass. It is decided that it is not safe to proceed with biopsy given the low platelet count and fibrinogen. The patient is presumptively diagnosed with KHE with the Kassabach-Merritt phenomenon (KMP) and started on 2 mg/ kg/d of corticosteroids plus sirolimus (1 mg/m2) twice daily. The infant continues to have oozing from intravenous sites and is transfused with cryoprecipitate. No other bleeding occurs, and the decision is made to forgo transfusing platelets. Over the next 2 weeks, the platelet count slowly increases to 50 000/mm3, and the fibrinogen increases to over 100 mg/dL without further transfusions. The leg mass becomes less violaceous and softer over this same time period. After 4 weeks the platelet count and fibrinogen remain at near normal levels, and the infant is weaned off corticosteroids and continues sirolimus with a goal trough of 5 to 8 ng/mL.
Etiology of KMP
KHE and TA are rare, potentially life-threatening vascular tumors and commonly present in early infancy as a firm, violaceous mass that infiltrates surrounding tissues. It can occur in any part of the body, may be superficial and easily recognized, or may present as an internal mass. KMP is known to occur only with these 2 specific vascular tumors and is seen in up to 70% of cases of KHE.3 KMP is characterized by a severe coagulopathy resulting in usually severe thrombocytopenia (platelet count <50 000/mm3), elevated D-dimer, hypofibrinogenemia with potentially prolonged prothrombin time, and activated partial thromboplastin time.4 The patient may also have significant anemia if bleeding occurs or from red blood cell shearing within the lesion. When associated with KMP, the vascular tumors may rapidly enlarge and become much darker in color and warm to the touch. Patients with KMP and KHE/TA in the abdomen or other internal tissues may have a delayed diagnosis and may only present with pain, a palpable mass, or signs of bleeding due to the coagulopathy. These lesions can be very large and expansive and may be at higher risk for KMP than smaller superficial lesions. Therefore, these vascular tumors should be on the differential of any child presenting with a picture of consumptive coagulopathy of unknown reason. The median age of diagnosis of KHE is about 5 months but is usually earlier in those with KMP than without (50 days vs 293 days).5
The pathophysiology of the coagulopathy in KHE/TA is not well understood. Platelet trapping within the vascular lesion is likely the initiating step. Abnormal lymphatic vessels and microthrombi formation increase sheer stress. This increases platelet activation in a von Willebrand–dependent process and promotes further platelet aggregation, ultimately leading to the activation of coagulation cascade, consumption of factors, and intralesional thrombosis and hemorrhage.6,7
Management of KHE/TA with KMP
The diagnosis of KHE is typically made based on clinical findings along with magnetic resonance imaging or ultrasound findings in a young child with a suspicious lesion. When hematologic abnormalities are present, the diagnosis is urgent, as treatment should be initiated immediately to prevent bleeding morbidity and mortality.8 Although a diagnosis based on histology from a biopsy is the most reliable method of confirmation, in many patients with KMP this is not possible due to the potential for bleeding, as was the case with our patient. When the diagnosis is in question, a biopsy may be safely performed following platelet, fresh frozen plasma, and/or cryoprecipitate administration.
The optimal treatment would be the complete resection of the tumor; however, this is rarely a possibility as most patients have extensive and infiltrative disease. Interventional radiology may attempt arterial embolization in select cases, resulting in shrinkage of the tumor to a degree to improve coagulopathy.9 However, today the mainstay of treatment is medical therapy. The outcomes of various medical therapies are based on observational studies and case series because no randomized clinical trials in KHE have been completed. A recent large retrospective review of KHE revealed that sirolimus has been the most common treatment in the past decade.5 Corticosteroids have been utilized to control KMP but are not generally used as monotherapy.10 When used with vincristine, the outcomes are improved, and more recently sirolimus has become the treatment of choice based on a more favorable side effect profile, although no evidence has shown it to have therapeutic benefits over vincristine.11 Vincristine is still an attractive option for tumors refractory to sirolimus.
Early management of KMP relies heavily on supportive care. Platelet transfusions should only be administered in cases of severe bleeding or before surgical biopsy or resection.8 This caution is due to platelets containing proangiogenic growth factors that could potentially exacerbate vascular lesion growth. Moreover, transfused platelets may become trapped within the lesion, leading to further immediate growth and the activation and consumption of coagulation factors.12 In cases of active bleeding or when fibrinogen levels fall below 100 mg/dL, cryoprecipitate or fresh frozen plasma transfusions are recommended.
