Abstract
Despite the dramatic improvements in outcomes for the majority of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients over the past 2 decades, a similar improvement has not been observed in the more advanced stages of the disease. Blast phase CML (BP-CML), although infrequent, remains poorly understood and inadequately treated. Consequently, the key initial goal of therapy in a newly diagnosed patient with chronic phase CML continues to be prevention of disease progression. Advances in genomic investigation in CML, specifically related to BP-CML, clearly demonstrate we have only scratched the surface in our understanding of the disease biology, a prerequisite to devising more targeted and effective therapeutic approaches to prevention and treatment. Importantly, the introduction of the concept of “CML-like” acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) has the potential to simplify the differentiation between BCR::ABL1-positive ALL from de novo lymphoid BP-CML, optimizing monitoring and therapeutics. The development of novel treatment strategies such as the MATCHPOINT approach for BP-CML, utilizing combination chemotherapy with fludarabine, cytarabine, and idarubicin in addition to dose-modified ponatinib, may also be an important step in improving treatment outcomes. However, identifying patients who are high risk of transformation remains a challenge, and the recent 2022 updates to the international guidelines may add further confusion to this area. Further work is required to clarify the identification and treatment strategy for the patients who require a more aggressive approach than standard chronic phase CML management.
Learning Objectives
Understand the implications of the revised definitions of CML phases with regards to identifying patients of highest potential for transformation
Understand the recent developments in disease biology and therapeutics in blast phase chronic myeloid leukemia
CLINICAL CASE 1
A 26-year-old man was diagnosed with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in the chronic phase (CP) following presentation with a marked leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 360 × 109/L), moderate anemia, and normal platelet count. He was classified as high risk by the ELTS score and was commenced on 100 mg/d dasatinib. While he demonstrated an early hematologic response to dasatinib and rapid fall in BCR::ABL1 values to below 10%, by 2 months, there was emergence of circulating lymphoblasts, and bone marrow biopsy specimen confirmed progression to lymphoid blast phase (BP).
Introduction
While the introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) revolutionized the landscape of therapeutic options in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), enabling most patients to reach optimal molecular targets and outcomes, there remains a subset of patients who either present in or progress to more advanced stages of the disease. Even upfront therapy with potent second-generation TKIs (2G-TKIs) does not completely negate the risk of progression to either accelerated phase (AP) or blast phase (BP) CML as demonstrated in long-term follow-up data from the key frontline TKI studies (Table 1), although that risk has been markedly reduced compared to frontline imatinib-treated patients. Reversion to chronic phase CML (CP-CML) remains critical, but long-term cure with TKI alone has rarely been achieved,1 necessitating early intervention with an allogeneic stem cell transplant where possible for those diagnosed with BP-CML who can achieve a second CP-CML.
Incidence of progression to accelerated and/or blast phase in the major frontline TKI studies in chronic phase CML
| Clinical trial (follow-up in years) . | Frontline TKI (dose) . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imatinib . | Nilotinib . | Dasatinib . | Bosutinib . | |
| IRIS42 (10 years) | 7% (400 mg) | |||
| TOPS43 (42 months) | 4.5% (400 mg)/2.5% (800 mg) | |||
| CML-IV44 (10 years) | 6% (400 mg)/5% (800 mg) | |||
| TIDEL-II45 (40 months) | 3.5% (600 mg) | |||
| ENESTnd46 (10 years) | 8.5% (400 mg) | 4% (300 mg BD)/2% (400 mg BD) | ||
| ENESTfirst (24 months) | 0.6% (300 mg BD) | |||
| DASISION47 (5 years) | 7% (400 mg) | 5% (100 mg) | ||
| BFORE48 (5 years) | 3% (400 mg) | 2% (400 mg) | ||
| Clinical trial (follow-up in years) . | Frontline TKI (dose) . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imatinib . | Nilotinib . | Dasatinib . | Bosutinib . | |
| IRIS42 (10 years) | 7% (400 mg) | |||
| TOPS43 (42 months) | 4.5% (400 mg)/2.5% (800 mg) | |||
| CML-IV44 (10 years) | 6% (400 mg)/5% (800 mg) | |||
| TIDEL-II45 (40 months) | 3.5% (600 mg) | |||
| ENESTnd46 (10 years) | 8.5% (400 mg) | 4% (300 mg BD)/2% (400 mg BD) | ||
| ENESTfirst (24 months) | 0.6% (300 mg BD) | |||
| DASISION47 (5 years) | 7% (400 mg) | 5% (100 mg) | ||
| BFORE48 (5 years) | 3% (400 mg) | 2% (400 mg) | ||
BD, twice daily.
