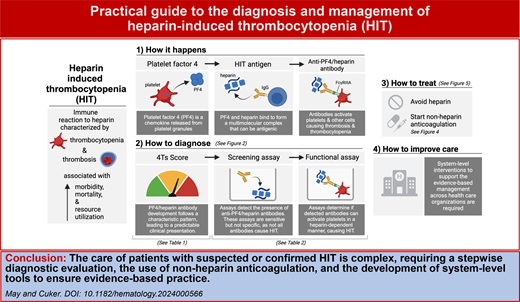
Abstract
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is an immune reaction to heparin associated with thrombocytopenia, thrombotic risk, and a high risk of morbidity and mortality. Given the frequent use of heparin and the common occurrence of thrombocytopenia in hospitalized patients, the diagnosis and management of HIT is a recurrent challenge in everyday inpatient care. This article presents practical guidance and tools to support the individual clinician providing evidence-based care to patients with suspected or confirmed HIT. The optimal diagnostic evaluation requires the stepwise use of risk-stratification tools and laboratory assays. Management requires the selection and use of nonheparin anticoagulation in these complex patients with both increased thrombotic risk and possible concurrent increased bleeding risk due to thrombocytopenia. Each step in the diagnostic and management process has important nuances and complexities, many of which vary based on patient characteristics and institutional resources. Given the many challenges of HIT care, truly practical management is best achieved when tools are implemented to support the delivery of consistent, high quality, and cost-effective care across health systems.
Learning Objectives
Perform an evidence-based, stepwise diagnostic evaluation of patients with concern for HIT
Select optimal non-heparin anticoagulation for patients with suspected and confirmed HIT
Identify system-level interventions to support delivery of consistent, high-quality care across health systems
Introduction
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a rare immune reaction to heparin exposure that results in thrombocytopenia and increased thrombotic risk. It is estimated to affect 1 in 1500 hospitalizations per year and is associated with increased morbidity, mortality, and health care utilization.1
HIT occurs when heparin and platelet factor 4 (PF4) form an antigenic, multimolecular complex, resulting in the production of PF4/heparin immunoglobulin G (IgG) (Visual Abstract). These antibodies activate platelets via Fc receptor (Freia) binding, also interacting with other cell types to cause thrombocytopenia and thrombosis.
Diagnosis is complex, requiring a series of steps including clinical probability assessment and nuanced laboratory assays. Management is complex as well, as treatment requires high-risk anticoagulants in patients who may also have an increased risk of bleeding on account of the thrombocytopenia. This leads to challenges in care beyond an individual patient-provider level, as health systems struggle to provide consistent, evidence-based care for suspected and confirmed HIT.
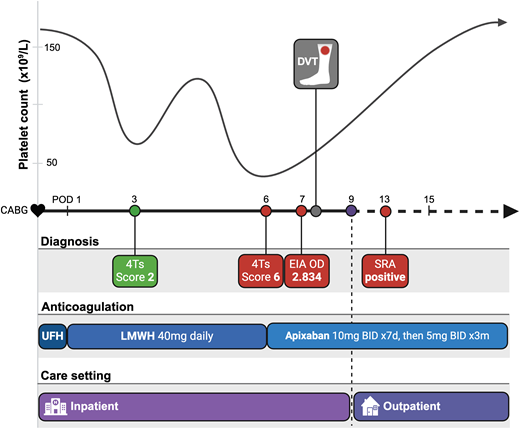
In this article, we review the foundational principles of the diagnosis and management of HIT, highlighting common pitfalls as well as published successes to support clinicians in the delivery of evidence-based care. Our discussion is based around a single case, with a time line of events presented in Figure 1.
Clinical case time line. The case begins with CABG and chronicles major events thereafter. The platelet count over time, with a classic “biphasic” pattern, is illustrated above the time line. Events in the diagnostic process are highlighted in green when less consistent with HIT and in red when more concerning for HIT. Assay results are indicated on the day results are returned; both EIA and SRA were collected on POD 6. The anticoagulation use across time is presented, with each agent highlighted in a unique shade of blue. The length of the shade illustrates the duration of that anticoagulant along the time line. The care setting indicates when the patient was hospitalized and discharged relative to the time line. BID, twice daily; DVT, deep vein thrombosis; LMWH, low-molecular-weight heparin; m, month; UFH, unfractionated heparin.
