Visual Abstract
Professional illustration by Patrick Lane, ScEYEnce Studios
Abstract
Refractory autoimmune mutilineage cytopenias can present in childhood associated with chronic nonmalignant lymphoproliferation (splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, and/or lymphadenopathy). Cytopenias due to peripheral destruction and sequestration have been well recognized since the 1950s and are often lumped together as eponymous syndromes, such as Evans syndrome and Canale-Smith syndrome. Though their clinical and genetic diagnostic workup may appear daunting, it can provide the basis for early intervention, genetic counseling, and empirical and targeted therapies. Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS), activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase delta syndrome (APDS), and many other related genetic disorders are otherwise collectively known as inborn errors of immunity (IEI). They present in early childhood as refractory autoimmune cytopenias due to immune dysregulation leading to lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and increased susceptibility to lymphoma. More recently, controlled clinical trials have shown that some of these immune system disorders with hematological manifestations might be more readily amenable to specific targeted treatments, thus preventing end-organ damage and associated comorbidities. Over the last 20 years, both rapamycin and mycophenolate mofetil have been successfully used as steroid-sparing long-term measures in ALPS. Current therapeutic options for APDS/PASLI (phosphoinositide 3-kinase [PI3K]-associated senescent T lymphocytes, lymphadenopathy, and immunodeficiency) include the orally bioavailable PI3Kδ inhibitor, leniolisib, which was licensed by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2023 for use in individuals older than 12 years as a targeted treatment. Paradigms learned from patients with rare genetic disorders like ALPS and APDS may help in exploring and streamlining molecular therapy strategies in the wider group of IEIs presenting with refractory cytopenias and lymphoproliferation.
Learning Objectives
Discuss recent advances in molecular genetics of autoimmune lymphoproliferative immune dysregulation with refractory cytopenias and risk of lymphoma
Understand that pathophysiology including risk of lymphoma in ALPS-FAS and APDS/PASLI early can make them readily amenable to therapies
Streamline different modalities, including genetic counseling, supportive care, and precision medicine–based targeted treatments
Introduction
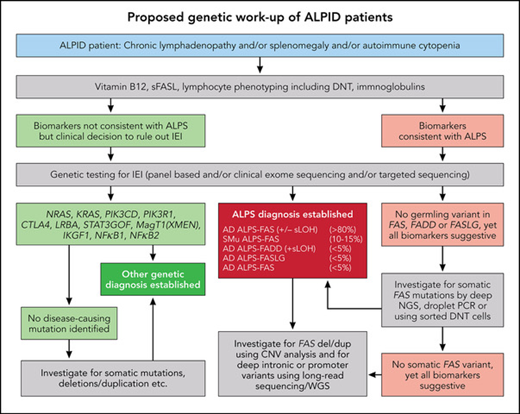
Many immunohematological diseases manifest as refractory autoimmune mutilineage cytopenias associated with chronic nonmalignant lymphoproliferation (splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, and/or lymphadenopathy). Cytopenias due to peripheral destruction and sequestration have been well recognized since the 1950s and 1960s and are often lumped together as eponymous syndromes, such as Evans syndrome1,2 and Canale-Smith syndrome.3 Their clinical and genetic diagnostic workup may appear challenging at the outset; nevertheless, it provides the basis for both empirical and targeted therapy for autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS), activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase delta syndrome (APDS), and many other related genetic disorders otherwise collectively known as inborn errors of immunity (IEI).4-8 More recently there have been attempts to create a broader framework for autoimmune lymphoproliferative immune-dysregulatory/immune-deficiency disorders (ALPIDs) that can benefit from a more detailed workup encompassing multidisciplinary specialty teams (Figure 1).9 These can include supportive care, preemptive therapies for chronic cytopenias, and surveillance for malignancies in the otherwise rare IEI. ALPS is unique among ALPIDs in that it is associated with a characteristic genetic pathophysiology encompassing both germline and somatic variants that confer it with a unique immunophenotype and biomarker profile. Patients with APDS/PI3K-associated senescent T lymphocytes, lymphadenopathy, and immunodeficiency (PASLI) can be treated with an orally bioavailable phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta (PI3Kδ) inhibitor, leniolisib, which was licensed by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2023 as a targeted treatment.