Other vascular anomalies with similar presentation
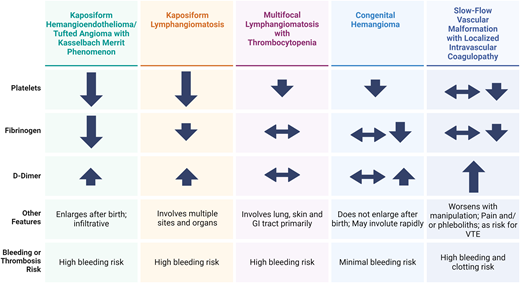
When presented with an infant with a vascular mass and coagulopathy, it should be recognized that other vascular malformations have features that overlap with KHE (Figure 1). Often imaging, knowledge of the clinical course, and histopathology are required to differentiate these conditions. These may include congenital hemangiomas, kaposiform lymphangiomatosis (KLA), and multifocal lymphangioendotheliomatosis with thrombocytopenia (MLT).
Comparison of the clinical features of coagulopathy associated with various vascular anomalies. GI, gastrointestinal. Adapted and reproduced from Mack and Crary28 with permission.
Comparison of the clinical features of coagulopathy associated with various vascular anomalies. GI, gastrointestinal. Adapted and reproduced from Mack and Crary28 with permission.
KLA is an exceedingly rare complex lymphatic anomaly characterized by extensive involvement of the mediastinum, lungs, bones, and abdomen.13,14 Patients with KLA often exhibit severe thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy resembling that seen in KMP. Unlike KHE, corticosteroids typically do not yield a significant improvement in KLA. Distinguishing features include the presence of a somatic activating NRAS mutation, which is absent in KHE.15 Both KLA and KHE exhibit elevated levels of angiopoietin-2, although this biomarker can aid in differentiation from other vascular lesions.16,17 MLT may also present with bleeding and thrombocytopenia with bleeding, originating directly from lesions in the gastrointestinal tract or lungs. D-dimer and fibrinogen are generally normal in MLT.18 Congenital hemangiomas may cause mild consumptive coagulopathy, but it is generally less severe, and these hemangiomas do not continue to grow postnatally, as KHE typically does.19 Large venous malformations may exhibit features of localized intravascular coagulopathy (LIC) with elevated D-dimer levels and, in severe cases, thrombocytopenia and hypofibrinogenemia.20 These should be distinguishable from other vascular anomalies based on imaging and physical exam findings.
CLINICAL CASE 2
A 24-year-old man with a diffuse, multifocal venous malformation of his back, chest wall, and left lower extremity presents due to recurrent left knee swelling and worsening pain. A previous biopsy of the involved tissue on his back revealed a somatic TEK/TIE2 mutation. Imaging of the left leg shows a diffuse venous malformation involving the tissue surrounding the knee as well as some intra-articular involvement and hemarthrosis that have led to degenerative joint disease. He is referred for knee replacement. Prior to that surgery, he undergoes multiple sclerotherapy sessions with interventional radiology to target the venous malformation around his knee joint with good local control. He is known to have a history of consumptive coagulopathy following surgical resection of a malformation on his back 5 years ago that led to significant bleeding postoperatively. He is being managed for chronic pain in his malformation and LIC with rivaroxaban at 10 mg/d. Labs at the time of referral to orthopedics reveal the following: a hemoglobin (Hb) level of 13.2 g/dL, aplatelet count of 82 000/mm3, D-dimer of 18.2 mg/L FEU, and fibrinogen level of 76 mg/dL. He is switched from rivaroxaban to lovenox subcutaneous injections 0.5 mg/kg twice daily for a week, and repeat labs show some improvement: platelet count, 121 000/mm3; D-dimer, 6.4 mg/L FEU; and fibrinogen, 132 mg/dL. The dose of lovenox is increased to 1 mg/kg twice daily with a resultant near- normal platelet count and fibrinogen the day prior to surgery. The D-dimer is still slightly elevated at 3.4 mg/L FEU. The lovenox is held for 24 hours, and the patient undergoes successful knee replacement surgery. His postoperative labs are a bit more concerning for worsening consumption: Hb, 11.4 g/dL; platelet count, 135 000/mm3; fibrinogen, 120 m/dL; and D-dimer, 8.6 mg/L FEU. Lovenox is restarted at treatment dosing. The following morning, his labs have improved, and there is no evidence of bleeding at the surgical site.
