Abstract
Interferon alpha (IFN-α) is a fascinating molecule with many biological properties yet to be fully understood. Among these properties, several have demonstrated usefulness for targeting malignant cells, including hematopoietic cells from patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms. Indeed, IFN-α has been used for decades across all myeloproliferative neoplasms, but only recently a new form, ropegIFN-α2b, was approved to treat patients with polycythemia vera. Many phase 2 and more recently phase 3 studies have demonstrated IFN-α's promise in treating patients with essential thrombocythemia and early-stage myelofibrosis. In addition, although not approved in that situation, IFN-α is the only cytoreductive therapy that can be used during pregnancy. Today, IFN-α is a key medicine for polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia, while its place in the management of myelofibrosis must be better defined. The advantages of IFN therapy include a well-known safety profile, high rates of clinical and molecular responses, and a unique ability to deeply reduce the mutant allele burden of most of the driver mutations causing myeloproliferative neoplasms. Recent preliminary data from prospective studies suggest that molecular responses may be correlated with prolonged event-free survival, raising the hope that IFN therapy may ultimately alter the natural history of many diseases.
Learning Objectives
Identify the patients who will benefit most from peg-IFN-α treatment
Explain the potential long-term benefits of peg-IFN-α therapy
Define peg-IFN-α treatment objectives and monitoring
CLINICAL CASE
A 64-year-old woman was referred for investigation of an elevated blood count detected during an episode of fatigue and headaches. Her history included arterial hypertension and a deep vein thrombosis 4 years earlier. The clinical examination was normal except for a slight palpable splenomegaly (2 cm). Her blood count showed a hemoglobin level of 20 g/dL, hematocrit of 61.7%, leukocytes of 12.8 × 109/L, and a platelet count of 750 × 109/L. Screening for the JAK2 V617F mutation was positive, with a variant allele frequency (VAF) of 58%, and the serum erythropoietin level was low. These findings led to the diagnosis of polycythemia vera (PV), considered high risk due to the patient's age and history of thrombosis.
Introduction
Interferon (IFN) was the first cytokine discovered in 1957 as a factor secreted by virus-infected cells.1 In humans the IFN family is composed of 7 species defined as type I (or viral), type II (or immune), and type III. Type I IFNs, which include interferon alpha (IFN-α), are involved in antiviral responses as well as in cancer and autoimmune diseases and are the most used in therapy, especially for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs).
The biology of IFN
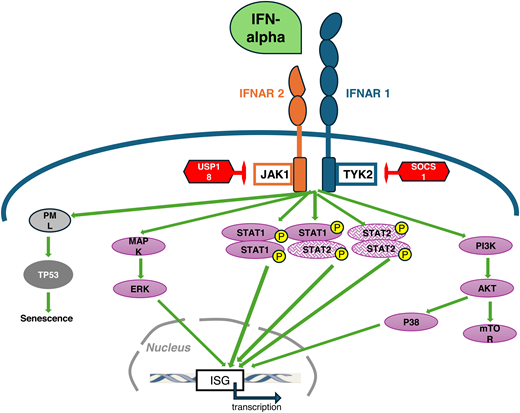
The IFN-α family is composed of 12 different IFN-α subtype proteins, with IFN-α2 the most used in therapy. Interferons have many biological effects, some of which can sometimes be opposing depending on the target cell. For example, they inhibit the proliferation and induce apoptosis of many cell types while they prolong the survival of memory T cells. IFN-α signals via the type I IFN receptor (IFNAR; composed of 2 chains, IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 [Figure 1]). IFNAR lacks intrinsic kinase activity and signals via the Janus kinases (Jak), Jak1, and TYK2 (Figure 1). The canonical activation pathway involves signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins, but alternative pathways have been described, as shown in Figure 1.2,3
Schematic representation of IFN-α receptor signaling. IFN-α receptor (IFNΑR) is composed of the IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 subunits and lacks intrinsic kinase activity, which is compensated by a constitutive association with the Janus tyrosine kinases (Jak) in their cytosolic portion: Tyk2 with IFNAR 1 and Jak1 with IFNAR2. The binding of IFN-α induces a major conformational change of IFNAR that brings Jak1 and Tyk2 in close contact, allowing cross-phosphorylation of the Jaks as the first activating event. The canonical type I IFN signaling pathway relies on the phosphorylation (P) and nuclear translocation of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins, STAT1 and STAT2, that can form homo- or heterodimers. Activated STAT dimers can translocate in the nucleus and ultimately bind to specific sequences within the promoters of IFN-stimulated genes (ISG), leading to their transcription. Alternative pathways have also been identified, involving MAP-kinases and phosphoinositide 3 (PI3)-kinases/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathways. In addition, IFNAR activation can lead to increased number and size of nuclear bodies composed of the promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML). Such enhanced formation of nuclear bodies may drive PML-dependent senescence, a mechanism that can be involved in the elimination of malignant stem cells.41 Negative regulatory molecules that block IFN type I signaling (represented in red) include the ubiquitin-specific peptidase (USP) USP18 and SOCS1 (suppressor of cytokine signaling 1), among others. USP18 binds to IFNAR2 and inhibits the phosphorylation of Jak1 by blocking its interaction with IFNAR2. SOCS1 can directly inhibit Jak1and Tyk2 activity.