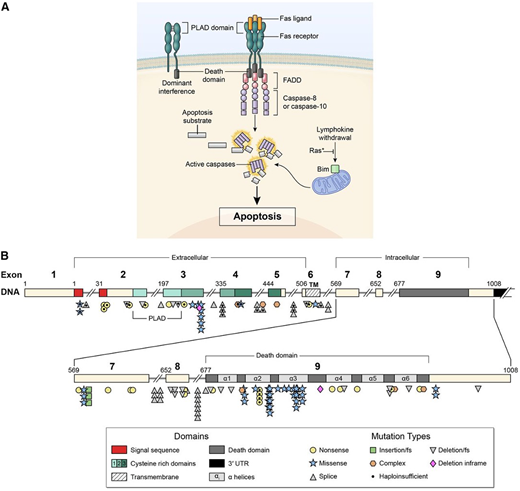
Signal transduction by the FAS receptor whose gene is mutated in ALPS. (A) Schematic of the signaling complex formed after the engagement of FAS by FAS ligand that leads to apoptosis. Shown at the top left is an example of a mutant FAS receptor chain lacking the death domain bound to a wild-type chain through the PLAD, which prevents it from signaling and therefore causes dominant interference. (B) Diagram showing the intron-exon structure of the FAS gene with delineation of exons coding for the extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular portions of the protein incorporating the death domain and the location and types of mutations associated with ALPS-FAS. It is notable that R250 in the α2 helical region of the death domain is the most frequently altered residue and exhibits haploinsufficiency due to reduced Fas surface expression, as well as dominant interference. From Price et al.37
Signal transduction by the FAS receptor whose gene is mutated in ALPS. (A) Schematic of the signaling complex formed after the engagement of FAS by FAS ligand that leads to apoptosis. Shown at the top left is an example of a mutant FAS receptor chain lacking the death domain bound to a wild-type chain through the PLAD, which prevents it from signaling and therefore causes dominant interference. (B) Diagram showing the intron-exon structure of the FAS gene with delineation of exons coding for the extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular portions of the protein incorporating the death domain and the location and types of mutations associated with ALPS-FAS. It is notable that R250 in the α2 helical region of the death domain is the most frequently altered residue and exhibits haploinsufficiency due to reduced Fas surface expression, as well as dominant interference. From Price et al.37
Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome
Autoimmunity results from the failure of self-tolerance, both central and peripheral tolerance. Central tolerance is fostered by apoptosis through elimination of unnecessary, immature effector cells in generative lymphoid organs (the bone marrow and thymus); while mechanisms of peripheral tolerance include anergy, deletion by apoptosis, and suppression by regulatory T cells to avoid autoimmunity and tissue damage.10 Apoptosis, the intrinsic death program of cells, is triggered by any of several effector molecules (including but not limited to FAS, FASL, FADD, and caspases as well as RAS and BIM) either through receptor-ligand interactions at the cell surface (the extrinsic pathway) or by the induction of mitochondrial enzymes (the intrinsic pathway). Lymphocyte apoptosis mediated by the cell surface receptor Fas plays a pivotal physiological role in terminating redundant and unwarranted immune responses. Originally characterized from a human diploid fibroblast cell line as the FS-7-associated surface antigen,4 FAS (CD95 and APO-1) is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily of proteins that directly triggers receptor-mediated apoptosis to maintain lymphocyte homeostasis and peripheral immune tolerance and to prevent autoimmunity.11
ALPS is caused by genetic alterations affecting FAS downstream signaling, abrogating expression or function of FAS. ALPS was one of the first genetically defined IEIs that presents with lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity. Many ALPS patients often present to a hematologist in early childhood for further assessment and management of otherwise inexplicable autoimmune hemolytic anemia, immune thrombocytopenia, and/or neutropenia, and some of them develop B-cell lymphoma.12 In the early 1990s a murine model of MRL/lpr−/− mouse was noted to share a signature cell type with ALPS. Mice with homozygous mutations for Fas-equivalent murine gene lpr develop hypergammaglobulinemia, glomerulonephritis, massive lymphadenopathy, and expansion of an otherwise rare and unique population of TCRαβ+ cells that lack expression of both CD4 and CD8, and hence they are known as double-negative (DN) T cells. These FAS-controlled (FC) T cells accumulate as TCRαβ+CD3+CD4−CD8− DNT (FC DNT) cells.13-15 This murine model provided insights into the pathophysiology of a similar syndrome being observed in humans. Diagnostic criteria for ALPS have been proposed based on clinical, immunological, and genetic parameters.9,16 Significant progress has been made over the last 30 years in understanding the complex genetic causes of this disease, its immunological basis, and the predictive power of biomarkers for its diagnosis. In that respect ALPS is unique among ALPIDs in that it is associated with a very characteristic immunophenotype and biomarker profile.17-19
Genetic diagnosis of ALPS