The difficulties in identifying and managing patients with disease that does not exemplify the classic CP-CML that most clinicians are familiar with will be discussed in this chapter. The challenges associated with the recent updates in international guidelines will also be explored. Understanding the disease biology of progression and/or BP-CML is imperative and differentiating de novo BP-CML from Philadelphia chromosome–positive (Ph+) acute leukemia is increasingly vital to ensure appropriate interpretation of results and optimal therapeutic decisions. Furthermore, the pathway to progression is not well understood with the pathognomonic BCR::ABL1 fusion alone likely insufficient to drive progression to BP-CML with studies examining genomic profiles in BP-CML uncovering additional genetic abnormalities in almost all cases.2 Exploring the impact of next-generation sequencing (NGS) in this context is highly relevant. Finally, appreciating the emerging developments in BP-CML therapeutics and the integration of these findings into the current treatment spectrum is necessary. Clinical cases will be used to illustrate key points raised in this chapter.
Reviewing the definitions
Defining the stages of CML has become more complicated with recent updates to the various classification systems, with the World Health Organization (WHO) abolishing AP-CML altogether (Table 2).3 Patient staging may be altered, which may in turn impact therapeutic decisions, depending on which guideline is being applied. The reduced incidence of progression to AP in addition to most de novo AP patients having similar responses to patients with CP-CML with TKI therapy formed the basis of the justification for this major alteration to the WHO position,3 with the overall consensus being that the triphasic natural course of CML has become less relevant in the TKI era. However, the removal of AP as a category implies that there is no intermediary phase where patients may be at higher risk of transformation, which as many clinicians will appreciate is a fallacy.
Classification systems used in chronic myeloid leukemia, including recent updated guideline recommendations
| . | European LeukemiaNet6,49 . | WHO 20165 . | ICC 20224 . | WHO 20223 . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accelerated phase | PB or BM blasts 15%-29% | PB or BM blasts 10%-19% | BM or PB blasts 10%-19% | |
| PB blasts + promyelocytes ≥30% | ||||
| PB basophils ≥20% | PB basophils ≥20% | Peripheral blood basophils ≥20% | ||
| Platelets ≤100 × 109/L (unrelated to therapy) | Platelets ≤100 × 109/L (unrelated to therapy) or >1000 × 109/L (unresponsive to therapy) | |||
| Splenomegaly (unresponsive to therapy) | ||||
| Cytogenetic evolution on treatment | ACA in Ph+ cells at diagnosis, including major route, complex karyotype, or 3q26.2 abnormalities, at diagnosis Cytogenetic evolution on treatment | ACA in Ph+ cells | ||
| Consider: ACAs in Ph+ cells Resistance to 2 TKIs Detection of a BCR::ABL1 kinase domain mutation | Provisional: Failure to achieve CHR to first TKI Any indication of resistance to 2 sequential TKIs Occurrence of >2 mutations on BCR::ABL1 during TKI | |||
| Blast phase | PB or BM blasts ≥30% | PB or BM blasts ≥20% | BM or PB blasts ≥20% | BM or PB blasts ≥20% |
| Extramedullary blast proliferation | Extramedullary blast proliferation | Myeloid sarcoma | Myeloid sarcoma | |
| Presence of morphologically apparent lymphoblasts (>5%) warrants consideration of lymphoid BP-CML | Presence of increased lymphoblasts in PB or BM |
| . | European LeukemiaNet6,49 . | WHO 20165 . | ICC 20224 . | WHO 20223 . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accelerated phase | PB or BM blasts 15%-29% | PB or BM blasts 10%-19% | BM or PB blasts 10%-19% | |
| PB blasts + promyelocytes ≥30% | ||||
| PB basophils ≥20% | PB basophils ≥20% | Peripheral blood basophils ≥20% | ||
| Platelets ≤100 × 109/L (unrelated to therapy) | Platelets ≤100 × 109/L (unrelated to therapy) or >1000 × 109/L (unresponsive to therapy) | |||
| Splenomegaly (unresponsive to therapy) | ||||
| Cytogenetic evolution on treatment | ACA in Ph+ cells at diagnosis, including major route, complex karyotype, or 3q26.2 abnormalities, at diagnosis Cytogenetic evolution on treatment | ACA in Ph+ cells | ||
| Consider: ACAs in Ph+ cells Resistance to 2 TKIs Detection of a BCR::ABL1 kinase domain mutation | Provisional: Failure to achieve CHR to first TKI Any indication of resistance to 2 sequential TKIs Occurrence of >2 mutations on BCR::ABL1 during TKI | |||
| Blast phase | PB or BM blasts ≥30% | PB or BM blasts ≥20% | BM or PB blasts ≥20% | BM or PB blasts ≥20% |
| Extramedullary blast proliferation | Extramedullary blast proliferation | Myeloid sarcoma | Myeloid sarcoma | |
| Presence of morphologically apparent lymphoblasts (>5%) warrants consideration of lymphoid BP-CML | Presence of increased lymphoblasts in PB or BM |
ACA, additional clonal cytogenetic abnormalities; BM, bone marrow; CHR, complete hematologic remission; PB, peripheral blood.