Schematic representation of IFN-α receptor signaling. IFN-α receptor (IFNΑR) is composed of the IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 subunits and lacks intrinsic kinase activity, which is compensated by a constitutive association with the Janus tyrosine kinases (Jak) in their cytosolic portion: Tyk2 with IFNAR 1 and Jak1 with IFNAR2. The binding of IFN-α induces a major conformational change of IFNAR that brings Jak1 and Tyk2 in close contact, allowing cross-phosphorylation of the Jaks as the first activating event. The canonical type I IFN signaling pathway relies on the phosphorylation (P) and nuclear translocation of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins, STAT1 and STAT2, that can form homo- or heterodimers. Activated STAT dimers can translocate in the nucleus and ultimately bind to specific sequences within the promoters of IFN-stimulated genes (ISG), leading to their transcription. Alternative pathways have also been identified, involving MAP-kinases and phosphoinositide 3 (PI3)-kinases/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathways. In addition, IFNAR activation can lead to increased number and size of nuclear bodies composed of the promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML). Such enhanced formation of nuclear bodies may drive PML-dependent senescence, a mechanism that can be involved in the elimination of malignant stem cells.41 Negative regulatory molecules that block IFN type I signaling (represented in red) include the ubiquitin-specific peptidase (USP) USP18 and SOCS1 (suppressor of cytokine signaling 1), among others. USP18 binds to IFNAR2 and inhibits the phosphorylation of Jak1 by blocking its interaction with IFNAR2. SOCS1 can directly inhibit Jak1and Tyk2 activity.
Physiological mechanisms involving SOCS1 (suppressor of cytokine signaling 1) and the ubiquitin-specific peptidase 18 (USP18) allow the downregulation of IFN-activated pathways to avoid excessive signaling that can be harmful (Figure 1).1 Indeed, the deregulation of different IFN signaling pathways has been observed in malignancies and autoimmune diseases in which chronic IFN activation can lead to systemic inflammation favoring the development of these conditions.
Properties and therapeutic use of IFN-α in myeloproliferative neoplasms
Several biological properties provided a robust rationale for the use of IFN-α in MPN, including the inhibition of proliferation of hematopoietic progenitors,4-6 disappearance of cytogenetic markers,7 and reversion from monoclonal to polyclonal patterns of hematopoiesis.8 More recent studies confirmed that mutated MPN progenitors could be more sensitive in vitro to IFN-α than their wild-type counterparts, and several animal models confirmed the targeted effect of IFN-α against MPN malignant stem cells.9-13
The first clinical studies showing the efficacy and safety of IFN-α therapy were reported in PV and essential thrombocythemia (ET) in 1988, followed later by studies in primary MF.14-16 Most of the early studies were small phase 2 trials using various commercial forms of IFN-α, but more recently, phase 3 trials have better defined its role in MPN.10,17-19 The development of pegylated forms, which have several advantages, including an enhanced plasma half-life that allows longer intervals between injections and lower toxicity, clearly improved the clinical use of IFN-α. We focus on the currently available pegylated forms, peg-IFN-α2a and ropeginterferon alpha 2b (ropegIFN). Of note, there is no evidence of a different biological activity between the 2a or 2b subtypes of IFN-α in MPN.
Pegylated interferon: who?