ALPS can be due to mutations of FAS, FASLG, and FADD genes, also designated as ALPS-FAS, ALPS-FASLG, ALPS-FADD, respectively.20-24 These FAS genetic alterations can be deletions or duplications. They can be germline (ALPS-FAS) with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern or somatic genetic events (ALPS-sFAS).25,26 The somatic events causing ALPS occur in cells of hematopoietic lineage that lead to FAS-altered B and T cells and accumulation of FC DNTs, as these cells have a survival and growth advantage due to their apoptosis defect. FAS mutations most often confer a dominant-negative effect due to missense mutations, allowing normal FAS expression but abrogating the interaction with FADD and profoundly impairing the FAS-induced apoptosis. Such mutations are associated with high clinical penetrance (>80%), and most carriers also develop clinical symptoms of ALPS. In contrast, genetic variants abolishing Fas protein expression of the mutant allele can lead to haploinsufficiency. Such mutations are associated with low clinical penetrance (10% to 80%) unless accompanied by a second genetic event.27 This event can be an independent somatic mutation on the other FAS allele or a somatic loss of heterozygosity (sLOH) (seen in approximately 80%). sLOH is usually caused by uniparental disomy, leading to loss of the wild-type allele compensated by a duplication of the mutated allele. In these cases, FC DNT cells are enriched for biallelic events (ALPS-FAS/sLOH) that frequently lead to the absence of FAS expression on FC DNTs. Patients can also harbor promoter region or deep intronic FAS mutations, deletions, or duplications, often associated with sLOH, reducing FAS expression. These complex genetic alterations should be suspected based on abnormal biomarkers, and they can be readily missed by EXOME sequencing. Hence many patients with suspicious clinical phenotype may require extended genetic workup (Figure 1).19,28
Biomarkers of ALPS
The following biomarkers can be studied in order of decreasing positive predictive value for ALPS among ALPID patients: sFASLG, IL-10, vitamin B12, CD3+TCRαβ+CD4−CD8− DNTs, and HDL cholesterol.17,18,26,29 Cutoff values depend on the assay used and locally established laboratory reference ranges.30 These alterations reflect impaired FAS signaling and are therefore present in all genetic constellations of ALPS with the obvious exception of sFASLG, which is absent in patients with ALPS-FASLG.24 The combination of elevated sFASLG and elevated serum vitamin B12 has the highest positive and negative predictive value for ALPS (92 and 97, respectively).19 Similarly, readily available laboratory tests like elevated serum vitamin B12 levels associated with very low HDL cholesterol in any patient with chronic cytopenias, enlarged spleen, and lymphadenopathy should lead to suspicion of ALPS-FAS and further genetic workup. While these biomarkers are highly sensitive and specific for identifying ALPS, the most widely used diagnostic laboratory parameter is the percentage of DNT among CD3+ T cells. Healthy individuals usually have DNT levels below 2.5%, but this reference range can only be applied to patients without T-cell lymphopenia, as lymphopenia can create spurious elevations of many lymphocyte subsets measured only in percentages. Most ALPS patients do not have lymphopenia, though there can be rare exceptions due to massive splenomegaly.
Hence it is desirable to compute absolute lymphocyte subset numbers (rather than percentages) from total lymphocyte counts derived from a complete blood count done in parallel with the immunophenotyping. Moderate DNT elevations (2.5% to 10%) are common in ALPS. Since sFASLG testing is not widely available, the combination of vitamin B12 and DNT can be used to predict ALPS. However, DNTs have the best sensitivity and specificity above 6%, and levels above 10% are rare in other ALPID patients. An increase in the percentage of FC DNT (best identified by the co-expression of CD45RA and CD38 or of CD5756) above 40% of total DNT is more specific for ALPS-FAS. FC DNTs rapidly die ex vivo; hence long shipment times to a central laboratory can reduce FC DNT levels.31 However, elevated DNTs are also notable in other IEIs like XMEN disease (X-linked immunodeficiency with magnesium defect, Epstein-Barr virus ([EBV] infection, and neoplasia) with deep immunophenotyping using time-of-flight mass cytometry.32
The overall recommendation is to do DNT, sFASLG, and vitamin B12 in ALPID patients; however, low or absent sFASLG levels in combination with elevated vitamin B12 and DNT can also point to ALPS-FASLG. In contrast, canonical apoptosis testing is poorly standardized and yields normal results in patients with somatic FAS mutations.25 This assay may still be relevant for classification of ALPS patients with undetermined genetic findings and in an academic scientific context, but it is not advised to be used in the routine diagnostic algorithm for ALPS patients (Figure 1).
Diagnosis of ALPS allows genetic counseling, prognostic clinical advice, and the option of mTOR targeted therapy with rapamycin for affected patients.6,33-36 The high predictive value of biomarkers outlines a pathway of genetic investigations that can ensure that this diagnosis is not missed. These molecular investigations can also raise awareness of a wide range of immune dysregulation associated with refractory cytopenia, some infection susceptibility, and an increased risk of lymphoma (Figure 2).37,38
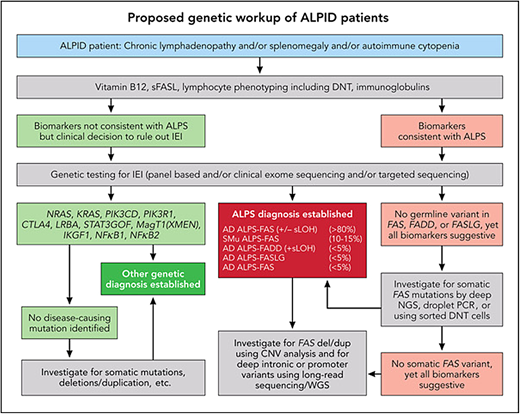
ALPS, APDS, and ALPID: diagnostic workup algorithm. Modified from Magerus Chatinet et al.18 Genetic testing should be done sooner rather than later, particularly in patients with relapsed/refractory autoimmune cytopenias and/or any family history suggestive of cytopenias or lymphoma. CNV, copy number variation; WGS, whole-genome sequencing.