Etiology of consumptive coagulopathy in SFVMs
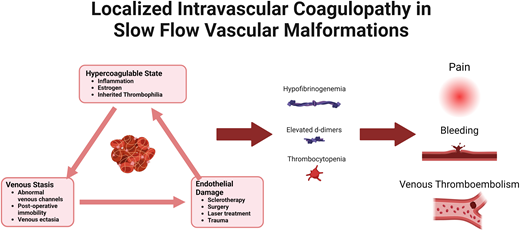
Venous, lymphatic, and capillary malformations are commonly classified as slow-flow vascular malformations (SFVMs), distinguishing them from high-flow malformations that contain arterial components. SFVMs are characterized by sluggish blood flow and dysplastic, valveless veins, leading to phenomena such as platelet entrapment and activation, fibrin deposition, activation of the coagulation cascade, thrombin generation, and consumption of coagulation factors and natural anticoagulants.21-23 LIC describes the consumptive coagulopathy associated with SFVMs. Typically, this consists of elevated D-dimer, and in more severe cases, patients have hypofibrinogenemia, thrombocytopenia, and prolongation of prothrombin time/activated partial thromboplastin time.21,22,24,25 Thrombosis within these abnormal vascular channels can present clinically with pain, warmth, or hard nodules, commonly referred to as phleboliths. Intralesional bleeding may also occur if secondary consumptive coagulopathy is present. An elevation of D-dimer may occur in 40% to 60% of patients with a venous component to their malformation.20,21,26 Hypofibrinogenemia and thrombocytopenia are less common and affect about 10% of patients.20,24 Generally, patients with more extensive or multifocal venous malformations have a higher risk of severe LIC.27
Management of LIC
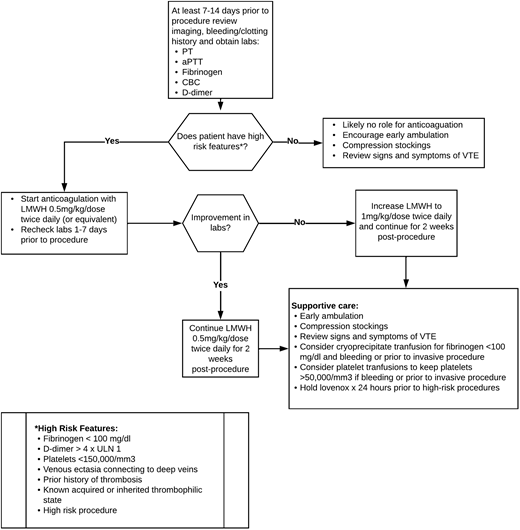
LIC may be spontaneous but is also frequently provoked or worsened by infections, inflammation, immobility, or invasive procedures. Short-term anticoagulation may be utilized to reduce this risk of LIC or VTE progression following procedures.26,28Figure 2 outlines a proposed approach to periprocedural anticoagulation.28 It is important to note that this algorithm is not evidence based, and other institutions may have a variable approach. The D-dimer cutoff for recommendations of periprocedural anticoagulation is not well defined, and D-dimer elevation alone without other features of LIC may not be sufficient to warrant anticoagulation.24,29,30 High-risk features including fibrinogen levels of less than 100 mg/dL, a platelet count of less than 150 000 mm3, venous ectasia, a personal history of thrombosis, known thrombophilia, or the presence of venous ectasia in combination with an elevated D-dimer may indicate a higher risk of VTE complications and may warrant more consideration of anticoagulation.2 It is also important to note that hypofibrinogenemia and thrombocytopenia may be risk factors for bleeding, and supportive care with transfusions of cryoprecipitate and/or platelets may be indicated to reduce the risk of perioperative bleeding. Generally, heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin are the anticoagulants of choice immediately prior to and after procedures.28 Direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs), which have gained popularity for the long-term management of LIC, pain, and VTE risk in patients with vascular malformations due to patient choice and ease of administration, may be used perioperatively in some centers or select cases but may not be as effective in managing the acute complications perioperatively, as we see from case 2.31 It is not recommended to hold the anticoagulation for extended periods perioperatively because this may worsen the underlying LIC, as was seen in our case, and put the patient at further risk of bleeding and/or clotting. This balance is just one of the many reasons a hematologist with expertise in the management of vascular anomalies should be a part of the multidisciplinary team. In patients who lack high-risk features, supportive care may be sufficient. This may also be true with low-risk procedures such as sclerotherapy and laser treatment, especially in a patient with isolated D-dimer elevation.26
Proposed periprocedural management of LIC to reduce risk of VTE. aPTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; CBC, complete blood count; PT, prothrombin time. Reproduced from Mack and Crary28 with permission.