Clinical case time line. The case begins with CABG and chronicles major events thereafter. The platelet count over time, with a classic “biphasic” pattern, is illustrated above the time line. Events in the diagnostic process are highlighted in green when less consistent with HIT and in red when more concerning for HIT. Assay results are indicated on the day results are returned; both EIA and SRA were collected on POD 6. The anticoagulation use across time is presented, with each agent highlighted in a unique shade of blue. The length of the shade illustrates the duration of that anticoagulant along the time line. The care setting indicates when the patient was hospitalized and discharged relative to the time line. BID, twice daily; DVT, deep vein thrombosis; LMWH, low-molecular-weight heparin; m, month; UFH, unfractionated heparin.
CLINICAL CASE
A 65-year-old man is admitted for coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). He underwent a left heart catheterization 2 weeks prior for which he did not receive heparin. CABG was performed with intraoperative unfractionated heparin. On postoperative day (POD) 1, he received enoxaparin at 40 mg/d for the prevention of venous thromboembolism. His platelet count was normal preoperatively and declined to 60 × 109/L on POD 3. Providers were concerned that the patient had HIT.
The complexity of HIT begins even before a clinician considers the diagnosis. Thrombocytopenia is common in hospitalized patients and is rarely due to HIT,2 so the diagnosis is considered more often than it is made. Furthermore, because thrombocytopenia is common, HIT may be overlooked, and a diagnosis may be missed or delayed. With a combined daily risk of thrombosis, amputation, and/or death of 6.1 % if left untreated,3 any misstep in the diagnostic process can have significant clinical consequences.
Diagnostic algorithm
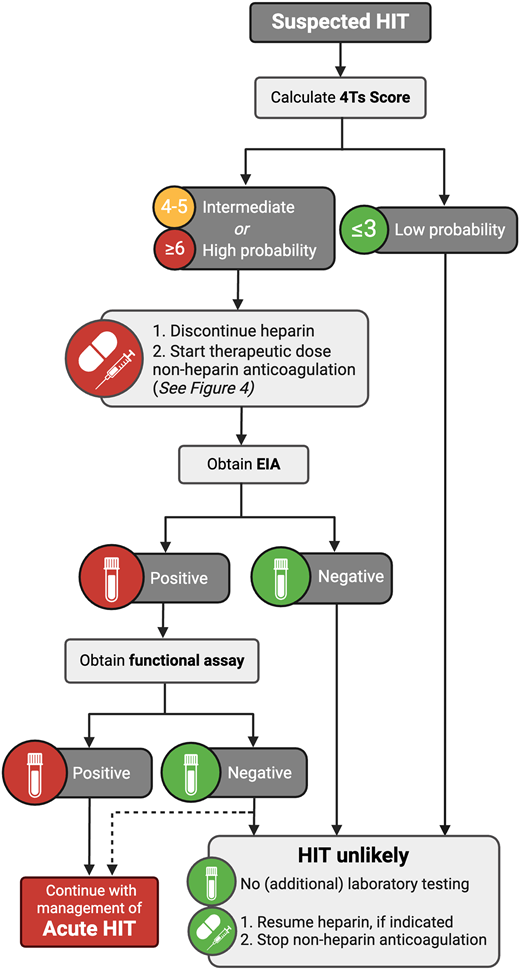
When a provider is concerned about HIT, available guidelines recommend a stepwise diagnostic approach, starting with a risk prediction score and only proceeding with laboratory testing in patients with a calculated increased risk (Figure 2).4,5 Importantly, although this algorithm is evidence based and well accepted as best practice, its real-world performance may be suboptimal, with ongoing challenges leading to both diagnostic delay and overtreatment.6
If there is clinical concern for HIT, the 4Ts Score is the most widely used and well-validated risk-prediction score and has excellent negative predictive value (0.998; 95% CI, 0.970-1.000).7 It includes 4 components, each of which assigns a point value based on defined criteria (Table 1). Unfortunately, the 4Ts Score can be challenging to calculate, and scoring may vary significantly between providers.8Table 1 presents tips and common pitfalls for calculating each of the components of the 4Ts Score. The HEP Score is another available risk prediction score, with a reported negative predictive value of 1.00 (95% CI, 0.84-1.00),7 which may perform better than the 4Ts score in trainees and those with less experience with HIT diagnosis.9
4Ts Score with tips and tricks
| 4Ts Score Component . | Tips and tricks . |
|---|---|
| Thrombocytopenia 2: Platelet count fall >50% and nadir ≥20 1: Platelet count fall 30%-50% or nadir 10-19 0: Platelet count fall <30% or nadir <10 | Calculate using the peak platelet count after heparin was started. |
| Patients do not have to be thrombocytopenic to earn points. If the peak platelet count is high enough, the platelet count can decline significantly to meet score criteria and still be in the normal range. | |
| Timing of platelet count fall 2: Clear onset between days 5-10 or fall ≤1 day (prior heparin exposure within 30 days) 1: Consistent with days 5-10 fall but not clear; onset after day 10 or fall ≤1 day (prior heparin exposure 30-100 days ago) 0: Fall <4 days without recent exposure | Calculate based on the first day of consistent platelet count fall. |