ALPS, APDS, and ALPID: diagnostic workup algorithm. Modified from Magerus Chatinet et al.18 Genetic testing should be done sooner rather than later, particularly in patients with relapsed/refractory autoimmune cytopenias and/or any family history suggestive of cytopenias or lymphoma. CNV, copy number variation; WGS, whole-genome sequencing.
Activated PI3K delta syndrome (APDS/PASLI)
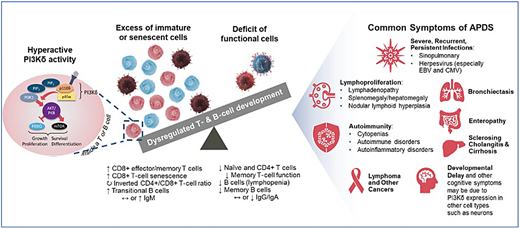
The PI3Kδ pathway is critical for lymphocyte homeostasis reflected in its development and function. Under physiological conditions, PI3Kδ activity in B and T cells is dynamically regulated during development and function, with periods of enhanced activity where FOXO and GSK3 (forkhead box O and glycogen synthase kinase 3) are inhibited and mTOR signaling (mechanistic target to rapamycin) occurs, and periods of dampened activity when mTOR is not activated and FOXO/GSK3 are disinhibited. Balanced PI3K activity results in proper lymphocyte development, differentiation, and function (Figure 3).
Pathophysiology of PI3Kδ hyperactivity leading to APDS/PASLI. Modified from Cant et al.43 CMV, cytomegalovirus.
Pathophysiology of PI3Kδ hyperactivity leading to APDS/PASLI. Modified from Cant et al.43 CMV, cytomegalovirus.
APDS, also known as PASLI, is an IEI resulting from pathogenic heterozygous variants in either of the 2 genes encoding the PI3Kδ heterodimer. Gain-of-function variants in PIK3CD encoding the catalytic subunit p110δ cause APDS1, whereas loss-of-function variants in PIK3R1 encoding the regulatory subunit p85α cause APDS2.39-41 Interaction of the 2 subunits is essential for heterodimer function and stability. Disruption of this interaction or loss of p85α-mediated inhibition due to pathogenic variants in PIK3CD or PIK3R1 result in hyperactive PI3Kδ signaling. This hyperactive signaling results in comparable immunologic consequences in both APDS1 and APDS2 (Figure 3).42
Clinical manifestations of APDS besides autoimmune cytopenia are distinct from ALPS and include sinopulmonary infections, lymphoproliferation affecting small airways and the gut, enteropathy, bronchiectasis, and increased risk of malignancy, especially lymphoma (Table 1). As the follow-up period increases for the clinical cohort of patients with both ALPS and APDS, the incidence of malignancies including lymphoma can change. In APDS, PI3Kδ is hyperactive, resulting in excessive FOXO/GSK3 inhibition and mTOR activation. As a result, lymphocytes do not develop properly, with an excess accumulation of both immature and senescent cells and a deficit of functional lymphocyte subsets.43 This concomitant deficiency and dysregulation create or contribute to the constellation of clinical manifestations. Patients with APDS may also display signs and symptoms due to neurological or cognitive impairment, liver disease, and atopy likely due to excess PI3Kδ activity in nonhematopoietic cells, including bronchial epithelium, synovium, and central nervous system cells.43
Cardinal clinical and diagnostic features of ALPS and APDS
| Genetic disease . | ALPS . | APDS . |
|---|---|---|
| Genes | FAS, FASLG, FADD | PIK3CD, PIK3R1 |
| Inheritance and penetrance | Autosomal dominant (FAS, FADD) Somatic variants (FAS) Incomplete penetrance | Autosomal dominant Complete penetrance |
| Pathobiology | Fas-mediated apoptosis | Increased PI3Kδ signal |
| Age of onset | Median 3 yrs | Median 1 yr |
| Lymphoproliferation | Splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy | Splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, mucosa-associated lymphoid hyperplasia (airways and gut) Nodular lymphoid hyperplasia |
| Increased risk of lymphoma | Yes (∼10% prevalence) | Yes (∼30% prevalence) |
| Immunoglobulins | Hypergammaglobulinemia | Increased IgM, hypogammaglobulinemia Reduced IgA |
| Immunophenotype | No lymphopenia Elevated DNT cells Often low class-switched B cells | Lymphopenia Increased transitional B cells Reduced naïve and class-switched B cells Increased CD57+/CD8+ T cells |