In patients with PV
Experts and academic organizations recommend using peg-IFN-α for the treatment of select patients with high-risk PV (Table 1).20-22 Favorable results from phase 3 studies have strengthened its use as a first-line therapy. In the PROUD- CONTINUATION-PV study that compared ropegIFN to hydroxyurea (HU) in a total of 254 patients, long-term follow-up over 6 years showed a clear benefit for patients treated with ropegIFN, including a higher rate of complete hematologic response (CHR, defined by hematocrit below 45% without phlebotomy, a normal white blood cell count, and a normal platelet count) of 54.5% with ropegIFN vs 34.9% with HU, a much greater reduction in the JAK2 V617F VAF to a median of 8.5% with ropegIFN vs 50.4% with HU, and a significantly higher probability of event-free survival (including thromboembolic events, disease progression to MF or acute leukemia, or death) in the ropegIFN treatment arm compared with the control treatment group (0.94 vs 0.82; log-rank test; P = .04).23 Risk events occurred in 5 out of 95 patients (5.3%) in the ropegIFN arm compared with 12 out of 74 patients (16.2%) in the control arm. Another phase 3 study compared peg-IFN-α2a to HU in a smaller number of treatment-naive patients with PV (n = 87).24 After 12 months of treatment, comparable CHR rates were observed (30% with HU, 28% with peg-IFN). Of note, the median JAK2 V617F VAF decreased consistently from baseline through month 24 in the peg-IFN arm but increased in the HU arm after month 12. Finally, in a recent review and meta-analysis of IFN treatment in patients with PV, the CHR rate was estimated at 49%.19
PegIFN in MPN: who and why
| MPN subtype . | Target population . | Why . | FDA/EMA approval . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polycythemia vera | High-risk first line | • High rate of CHR • High rate of MR • Possible EFS improvement | Yes/yes Only for ropegINF-α2b |
| High-risk second line | • High rate of CHR • High rate of MR • Possible EFS improvement | Yes/yes Only for ropegINF-α2b | |
| Low risk | In only 1 study, compared to PHL + ASA: • Higher rate of CHR • Improvement in symptoms • Higher rate of MR | Yes/yes Only for ropegINF-α2b | |
| Pregnancy | • Reduced risk of miscarriage • Improved maternal and fetal outcomes | No/no | |
| Essential thrombocythemia | High-risk first line | • High rate of CHR • High rate of MR | No/no |
| High-risk second line | • High rate of CHR • High rate of MR | No/no Ongoing phase 3 studies with ropegINF-α2b | |
| Pregnancy | • Reduced risk of miscarriage • Improved maternal and fetal outcomes | No/no | |
| Myelofibrosis | Low risk and early stage (splenomegaly <6 cm BCM, no grade 3 fibrosis) | • Possible resolution of fibrosis • Possible MR | No/no Ongoing phase 2 studies with ropegINF-α2b |
| Prefibrotic myelofibrosis | • Possibly avoid disease progression to overt myelofibrosis | No/no Ongoing phase 2 studies with ropegINF-α2b |
| MPN subtype . | Target population . | Why . | FDA/EMA approval . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polycythemia vera | High-risk first line | • High rate of CHR • High rate of MR • Possible EFS improvement | Yes/yes Only for ropegINF-α2b |
| High-risk second line | • High rate of CHR • High rate of MR • Possible EFS improvement | Yes/yes Only for ropegINF-α2b | |
| Low risk | In only 1 study, compared to PHL + ASA: • Higher rate of CHR • Improvement in symptoms • Higher rate of MR | Yes/yes Only for ropegINF-α2b | |
| Pregnancy | • Reduced risk of miscarriage • Improved maternal and fetal outcomes | No/no | |
| Essential thrombocythemia | High-risk first line | • High rate of CHR • High rate of MR | No/no |
| High-risk second line | • High rate of CHR • High rate of MR | No/no Ongoing phase 3 studies with ropegINF-α2b | |
| Pregnancy | • Reduced risk of miscarriage • Improved maternal and fetal outcomes | No/no | |
| Myelofibrosis | Low risk and early stage (splenomegaly <6 cm BCM, no grade 3 fibrosis) | • Possible resolution of fibrosis • Possible MR | No/no Ongoing phase 2 studies with ropegINF-α2b |
| Prefibrotic myelofibrosis | • Possibly avoid disease progression to overt myelofibrosis | No/no Ongoing phase 2 studies with ropegINF-α2b |
ASA, aspirin; BCM, below costal margin, EFS, event-free survival; EMA, European Medicine Agency; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; PHL, phlebotomy.