Proposed periprocedural management of LIC to reduce risk of VTE. aPTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; CBC, complete blood count; PT, prothrombin time. Reproduced from Mack and Crary28 with permission.
Anticoagulation for pain in SFVMs
Pain in the vascular malformation is generally multifactorial, resulting from inflammation, cellulitis, intralesional thrombosis or bleeding, venous insufficiency, or other factors. Pain has been reported to respond to anticoagulation, especially if LIC is present or phleboliths are palpated within the painful area.2,32 Some patients may experience an improvement in pain even in the absence of these findings. Some patients have been treated with antiplatelet therapy with varying response, but more recently low-molecular-weight heparin or DOACs are the treatment of choice.31,33 A multi-institutional clinical trial through the Consortium of iNvestigators of Vascular AnomalieS (CaNVAS) was recently completed, and preliminary results showed a decrease in D-dimer and pain scores and an improvement in health-related quality of life after 2 weeks of treatment with a DOAC.34
Risk factors for VTE in VM
The prevalence of VTE in patients with combined vascular malformations, notably those with Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome (KTS); congenital lipomatous (fatty) overgrowth, vascular malformations, epidermal nevi, and scoliosis/skeletal/spinal anomalies; or other conditions under the umbrella of PIK3CA-related overgrowth syndromes (PROS), has been documented to range between 8% and 12.5%, with mortality rates reported between 20% and 50%.27,35,36
One of the most reliable predictors of VTE in patients with PROS is the presence of venous ectasia or persistent embryonic veins.37 Venous ectasia involves veins that are dilated to 2 to 3 times the normal size compared to surrounding veins or the expected vein size for the patient's age. Persistent embryonic veins, which are valveless, may directly drain into deeper veins like the femoral or iliac vein. These often manifest as lateral medial/marginal veins or sciatic veins in PROS, with a varying prevalence up to 60% to 80%.38,39 In a nested case-control study within a larger cohort of KTS patients, in which the incidence of VTE was 32.4%, 3 specific ectatic venous anomalies were independently associated with an increased risk of thrombosis.37 Management of these aberrant veins, either by closure through sclerotherapy or surgical removal, can mitigate the risk of VTE.40 In addition to venous ectasia, a case-control study of 46 patients with SFVMs identified significant increases in VTE risk when the malformation's surface area was 10 cm2 or greater (odds ratio, 6.18), palpable phleboliths were present (OR, 20.17), or D-dimer levels exceeded 500 mg/L (OR, 17.1).27
As discussed in the previous case, the risk of VTE has been shown to be highest following surgical procedures. One study showed that 64% of pulmonary embolisms occurred following surgery or sclerotherapy.41 All procedures do not confer equal risk, with laser and sclerotherapy procedures having lower but not nonexistent risk, especially if venous ectasia is present.26 Conservative treatment with compression garments may also be considered for management of low-risk patients. Other traditional VTE risk factors (eg, obesity, thrombophilia, estrogen) may further increase the risk in patients with vascular malformations, but this has not been well studied.
Conclusion
In summary, the classification and management of vascular anomalies require a comprehensive understanding of their hematologic implications. Early recognition and appropriate intervention are crucial to prevent severe complications such as KMP and VTE. The complexity of these cases necessitates a multidisciplinary approach, involving hematologists-oncologists to optimize patient outcomes. Continued research and collaboration are essential to advance the treatment and understanding of these challenging conditions.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
Shelley E. Crary: Advisory Board: Pfizer, Medexus, Sanofi; consultancy: ASC Therapeutics, Novartis.
Off-label drug use
Shelley E. Crary: Enoxaparin/Lovenox and DOACs are off-label use for vascular malformations.