| Autoimmune findings | Cytopenias, hepatitis, nephritis, uveitis | Cytopenias, enteropathy, hepatitis, cholangitis, bronchiectasis |
| Infection susceptibility | Not significant | Sinopulmonary infections Chronic herpes viral infections (EBV, CMV) |
| Biomarkers | Elevated serum vitamin B12, sFASL, and IL-10 levels | Increased pAkt and S6 phosphorylation |
| Immunomodulatory therapies | High-dose corticosteroids, IVIG mycophenolate mofetil | High-dose corticosteroids, IVIG, and rapamycin |
| Targeted therapy | mTOR inhibitor (rapamycin) | PI3K delta inhibitor (leniolisib) |
| Genetic disease . | ALPS . | APDS . |
|---|---|---|
| Genes | FAS, FASLG, FADD | PIK3CD, PIK3R1 |
| Inheritance and penetrance | Autosomal dominant (FAS, FADD) Somatic variants (FAS) Incomplete penetrance | Autosomal dominant Complete penetrance |
| Pathobiology | Fas-mediated apoptosis | Increased PI3Kδ signal |
| Age of onset | Median 3 yrs | Median 1 yr |
| Lymphoproliferation | Splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy | Splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, mucosa-associated lymphoid hyperplasia (airways and gut) Nodular lymphoid hyperplasia |
| Increased risk of lymphoma | Yes (∼10% prevalence) | Yes (∼30% prevalence) |
| Immunoglobulins | Hypergammaglobulinemia | Increased IgM, hypogammaglobulinemia Reduced IgA |
| Immunophenotype | No lymphopenia Elevated DNT cells Often low class-switched B cells | Lymphopenia Increased transitional B cells Reduced naïve and class-switched B cells Increased CD57+/CD8+ T cells |
| Autoimmune findings | Cytopenias, hepatitis, nephritis, uveitis | Cytopenias, enteropathy, hepatitis, cholangitis, bronchiectasis |
| Infection susceptibility | Not significant | Sinopulmonary infections Chronic herpes viral infections (EBV, CMV) |
| Biomarkers | Elevated serum vitamin B12, sFASL, and IL-10 levels | Increased pAkt and S6 phosphorylation |
| Immunomodulatory therapies | High-dose corticosteroids, IVIG mycophenolate mofetil | High-dose corticosteroids, IVIG, and rapamycin |
| Targeted therapy | mTOR inhibitor (rapamycin) | PI3K delta inhibitor (leniolisib) |
CMV, cytomegalovirus.
Genetics of APDS/PASLI
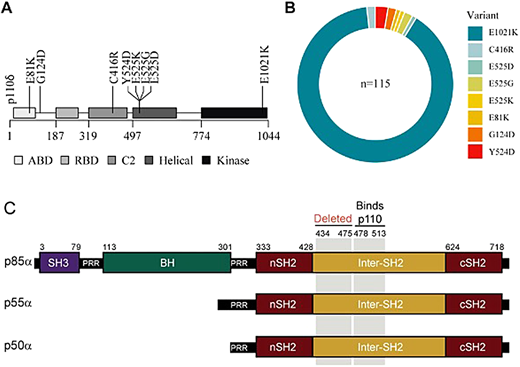
In a recently published cohort by Maccari et al,44 among the 170 patients with APDS from 46 centers, 115 had heterozygous disease-causing variants in PIK3CD and 55 in PIK3R1. Eight disease-causing variants were found spanning p110δ isoform of PIK3CD, with E1021K accounting for 90% (Figure 3A and B). APDS patients have low genetic heterogeneity, with only 8 different variants in p110δ seen among these 115 patients included in the cohort (Figure 4A and B). All reported patients with APDS2 carry deleterious splice-site disease-causing variants resulting in skipping of exon 11 of p85α (Figure 4C).
(A–B) (modified from Maccari et al44): overview of PIK3CD disease-causing variants in the ESID registry patients and their variant distribution. (C) PIK3R1 variant (modified from Lucas et al39) shows affected APDS2 patients are heterozygous for a PIK3R1 splice-site mutation that causes an in-frame deletion of exon 11. Protein schematic for p85α, p55α, and p50α isoforms of PIK3R1 indicating amino acid residue numbers (top), structural domains, region deleted by the patient splice mutation, and the p110-binding region. BH, breakpoint cluster region homology; nSH2 and cSH2, N-terminal and C-terminal Src homology 2; PRR, proline-rich region; SH3, Src homology 3.
(A–B) (modified from Maccari et al44): overview of PIK3CD disease-causing variants in the ESID registry patients and their variant distribution. (C) PIK3R1 variant (modified from Lucas et al39) shows affected APDS2 patients are heterozygous for a PIK3R1 splice-site mutation that causes an in-frame deletion of exon 11. Protein schematic for p85α, p55α, and p50α isoforms of PIK3R1 indicating amino acid residue numbers (top), structural domains, region deleted by the patient splice mutation, and the p110-binding region. BH, breakpoint cluster region homology; nSH2 and cSH2, N-terminal and C-terminal Src homology 2; PRR, proline-rich region; SH3, Src homology 3.