More recently, it was suggested that a subset of patients with low-risk PV could benefit from ropegIFN therapy, based on the positive results of a study that randomized phlebotomy and aspirin vs the same strategy plus a fixed low dose (100 mcg/ 2 wk) of ropegIFN in a total of 127 patients.25 The addition of ropegIFN to standard treatment resulted in a significantly higher rate of hematocrit control below 45% without disease progression, more complete hematologic responses, improvement in symptoms, and reduction in JAK2 V617F VAF after 12 and 24 months of treatment. This study has some limitations (small number of patients and short follow-up) and should be confirmed in a larger population of low-risk patients with longer follow-up to assess the relevance of these results.
In patients with ET
Only 1 clinical study randomized peg-IFN-α2a vs HU in 81 treatment-naive patients with high-risk ET.24 The proportion of patients in CHR at 12 months was comparable, 45% for HU and 44% for peg-IFN. Too few events were observed in the relatively short follow-up period to see any difference between the 2 treatment arms.
A systematic review and meta-analysis analyzed the results reported from 30 clinical studies of IFN (peg and nonpeg) in 730 patients with ET.19 The CHR rate was 59%, and the rate of thromboembolic complications was low, 1.2% per patient-year. Only 2 studies reported the rate of complete and partial molecular response (MR) for the JAK2 V617F mutation, which were 26% and 90%, respectively. One study included only patients with calreticulin (CALR) mutations, showing that IFN-α could also target this driver mutation with a decrease of mutant CALR VAF from 41% to 26% after treatment, including in 2 patients who achieved complete MR.26,27 Phase 3 studies testing ropegIFN are ongoing in patients with ET resistance or intolerance to other available therapies, including a randomized study with anagrelide (NCT04285086), which will better define the role of this form of IFN in ET.28
In patients with myelofibrosis
Far fewer studies are available to assess the role of IFN in myelofibrosis (MF). In early stages with a low grade of fibrosis, some studies showed a benefit in terms of the reduction of bone marrow fibrosis.29 Another study found that a spleen enlargement of more than 6 cm below the costal margin was the only independent factor associated with IFN treatment failure.16 In line with these data, peg-IFN is only recommended for the treatment of lower-risk symptomatic MF in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines.30 RopegIFN is also currently being tested in early stage, low-risk MF and n patients with prefibrotic MF in phase 2 studies (NCT04988815, NCT05731245).
A meta-analysis found 10 studies of IFN that included a total of 141 patients with MF.18 The overall response rate was 49.9% with an objective spleen size reduction in 20% to 67% of patients when reported. There were too few data available to properly evaluate bone marrow histopathology changes or MR. Similarly, the reporting of adverse events was inconsistent, making it difficult to assess tolerance. However, the reported discontinuation rate was 0.5% per year with peg forms and 35.8% with nonpeg IFNs.
Pregnancy
In younger women who wish to become pregnant, only IFN-α can be used as cytoreductive therapy when needed, although it is not approved in this situation.31-33 In addition to low-dose aspirin (and low-molecular-weight heparin in certain circumstances), IFN-α can be used before pregnancy to reduce the risk of miscarriage in patients with prior maternal or fetal pregnancy complications and in patients with thrombocytosis above 1000 × 109/L. During pregnancy, blood counts spontaneously decrease, and we propose using the minimal dose of IFN-α necessary to maintain platelets below 600 × 109/L and hematocrit below 45% by monitoring blood counts and injecting IFN-α only when these thresholds are exceeded. After delivery, platelets can rebound, and careful monitoring of blood counts is necessary during the first 6 weeks. Because of very low levels in milk and poor oral absorption, it is unlikely that interferon use by a nursing mother presents any serious risk to the breastfed infant (see Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed).34
Pegylated interferon: why?