| In cardiovascular surgery, platelet count fall is often “biphasic,” where the platelet count declines due to surgery, rebounds, and then declines again due to HIT (Figure 1). | |
| A fall ≤1 day after heparin exposure is due to preformed anti-PF4/heparin antibodies that continue to circulate after a recent heparin exposure. A fall after 5 days occurs because that is the time it takes to develop new IgG antibodies after heparin exposure. | |
| Thrombosis or other sequelae 2: New thrombosis or skin necrosis; acute systemic reaction post-IV heparin bolus 1: Progressive or recurrent thrombosis; nonnecrotizing skin lesions, suspected thrombosis (not proven) 0: None | Points only for thrombosis that occurs or progresses after heparin exposure and while the platelets are declining (or shortly before), not thrombosis that occurred well before heparin exposure and platelet decline. |
| Other causes of thrombocytopenia 2: None apparent 1: Possible 0: Definite | This variable most frequently contributes to interprovider variation.8 Consider using the other causes of thrombocytopenia included in the HEP Score39 as a guide: chronic thrombocytopenia, newly initiated nonheparin medication known to cause thrombocytopenia, severe infection, severe DIC, indwelling intra-arterial device, CPB within 96 hours. |
| 4Ts Score Component . | Tips and tricks . |
|---|---|
| Thrombocytopenia 2: Platelet count fall >50% and nadir ≥20 1: Platelet count fall 30%-50% or nadir 10-19 0: Platelet count fall <30% or nadir <10 | Calculate using the peak platelet count after heparin was started. |
| Patients do not have to be thrombocytopenic to earn points. If the peak platelet count is high enough, the platelet count can decline significantly to meet score criteria and still be in the normal range. | |
| Timing of platelet count fall 2: Clear onset between days 5-10 or fall ≤1 day (prior heparin exposure within 30 days) 1: Consistent with days 5-10 fall but not clear; onset after day 10 or fall ≤1 day (prior heparin exposure 30-100 days ago) 0: Fall <4 days without recent exposure | Calculate based on the first day of consistent platelet count fall. |
| In cardiovascular surgery, platelet count fall is often “biphasic,” where the platelet count declines due to surgery, rebounds, and then declines again due to HIT (Figure 1). | |
| A fall ≤1 day after heparin exposure is due to preformed anti-PF4/heparin antibodies that continue to circulate after a recent heparin exposure. A fall after 5 days occurs because that is the time it takes to develop new IgG antibodies after heparin exposure. | |
| Thrombosis or other sequelae 2: New thrombosis or skin necrosis; acute systemic reaction post-IV heparin bolus 1: Progressive or recurrent thrombosis; nonnecrotizing skin lesions, suspected thrombosis (not proven) 0: None | Points only for thrombosis that occurs or progresses after heparin exposure and while the platelets are declining (or shortly before), not thrombosis that occurred well before heparin exposure and platelet decline. |
| Other causes of thrombocytopenia 2: None apparent 1: Possible 0: Definite | This variable most frequently contributes to interprovider variation.8 Consider using the other causes of thrombocytopenia included in the HEP Score39 as a guide: chronic thrombocytopenia, newly initiated nonheparin medication known to cause thrombocytopenia, severe infection, severe DIC, indwelling intra-arterial device, CPB within 96 hours. |
Each of the 4 components of the 4Ts Score are listed: thrombocytopenia, timing of platelet count fall, thrombosis and other sequelae, and other causes of thrombocytopenia. The point value and its corresponding criteria are listed below each component. In the column to the right of each component are tips and tricks to inform accurate calculation. A total score of 0-3 corresponds with a low risk, 4-5 with an intermediate risk, and ≥6 with a high risk of HIT.