Increased risk of susceptibility to lymphoma in ALPS and APDS/PASLI
As previously reported, ALPS-FAS patients have a greater relative risk of lymphoma than previously described. The age at diagnosis ranged from 5 to 60 years (median 18 years). The male to female ratio was 14:4. Sixteen patients with B-lineage lymphomas were seen in a cohort of 150 ALPS-FAS patients that included 10 cases of Hodgkin's lymphoma compared with 0.067 expected in the general population, giving an observed to expected (O/E) ratio of 149 (95% CI = 71-274). Six cases of non-Hodgkin lymphoma were observed in ALPS-FAS patients compared with the 0.099 expected (O/E = 61; 95% CI = 22-132). Both O/E ratios were highly significant. Standardized incidence ratio values for ALPS-FAS patients are 149 and 61 for Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma, respectively. All patients with lymphoma had dominant-interfering FAS mutations affecting the death domain except for 1 affecting the extracellular domain. Because haploinsufficient patients may constitute almost a fifth of the ALPS population, the incidence of lymphoma is even higher among patients with dominant- interfering mutations, implying that more disruptive FAS mutations may confer a greater propensity to lymphomagenesis.37
APDS/PASLI patients have a higher tendency to develop B-lineage lymphomas (12% to 25%) as reported in multiple publications.44-46 The series of 170 patients with APDS reported from the European Society for Immunodeficiencies (ESID) Registry by Maccari et al included 22 malignant lymphomas (14%). Lymphomas in these APDS patients included 7 Hodgkin lymphomas, 10 non-Hodgkin lymphomas, 1 intestinal large B-cell lymphoma with plasmablastic differentiation, 1 follicular lymphoma, 1 large B-cell lymphoma, 1 mature T-cell/natural killer–cell lymphoma, and 1 lymphoma without further histological information; 17 of 22 lymphoma cases were preceded by chronic benign lymphoproliferation. Of note, 10 of 20 lymphoma cases in APDS were reportedly EBV associated. Moreover, among the 22 patients with APDS who had lymphoma, 4 also had other malignancies (2 ovary neoplasms; 1 papillary renal cell carcinoma; 1 malignant neoplasm of the submandibular gland). Furthermore, 1 patient each with APDS had a B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia, hepatocellular carcinoma, breast ductal carcinoma in situ, papillary thyroid carcinoma, and rhabdomyosarcoma. The median age at diagnosis of any malignancy was 19 years among these cohorts of patients. Similarly, 21 of 80 (26%) patients with APDS1 seen at a single center have been diagnosed with B-cell lineage malignant lymphoma, and more than half of them appear to be EBV driven (data presented as personal communication from coauthors). Diagnosis of malignant lymphoma in the background chronic nonmalignant lymphoproliferation can be challenging for the inexperienced (illustrative examples shown in Figures 5 and 6).
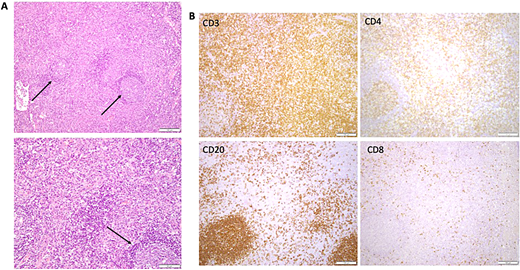
Illustrative lymph node histopathology in ALPS-FAS. (A) Paracortical expansion, which is typical for ALPS. Arrows point to reactive follicles. Lower panel showing higher-power view of the cellular composition of the paracortex, bottom arrow showing reactive follicle. (B) Immunohistochemistry showing CD3, CD4, and CD8 stain to highlight presence of double-negative T cells in the paracortical expansion. Bottom left panel shows reactive B-cell follicle (CD20).
Illustrative lymph node histopathology in ALPS-FAS. (A) Paracortical expansion, which is typical for ALPS. Arrows point to reactive follicles. Lower panel showing higher-power view of the cellular composition of the paracortex, bottom arrow showing reactive follicle. (B) Immunohistochemistry showing CD3, CD4, and CD8 stain to highlight presence of double-negative T cells in the paracortical expansion. Bottom left panel shows reactive B-cell follicle (CD20).
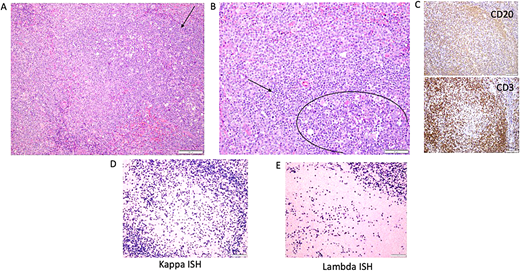
Illustrative lymph node histopathology in APDS1. (A) Arrow is pointing toward the germinal centers identified by the presence of larger cells and numerous tangible body macrophages. (B) Circle defines the germinal centers with a rim of small lymphocytes with condensed chromatin (T cells). (C) CD3 and CD20 images showing out circle of monocytoid B cells (CD20). (D–E) Another feature that is often seen as marked plasmacytosis, like in this case with kappa greater than lambda (in tissue the ratio can be up to 4:1). ISH, in situ hybridization.
Illustrative lymph node histopathology in APDS1. (A) Arrow is pointing toward the germinal centers identified by the presence of larger cells and numerous tangible body macrophages. (B) Circle defines the germinal centers with a rim of small lymphocytes with condensed chromatin (T cells). (C) CD3 and CD20 images showing out circle of monocytoid B cells (CD20). (D–E) Another feature that is often seen as marked plasmacytosis, like in this case with kappa greater than lambda (in tissue the ratio can be up to 4:1). ISH, in situ hybridization.