In addition to the high rates of clinical and hematological responses discussed above, there are other potential benefits in favor of IFN therapy. First, to date IFN is the treatment capable of reducing the myeloproliferative malignant clone the most quickly and deeply, as measured by the reduction of the allele burden of the driver mutation.35 In a phase 3 randomized study, the median JAK2 V617F VAF decreased from 37.3% to 8.5% after 5 years of treatment with ropegIFN, compared to an increase from 38.1% to 44.4% in the control arm (88% treated with HU).36 In addition, the JAK2 V617F VAF decreased below 1% in 19.6% of patients treated with ropegIFN, compared with only 1.4% in the control arm. Such long-term deep MR cannot be achieved with HU but can be observed with ruxolitinib: in a more advanced population of PV patients previously intolerant or resistant to HU, a randomized study found that 56% of patients treated with ruxolitinib had more than 50% reduction of JAK2 V617F VAF on the long term.37
The clinical relevance of these MRs has been long debated. In the MAJIC-PV study, a rapid JAK2 V617F MR at 12 months was associated with improved event-free survival (events occurred in 24% of molecular responders vs 43% of nonresponders), providing the first evidence of a major clinical benefit for patients who achieve MR. Similar significantly improved event-free survival in patients with MR was also very recently reported in patients treated with ropegIFN, with risk events observed in 3.8% of patients with MR compared with 15.7% of patients with no MR.38
In addition to these prospective studies data, 2 retrospective studies provided evidence for better outcomes in patients with MPN treated with IFN. In high-risk PV, a single-center retrospective study found that the 20-year myelofibrosis-free survival (MFS) was 89% in patients treated with IFN compared to 41% for those treated with HU. In this population, the 20-year overall survival was 66% for IFN compared to 40% for HU. Similarly, better MFS in patients treated with IFN was reported in a retrospective international study of 348 adolescents and young adults with ET and PV diagnosed before the age of 25.39 In this very young population, 20-year MFS was 100% with IFN, 74% for HU, and 74% for patients who received no cytoreductive therapy.
Finally, as has been reported in chronic myeloid leukemia, it seems possible to achieve treatment-free remission after IFN-α therapy. In a retrospective study of 381 patients treated with IFN-α with a median follow-up of 72.4 months, we found that 66.9% of the 250 patients who discontinued therapy were in CHR and that the probability of maintaining CHR without further treatment was significantly higher in patients who had achieved at least 2 years of CHR and had a JAK2 V617F VAF below 10% before stopping IFN-α.40
CLINICAL CASE (continued)
Treatment with ropegIFN was started at 100 µg/2 wk and progressively increased to 400 µg/2 wk. CHR was achieved after 4 months, and the spleen was no longer palpable. No clinical adverse effects were reported. A slight elevation of liver enzymes was observed after 4 weeks and resolved after 3 months without treatment modification. Antinuclear antibodies were detected in 1 out of 80 patients after 6 months, were asymptomatic, and remained stable over time. Due to a durable CHR, ropegIFN doses were gradually reduced to 300 µg/2 wk at 12 months and 250 µg/4 wk after 24 months. Molecular follow-up showed that the JAK2 V617F VAF decreased to 28% at 12 months, 14% at 2 years, and 7% at 5 years.
Pegylated interferon: how?
A key concern about the use of IFN is tolerance. Its toxicity profile is perfectly documented (extensively described in reference) and has not change in nature with time and the development of new pharmaceutical formulations.1 In contrast, the development of pegylated forms has clearly improved tolerance, and the latest monopegylated formulation, ropegINF, seems to further reduce the incidence of several IFN-related common side effects such as flu-like symptoms, musculoskeletal pain, and endocrine or psychiatric complications.23 Still, careful research on the possible contraindications must be performed before treatment initiation (Table 2). During treatment any potential toxicities should also be regularly monitored and include liver tests and screening for autoantibodies.