Deviation from the recommended diagnostic algorithm occurs, as clinicians may proceed straight to laboratory testing without risk stratification. This can lead to the unnecessary use of laboratory resources as well as adverse clinical events associated with unnecessary heparin cessation or the use of nonheparin anticoagulation.10,11 There are many published efforts to provide clinical decision support (eg, order sets, clinical pharmacist order review) and/or require 4Ts Score calculation prior to laboratory ordering, but they have been implemented with mixed success.12 Multiple factors may contribute to the lack of evidence-based diagnostic evaluation, including provider time constraints and a lack of confidence in the individual ability to accurately calculate the 4Ts Score. Creative solutions to address this problem have been developed, such as a modified 4Ts Score that can be completely computer calculated and a machine-learning model that also incorporates screening assay results.13,14
HIT diagnosis in patients after cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) poses additional challenges. The incidence of HIT after CPB is approximately 0.5% to 2%,15 but anti-PF4/heparin antibodies are detectable in 20% to 50% of patients.16,17 Therefore, 4Ts Score calculation is even more important due to the high incidence of false-positive screening assays. The platelet count trajectory can be a helpful diagnostic clue, as patients with HIT after CPB typically demonstrate a “biphasic” pattern, in which the platelet count initially declines due to surgery, rebounds, and then declines again due to HIT (Figure 1). A continuous platelet count decline after CPB is unlikely to be due to HIT.18
CLINICAL CASE (continued)
The 4Ts Score was calculated to be 2. Given the low clinical probability of HIT, laboratory testing was not ordered, and enoxaparin prophylaxis was continued. The platelet count improved to 135 × 109/L on POD 5, but on POD 6 the platelet count again declined to 52 × 109/L. The 4Ts Score was calculated to be 6. Heparin was stopped, and apixaban at 10 mg twice daily was started. Laboratory testing for HIT was requested. An enzyme immunoassay (EIA) returned positive, with an optical density (OD) of 2.834.
Laboratory assays
Laboratory assays for HIT are best understood based on their connection to disease pathophysiology. Screening assays are obtained first and determine if anti-PF4/heparin antibodies are present. Next, functional assays determine if those antibodies have the ability to activate platelets in a heparin-dependent manner. This stepwise diagnostic algorithm exists because of the limitations of available laboratory testing. Screening assays are sensitive but not specific, while functional assays are specific but resource-intensive with limited availability (ie, at most institutions they require “send-out” to a reference laboratory with a long turnaround time). Because multiple assay options exist within these 2 categories, it is paramount that clinicians understand the diagnostic assays available at their institutions. Table 2 presents helpful questions to discuss with a coagulation laboratory to ensure provider understanding of the assays used in their personal practice.
Getting to know your institution's HIT assays
| Assay type . | What questions should you ask your coagulation laboratory? . | Why is it important to know? . |
|---|---|---|
| Screening assay(s) | Which assay(s) do we use to screen for HIT? | Many options exist. EIAs are the prototypical immunoassay. Rapid immunoassays also exist. |
| What is the sensitivity and specificity of our assay(s)? | Every assay has unique performance characteristics. Understanding the performance characteristics of an assay is essential in clinical risk prediction. | |
| If we have access to an EIA, tell me more about it: Do we report the OD? Is it IgG specific or not? | The likelihood of HIT increases with a higher OD. Specificity is higher with an IgG-only EIA. | |