Short-term and long-term management of ALPS and APDS/PASLI
ALPS
ALPS was identified as a genetically defined IEI more than 30 years ago in the 1990s. Its natural history has been well described; it is characterized by cardinal clinical symptoms with well-understood genetic etiology leading to treatment recommendations based on its risk factors and diagnostic biomarkers.6,35,37,47,48 Unlike most of the self-limiting autoimmune cytopenias sporadically seen in hematology practice, multilineage cytopenias due to ALPS and other IEIs are often refractory and remain chronic, as their inherited genetic defect is not going to go away. However, no intervention might be indicated in many ALPS patients unless they present with clinically significant cytopenias, as seen in nearly 30% of the patients. These can be due to splenic sequestration, bone marrow infiltration with nonmalignant lymphoproliferation consisting of clustering islands of T and B lymphocytes, and/or autoimmune peripheral destruction of blood cells in the reticuloendothelial system.
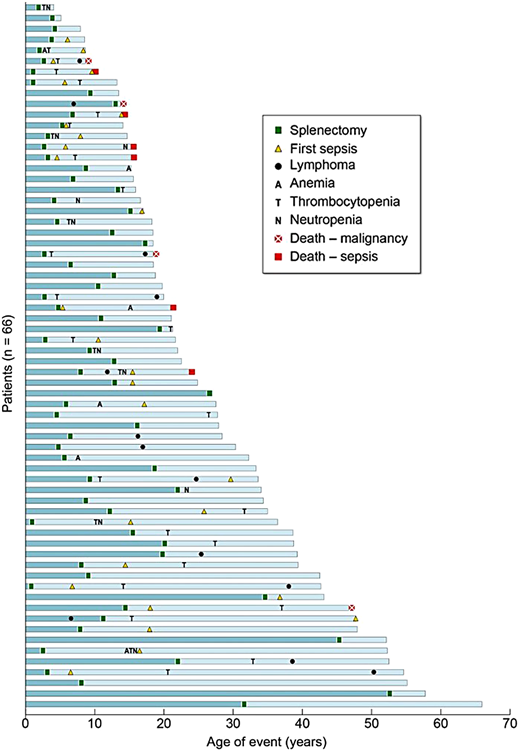
Historically, more ALPS patients have died due to overwhelming sepsis following splenectomy to manage their chronic cytopenias than due to any other cause, including malignancies (Figure 7).37 Hence, current treatment recommendations for ALPS underscore the importance of avoiding splenectomy at any cost, specifically by long-term use of corticosteroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents like mycophenolate mofetil and sirolimus. Treatment interventions for ALPS patients at any age should include clinical workups for ruling out malignancies as indicated by clinical presentation of sudden focal enlargement of a group of lymph nodes with systemic symptoms. However, routine annual surveillance imaging with positron emission tomography scans and computed tomography scans has been found to be unhelpful in the absence of pertinent clinical context.49 Patients most frequently present with clinically significant and refractory cytopenias in childhood and as young adults. The initial management of autoimmune cytopenias, including autoimmune hemolytic anemia, immune-mediated thrombocytopenia, and autoimmune neutropenia in patients with ALPS, is not any different from management of sporadic immune cytopenias in other patient populations. However, both splenectomy and rituximab use have been shown to have significant comorbid toxicities leading to opportunistic, often fatal pneumococcal sepsis and prolonged hypogammaglobulinemia, respectively. Hence both splenectomy and rituximab should be avoided in ALPS.50,51
Causes and consequences of splenectomy in ALPS-FAS. Outcomes for all 66 patients undergoing splenectomy are shown. Each blue bar represents the timeline of events in 1 patient's lifetime, and all the bars are stacked from the oldest patient in the cohort at the bottom to the youngest at the top. All 6 deaths due to sepsis were in patients who underwent splenectomy at a younger age (<10 years).
Causes and consequences of splenectomy in ALPS-FAS. Outcomes for all 66 patients undergoing splenectomy are shown. Each blue bar represents the timeline of events in 1 patient's lifetime, and all the bars are stacked from the oldest patient in the cohort at the bottom to the youngest at the top. All 6 deaths due to sepsis were in patients who underwent splenectomy at a younger age (<10 years).
Short-term medications should include very high-dose intravenous corticosteroids (doses of methyl prednisolone up to 10 to 30 mg/kg/day may have to be used) and intravenous immunoglobulins at immunomodulatory doses (IVIG 1 to 2 gm/kg) as well as TPO mimetic agents for moderate to severe immune thrombocytopenia. Both rapamycin and mycophenolate mofetil have been successfully used by many clinicians as steroid- sparing long-term measures. Rapamycin certainly has a better efficacy profile in terms of amelioration of lymphoproliferation reflected through shrinkage of lymph nodes and spleen size, normalization of biomarkers like FC-DNT cells, and serum vitamin B12 levels compared with mycophenolate mofetil if patients can tolerate the associated toxicity.35 Clinicians caring for these patients need to be familiar with their disease course, vigilant for the complications, including lymphoma development, and wary of the long-term toxicity and accompanying morbidity of any pharmacological intervention they might contemplate, as this should include periodic monitoring of 24-hour trough levels for rapamycin to adjust the dose in individual patients, for example. The targeted 24-hour nadir trough level of rapamycin should range between 7.5 and 15 ng.