How I use peg-IFN-α in practice
| . | Safety . | Efficacy . |
|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | • Exclusion of contraindications (per drug label) • Search for potential cardiac or ophthalmologic abnormalities • Screen for autoimmunity (at least antinuclear Ab) and TFT | • Measure spleen size by echography • Assess driver mutation allele burden • If possible screen for additional mutations by NGS |
| Treatment initiation | • Start at low dose | • Titration until CHR |
| peg-IFN-α2a | 45 µ/wk | By 45 µ/2wk Max dose 180 µ/wk |
| ropegIFN-α2b | 100 µ/2wk | By 50 µ/2wk Max dose 500 µ/2wk |
| Monitoring during treatment | • Screen for mood disturbances, thyroid dysfunction, type 1 diabetes • CBC/mo • LFT, TFT/6 mo | • CBC/mo • Spleen size and mutation/y |
| Dose adjustments | According to potential toxicities | Progressive decrease after 1 year in case of lasting CHR |
| pegIFN-α2a | By 45 µ per injection every 6 months down to 45 µ/wk, then by expanding interval to every 2wk | |
| ropegIFN-α2b | By 50 µ per injection every 6 months down to 100 µ/2wk, then by expanding interval to every 4wk | |
| Discontinuation | In case of intolerance | In patients with at least 2 years of continuous CHR on IFN and JAK2 V617F VAF <10% |
| . | Safety . | Efficacy . |
|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | • Exclusion of contraindications (per drug label) • Search for potential cardiac or ophthalmologic abnormalities • Screen for autoimmunity (at least antinuclear Ab) and TFT | • Measure spleen size by echography • Assess driver mutation allele burden • If possible screen for additional mutations by NGS |
| Treatment initiation | • Start at low dose | • Titration until CHR |
| peg-IFN-α2a | 45 µ/wk | By 45 µ/2wk Max dose 180 µ/wk |
| ropegIFN-α2b | 100 µ/2wk | By 50 µ/2wk Max dose 500 µ/2wk |
| Monitoring during treatment | • Screen for mood disturbances, thyroid dysfunction, type 1 diabetes • CBC/mo • LFT, TFT/6 mo | • CBC/mo • Spleen size and mutation/y |
| Dose adjustments | According to potential toxicities | Progressive decrease after 1 year in case of lasting CHR |
| pegIFN-α2a | By 45 µ per injection every 6 months down to 45 µ/wk, then by expanding interval to every 2wk | |
| ropegIFN-α2b | By 50 µ per injection every 6 months down to 100 µ/2wk, then by expanding interval to every 4wk | |
| Discontinuation | In case of intolerance | In patients with at least 2 years of continuous CHR on IFN and JAK2 V617F VAF <10% |
Ab, antibodies; CBC, complete blood count; LFT, liver function tests; NGS, next-generation sequencing; TFT, thyroid function tests.
Tolerance is a key issue since the full benefits of IFN therapy occur after long exposure to the drug. Therefore, we suggest starting at a low dose and titrate to achieve CHR because most adverse reactions occur during the first weeks and decrease with chronic exposure. The prophylactic use of paracetamol for 1 to 2 days after the first couple of injections may be proposed to reduce the occurrence of flu-like symptoms and musculoskeletal pain. The starting dose is usually 45 µ/wk for peg-IFN-α2a and 100 µ/2 wk for ropegIFN (Table 2).
Once CHR is reached and stable, one can consider a progressive dose reduction every 6 months. If CHR persists for at least 2 years at very low doses, it may be possible to discuss stopping treatment once a good MR is achieved (JAK2 V617F VAF at least below 10%).40
CLINICAL CASE (continued)
RopegINT treatment was stopped after 5 years, and the patient was still in CHR without cytoreductive treatment after 2 years of follow-up. The JAK2 V617F mutation was still detectable, fluctuating between 1% and 5%, and the antinuclear autoantibodies disappeared.
Conclusion
IFN-α has been used to treat MPNs for decades with good hematological efficacy, in particular in patients with PV and ET. Adverse effects are clearly an issue, but the development of pegylated forms and further improvement with monopegylation have greatly improved tolerance for the treatment and allowed more patients to be treated for longer periods. As a result, new advantages have been demonstrated compared to other available cytoreductive treatments. The first is the specific targeting of the myeloproliferative clone, as clearly demonstrated by the high rate of rapid and deep MRs for driver mutations. More recently, 2 prospective studies have shown that MR could provide a clinical benefit in terms of improved long-term event-free survival. Finally, in patients achieving both a CHR and a deep and stable MR, treatment discontinuation may be considered with the possibility of treatment-free remission.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
Jean-Jacques Kiladjian: advisory board: Novartis, GSK, AOP Orphan, Incyte, PharmaEssentia, Bristol Myers Squibb; consultancy: Novartis, GSK, AbbVie; travel grants: Novartis.
Off-label drug use
Jean-Jacques Kiladjian: This review discusses the off-label use of interferon alpha in essential thrombocythemia and myelofibrosis.