| What is the turnaround time of our assay(s)? | Some assays take minutes to run; some take hours. Some labs batch samples so results can take days to return. Knowing when to expect results can help inform management. | |
| Functional assay(s) | Which assay(s) do we use? | Options exist, although fewer than screening assays. SRA is considered the “gold standard,” but others exist, including HIPA and PEA. |
| Do we use laboratory techniques to remove any residual heparin from the sample prior to performing the assay? | Residual heparin can interfere with assay performance. If not removed, additional care must be taken to ensure the sample is collected at least 1 hour after heparin is stopped. | |
| What is the sensitivity and specificity of our assay(s)? | Every assay has unique performance characteristics. Even within assay classes, performance can vary by lab. Understanding the performance characteristics of an assay is essential in clinical risk prediction. | |
| What is the turnaround time of our assay(s)? | Most institutions do not run functional assays in-house. Knowing when to expect results can help inform management. |
| Assay type . | What questions should you ask your coagulation laboratory? . | Why is it important to know? . |
|---|---|---|
| Screening assay(s) | Which assay(s) do we use to screen for HIT? | Many options exist. EIAs are the prototypical immunoassay. Rapid immunoassays also exist. |
| What is the sensitivity and specificity of our assay(s)? | Every assay has unique performance characteristics. Understanding the performance characteristics of an assay is essential in clinical risk prediction. | |
| If we have access to an EIA, tell me more about it: Do we report the OD? Is it IgG specific or not? | The likelihood of HIT increases with a higher OD. Specificity is higher with an IgG-only EIA. | |
| What is the turnaround time of our assay(s)? | Some assays take minutes to run; some take hours. Some labs batch samples so results can take days to return. Knowing when to expect results can help inform management. | |
| Functional assay(s) | Which assay(s) do we use? | Options exist, although fewer than screening assays. SRA is considered the “gold standard,” but others exist, including HIPA and PEA. |
| Do we use laboratory techniques to remove any residual heparin from the sample prior to performing the assay? | Residual heparin can interfere with assay performance. If not removed, additional care must be taken to ensure the sample is collected at least 1 hour after heparin is stopped. | |
| What is the sensitivity and specificity of our assay(s)? | Every assay has unique performance characteristics. Even within assay classes, performance can vary by lab. Understanding the performance characteristics of an assay is essential in clinical risk prediction. | |
| What is the turnaround time of our assay(s)? | Most institutions do not run functional assays in-house. Knowing when to expect results can help inform management. |
Screening assays
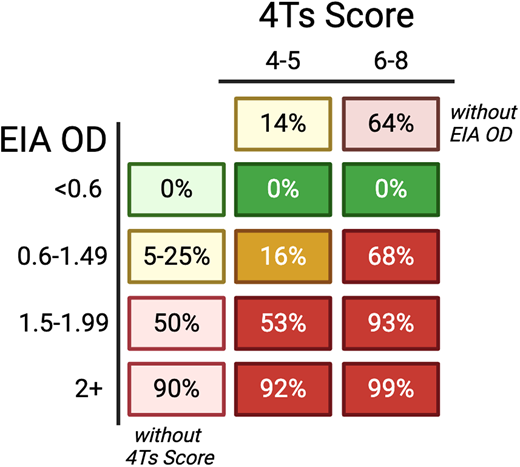
The prototypical screening assay is the EIA, which detects anti-PF4/heparin antibodies in patient serum or plasma using plate wells coated with PF4 complexed with heparin or a similar polyanion. It has high sensitivity (95%; 95% CI, 95%-99%) but limited specificity (82%; 95% CI, 84%-90%), with greater specificity with EIAs that are IgG-specific (rather than polyspecific, also detecting IgA and IgM).19 EIAs also provide an OD, which increases with increasing concentration of anti-PF4/heparin antibodies. Figure 3 provides estimates of the likelihood of HIT incorporating the EIA OD and the 4Ts Score independently and combined, which can be a useful tool to inform clinical decision-making. Multiple rapid immunoassays also exist that can give results in less than 30 minutes using varying techniques with unique performance characteristics.20,21 Again, clinician understanding of the screening assay(s) used in their personal clinical practice is essential.