APDS/PASLI
As the genetic etiology of APDS/PASLI was only discovered and published as recently as 10 years ago (2013-2014), its natural history and treatment paradigms are still evolving from emerging worldwide retrospective observational studies and their published reports. Many patients with APDS seem to require immunoglobulin replacement therapy and prophylactic antibiotics due to hypogammaglobulinemia, lymphoproliferative airway disease, and repeated sinopulmonary infections leading to bronchiectasis. However, our understanding of the natural history of APDS/PASLI is still limited to retrospective registry data, and no clear risk factors for severe disease have been identified besides lymphoproliferation, autoimmune cytopenias, and risk of lymphoma.41 Both APDS1 and APDS2 present with some cytopenia in 50% to 60% of the patients. Most frequently noted, grade 4 cytopenias in APDS1 happen to be autoimmune hemolytic anemia (13%), followed by thrombocytopenia (4%) and neutropenia (4%). Almost 50% of the APDS1 patients also present with some degree of lymphopenia.
The most promising current therapeutic options for APDS/ PASLI include the orally bioavailable PI3Kδ inhibitor leniolisib. It was licensed as a targeted treatment by the FDA in 2023 for use in adults and children older than 12 years with APDS/PASLI following successful completion of a randomized placebo- controlled phase 3 clinical trial in 31 patients.8,52,53 Leniolisib is dispensed as a 70 mg tablet and has been used as a twice-daily oral regimen since 2016 with no drug-related adverse events.54,55 Rapamycin and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation have been used in some patients, though outcome data for the latter include significant risk of stem cell graft failure.56 Though it is heartening to note availability of targeted treatment for a rare orphan disease so soon after its genetic etiology was discovered, access to early genetic diagnosis in children presenting with chronic refractory cytopenias and lymphoproliferation is imperative. The role of standard of care and use of these therapies in the long-term management of patients with APDS remains to be determined. Any of these interventions and their potential side effects must be balanced against the risks of the evolving natural disease course. It will be interesting to see in the future how targeted treatment with PI3Kδ inhibitors will impact the long-term evolution of disease manifestations, including end- organ damage in APDS/PASLI.44
Recent results of a phase 3 trial and long-term outcome data using PI3Kδ inhibitors like leniolisib show promising efficacy, especially regarding the lymphoproliferative disease component of the disease, with a very good safety profile.7,8,43,54,55 The poorer prognosis for pediatric patients with early disease onset identified in published ESID registry cohorts highlights the importance of early diagnosis and implementing collaborative multicenter clinical trials using targeted therapeutics in rare diseases involving younger patients with IEIs (such as the recently implemented leniolisib clinical trial in Pediatric Patients Aged 4 to 11 Years With APDS; NCT05438407). Moreover, paradigms learned from managing patients with rare genetic disorders like ALPS and APDS can be applied in streamlining the therapeutic strategies in the broader group of IEIs with cytopenia and lymphoproliferation. These conditions include CHAI (CTLA4 haploinsufficiency with autoimmune infiltration; CTLA4 haploinsufficiency), LATAIE (LRBA deficiency with autoantibodies, regulatory T-cell defects, autoimmune infiltration, and enteropathy; LRBA mutations), RALD (Ras-associated autoimmune leukoproliferative disorder; MAPK pathway mutations), monogenic early-onset lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity due to STAT3 gain-of-function syndromes, and many others, as new genetic disorders of the immune system are discovered regularly.57-59
However, the mainstay of treatment for autoimmune cytopenias in the clinic over the years has remained empirical and consists of the trinity of corticosteroids, immunoglobulin infusions (both in use since the 1950s), and B-cell depletion therapy with rituximab (in clinical use since 1997) and their associated short- and long-term toxicities.60,61 Phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials of targeted therapies in patients presenting with autoimmune cytopenias in orphan diseases are imperative and remain the critical unmet need today. There is substantial clinical overlap, yet their molecular drivers of lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity are distinct, and targeted therapies are available for many of these conditions. Unfortunately, in most of them, data demonstrating efficacy of targeted therapies are based on empirical anecdotal reports or nonrandomized trials.59
Acknowledgment
This research was funded by the Division of Intramural Research program of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases/ National Institutes of Health.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
V. Koneti Rao received study-related financial support from Novartis and Pharming for the leniolisib clinical trial under CRADA (Cooperative Research & Development Agreements).
Stefania Pittaluga has no competing financial interests to declare.
Gulbu Uzel received study-related financial support from Novartis and Pharming for the leniolisib clinical trial under CRADA.
Off-label drug use
V. Koneti Rao: mycophenolate mofetil, rapamycin.
Stefania Pittaluga: None.
Gulbu Uzel: None.