Probability of HIT based on 4Ts Score and EIA OD. Lighter shading indicates the estimated probability of the individual component (4Ts Score independent of EIA OD7 and EIA OD independent of 4Ts Score40). Darker shading indicates estimated probability, accounting for a combination of the 4Ts Score and EIA OD.41,42 Percentages will vary with different EIA assays. Reproduced with permission from May et al.38
Probability of HIT based on 4Ts Score and EIA OD. Lighter shading indicates the estimated probability of the individual component (4Ts Score independent of EIA OD7 and EIA OD independent of 4Ts Score40). Darker shading indicates estimated probability, accounting for a combination of the 4Ts Score and EIA OD.41,42 Percentages will vary with different EIA assays. Reproduced with permission from May et al.38
Functional assays
The gold standard functional assay is the serotonin release assay (SRA), which measures platelet activation to varying concentrations of heparin based on the release of radiolabeled serotonin from platelet granules. The SRA has high sensitivity and specificity (approximately 95% for both),22 but real-world performance varies due to variations in this assay across institutions, ranging from differences in preanalytical handling to testing methodologies and to result interpretation and reporting.23 The SRA has important limitations. Because the assay requires platelets from selected donors and uses radioactivity, it is only performed in specialized centers, which often results in significant lag time between sample collection and result. Furthermore, the SRA can rarely be falsely negative (see the dotted line on Figure 2).24
While the SRA measures the ability of anti-PF4/heparin antibodies to activate platelets by measuring the amount of serotonin they release, other functional assays use different techniques. The heparin-induced platelet activation assay is widely used in Europe and measures platelet activation based on a visual assessment of sample turbidity with a sensitivity and specificity comparable to the SRA.25 The P-selectin expression assay (PEA) is a newer functional assay that measures platelet P-selectin (CD62p) expression by flow cytometry (sensitivity, 94%; specificity, 88%).26,27 The PEA is PF4 enhanced, meaning additional PF4 is added to the sample, so along with other PF4-enhanced functional assays (eg, the PF4-enhanced platelet activation assay [PF4-SRA]), it can detect SRA-negative HIT.27-29 Furthermore, because of simpler technique the PEA may offer institutions a functional assay option that can be run internally, facilitating earlier HIT diagnosis or exclusion.
CLINICAL CASE (continued)
Bilateral lower-extremity ultrasounds were obtained and revealed a proximal deep vein thrombosis in the left lower extremity. Given clinical stability, the patient was discharged on POD 9 and advised to continue apixaban 10 mg twice daily. On POD 13, the SRA returned positive, confirming the diagnosis of HIT. The patient was seen in the hematology clinic on POD 15, by which time the platelet count had normalized. Upon completing 7 days of apixaban at 10 mg twice daily, he was transitioned to 5 mg twice daily with a plan to continue for 3 months. The patient was educated on the importance of heparin avoidance and given resources to obtain a medical alert bracelet with instructions to wear it for 3 months.
Anticoagulation selection
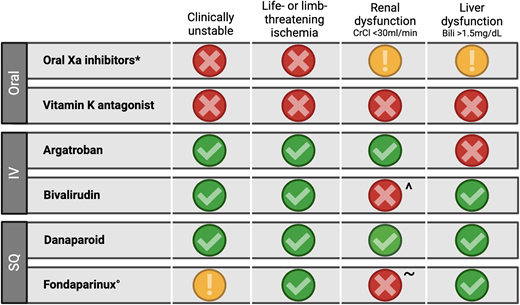
The 2 key principles of acute HIT management are (1) avoid heparin and (2) use nonheparin anticoagulation. Figure 4 provides guidance for selecting a nonheparin anticoagulant in acute HIT, accounting for 2 patient-specific factors (clinical stability and the presence of severe ischemia) and 2 anticoagulant-specific factors (renal clearance and hepatic clearance). Available guidelines recommend selecting an anticoagulant based on these factors as well as others, including drug and monitoring availability, the desired route of administration, cost, and the experience of the treating clinician.4
Anticoagulation selection in acute HIT. Options for anticoagulation in acute HIT are guided by 4 clinical criteria. A green check indicates the agent is preferred. A yellow exclamation point indicates the agent is not preferred but can be used with caution based on availability and consideration of the balance of risks and benefits. A red X indicates the agent is not recommended. *Existing data with rivaroxaban, apixaban; ^If argatroban not available, can use with close monitoring due to accumulation risk; °Trivial risk of reported HIT, but safe use in acute HIT is well-documented31; ~Use in renal dysfunction has been reported.43 Bili, bilirubin; CrCl, creatinine clearance; IV, intravenous; SQ, subcutaneous. Adapted with permission from May et al.38
Anticoagulation selection in acute HIT. Options for anticoagulation in acute HIT are guided by 4 clinical criteria. A green check indicates the agent is preferred. A yellow exclamation point indicates the agent is not preferred but can be used with caution based on availability and consideration of the balance of risks and benefits. A red X indicates the agent is not recommended. *Existing data with rivaroxaban, apixaban; ^If argatroban not available, can use with close monitoring due to accumulation risk; °Trivial risk of reported HIT, but safe use in acute HIT is well-documented31; ~Use in renal dysfunction has been reported.43 Bili, bilirubin; CrCl, creatinine clearance; IV, intravenous; SQ, subcutaneous. Adapted with permission from May et al.38
Vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) have long been the foundation of oral anticoagulation in HIT, but they introduce 2 agent-specific challenges. First, they cannot be used in acute HIT and can only be started after platelet count recovery due to the risk of catastrophic thrombosis when combining the prothrombotic state of HIT with the prothrombotic state induced by VKA initiation. Second, they require bridging until a therapeutic international normalized ratio (INR) is achieved, which is generally performed with an intravenous (IV) direct thrombin inhibitor (DTI; bivalirudin or argatroban) in patients with HIT. This can increase bleeding risk due to the inaccuracy of the INR with a concurrent DTI, as well as prolong hospital stays to continue an IV infusion while awaiting a therapeutic INR.
Unlike VKAs, oral factor Xa inhibitors have an immediate anticoagulant effect and can therefore be used as the initial nonheparin anticoagulant upon suspicion for HIT regardless of platelet count (although they are generally avoided in patients who are clinically unstable or have severe limb/organ ischemia; Figure 4). The oral Xa inhibitors, specifically rivaroxaban and apixaban, are also the guideline-based preferred oral agent for subacute HIT management (ie, once the platelet count has normalized).4 The recommendation for oral Xa inhibitors over VKAs is based on extrapolation of the likely lower bleeding risk but a similar risk of thrombotic events with oral Xa inhibitors compared to VKAs in patients with VTE without HIT.30 There are less data available on the use of other direct oral anticoagulants (dabigatran, edoxaban).
Fondaparinux is administered subcutaneously and can similarly be started as initial HIT therapy regardless of platelet count. Some providers may be hesitant to use fondaparinux due to the mistaken concern that it causes HIT, but this is extremely rare, and it can be safely used.31
From a health system perspective, each nonheparin anticoagulant has unique benefits and challenges. Both oral factor Xa inhibitors and fondaparinux offer the opportunity for earlier discharge compared to VKAs due to the avoidance of IV bridging, which can significantly decrease health care utilization. Our patient case highlights that clinically stable patients can be discharged on an oral Xa inhibitor or fondaparinux while thrombocytopenic (greater than 50 × 109/L) and even before the SRA result returns, as long as close outpatient follow-up is available (Figure 1). Data suggest that fondaparinux is the most cost-effective anticoagulant option, due in large part to the higher cost of oral factor Xa inhibitors.32 IV DTIs are also associated with increased care costs and high bleeding risk. Given the complexity of agent selection and management, some institutions have established anticoagulation stewardship programs, frequently focusing on anticoagulation in patients with suspected or confirmed HIT. Such programs have demonstrated benefits, including decreasing the unnecessary use of IV DTIs, increasing use of fondaparinux and oral Xa inhibitors, and decreasing the time from acute HIT diagnosis to discharge.33,34
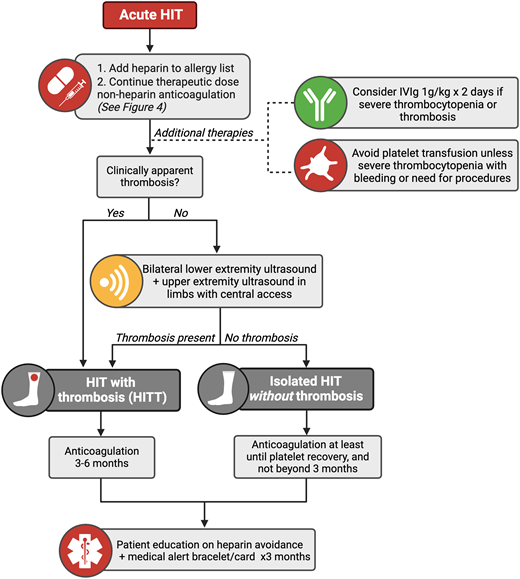
Duration of anticoagulation
The duration of anticoagulation in HIT is based on the presence or absence of thrombosis (Figure 5). Many patients with HIT may develop clinical signs and symptoms of venous or arterial thrombosis that prompt identification. In patients without overt thrombosis, a bilateral lower-extremity ultrasound to screen for DVT is recommended.4 If a patient has a central venous catheter, an upper-extremity ultrasound of the limb with the catheter is also recommended.4
Algorithm for the management of HIT. IVIg, intravenous immunoglobulin.
Patients with HIT with thrombosis require 3 to 6 months of nonheparin anticoagulation, similar to treatment of a patient with VTE provoked by a major transient risk factor.4,5 In HIT without thrombosis, also referred to as isolated HIT, guidelines recommend continuing nonheparin anticoagulation for a minimum duration of at least until platelet count recovery and recommend against continuing for 3 months or more.4 Durations in between that minimum and the maximum of 3 months may be used, recognizing that the optimal duration is unknown.
Additional therapies
In addition to nonheparin anticoagulation, other therapies may influence HIT care and outcomes. The transfusion of platelets is generally avoided, as available data suggest it may increase arterial thrombotic risk (adjusted odds ratio, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.2-3.3) and mortality (adjusted odds ratio, 3.4; 95% CI, 1.2-9.5).35 However, in patients with profound thrombocytopenia with bleeding or who require high-risk procedures, transfusion can be considered.4
IV immunoglobulin use in HIT is hypothesized to competitively inhibit the binding of anti-PF4/heparin antibodies to Fc receptors on platelets and other cell types. Available reports of use (1 g/ kg/d for 2 days) in patients with severe/refractory thrombocytopenia and/or thrombosis suggest it improves clinical outcomes.36
The ideal therapy for HIT is one that prevents its occurrence. Clinical trials are ongoing for a new agent administered even prior to laboratory diagnosis, with the goal of blocking platelet activation via inhibition of the 12-lipooxygenase pathway and therefore interrupting the development of clinical HIT (NCT05785819). In the similar theme of HIT prevention, limiting or even eliminating the use of unfractionated heparin at a health system level has been shown to decrease HIT incidence.37
Future heparin avoidance
The resolution of HIT typically follows an expected trajectory based on the time line of clearance of anti-PF4/heparin antibodies: first, platelet count normalization, then functional assay normalization, and last, screening assay normalization. Although the dogma is to avoid all heparin after acute HIT diagnosis, there are certain scenarios that warrant more nuanced considerations.
The highest risk of HIT exacerbation/recurrence is known to be when a patient remains thrombocytopenic and functional assays remain positive, so heparin avoidance is strongly recommended.4,5 If a patient absolutely requires heparin exposure during this period (eg, urgent CPB), measures to remove or control circulating antibodies are required.15 The avoidance of reexposure is preferred in a patient with remote HIT (ie, the patient is no longer thrombocytopenic, and all serologic studies are negative), but brief reexposure may be considered if nonheparin anticoagulation is not on option.
Reflecting this chronological decline in risk but recognizing limited evidence, guidelines recommend that patients use a medical alert bracelet or card for 3 months after acute HIT diagnosis but no longer than that.4 Mention of the diagnosis of HIT and the need to avoid heparin should be included on the alert device. However, it is essential to both educate patients to notify all providers of their HIT history and keep heparin on the patient's list of allergies indefinitely to avoid unnecessary exposure.
Conclusion
Although a rare condition, the diagnosis and management of HIT is a frequently encountered challenge for patients, clinicians, and health systems. A stepwise approach to diagnosis is evidence based and guideline supported, but deviation from the recommended algorithm is common. Management requires the use of nonheparin anticoagulation in patients with a high thrombotic risk but often accompanying bleeding risk, which escalates care complexity. Heparin avoidance can also introduce long-term challenges, given certain medical scenarios in which heparin use may be required. Collectively, caring for patients with suspicion for or confirmed HIT requires the development of provider-level knowledge and expertise as well as the creation of tools at a system level to support evidence-based clinical decision-making.
Acknowledgment
Figures created with BioRender.com.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
Jori May: no competing financial interests to declare.
Adam Cuker: no competing financial interests to declare.
Off-label drug use
Jori May: The use of bivalirudin, danaparoid, fondaparinux, intravenous immunoglobulin, oral Xa inhibitors (apixaban, rivaroxaban), and warfarin is off-label for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
Adam Cuker: The use of bivalirudin, danaparoid, fondaparinux, intravenous immunoglobulin, oral Xa inhibitors (apixaban, rivaroxaban), and warfarin is off-label for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.