Surprisingly, the cytogenetic profile is not taken into account at any point with the updated WHO guidelines.3 Almost all of the other guidelines incorporate additional cytogenetic abnormalities (ACAs) as a key definition of AP-CML with minor differences such as inclusion of 3q26.2 rearrangements and complex cytogenetics in the previous iterations of the WHO.4-6 The original ACAs are defined as trisomy 8, additional Ph translocation, isochromosome 17q, and trisomy 19. Additional high-risk cytogenetic lesions, including trisomy 21, 3q26.2, monosomy 7/7q-, 11q23, and a complex karyotype, together with the original ACAs were identified as conferring an inferior overall survival (OS) and a higher propensity to be present at BP-CML.7 In fact, when these events were observed in conjunction with lower blast counts (defined as 1%-15%), it also heralded disease progression and inferior OS.7 Cytogenetic interrogation of the SPIRIT2 cohort, which compared upfront dasatinib to imatinib in newly diagnosed patients with CP-CML, revealed that the presence of ACAs did not correlate with either the Sokal or ELTS but was independently predictive of progression-free survival (PFS).8 While the PFS was dominated by non-CML deaths without evidence of progression and so perhaps masks the true impact of ACAs (original and modified), the freedom from progression analysis clearly demonstrated that the presence of any one of these lesions conferred an inferior freedom from progression compared to the absence of ACAs (76% vs 98%, P < .001) detected at diagnosis.8 Data from a retrospective analysis of patients with CML treated at the MD Anderson Cancer Center also confirmed an inferior OS and molecular responses, especially in association with selected ACAs, including i(17), monosomy 7/7q-, and 3q26.2 rearrangements.9 Specific evaluation for the 3q26.2 abnormalities that contain the EVI1 locus, which when observed in acute myeloid leukemia characterizes a highly aggressive course with poor prognosis, similarly highlights a subset of patients with CML who have a very poor OS.10 Emergence of 3q26.2 abnormalities in either CP or AP-CML had a high rate of transformation to BP, with the median time to progression approximating 3 months, while also drawing attention to a group of patients with a substandard response to TKI therapy.10 A smaller French study evaluating 42 patients with AP-CML also confirmed the presence of ACAs predicted for a higher rate of failure and inferior PFS, especially if the hematologic features of AP-CML were evident.11
Perhaps instead of abolishing AP-CML altogether, it may have been prudent to simply tighten the definition surrounding AP-CML as some of these higher-risk patients are not recognized within the current WHO guidelines.3 The International Consensus Classification (ICC), also updated in 2022, has simplified the definition of AP-CML to only take into account 3 variables—blasts, basophil count, and the presence of ACAs in Ph+ cells.4 The variables that were considered “softer” definers of AP such as platelet count and splenomegaly response are not even considered by the ICC, and it may be reasonable to now omit these in the context of stronger evidence addressing the other parameters. Irrespective of the definition used, AP-CML can be treated as high-risk CP-CML with TKI monotherapy. However, we do recommend close scrutiny of response in patients with AP-CML since TKI monotherapy may be inadequate in select patients, such as those with 3q26.2 rearrangements.10 Allogeneic stem cell transplant (Table 3) or enrollment in clinical trials investigating agents that can target EVI1, such as BET or PARP inhibitors, should be considered.
Recommendations regarding which patients should be considered for allogeneic stem cell transplantation
| High-risk features indicating the need to initiate a donor search for transplant-eligible patients . |
|---|
| The presence of specific cytogenetic abnormalities at diagnosis or acquisition while on therapy, including • Isochromosome 17q • 3q26.2 • Monosomy 7/7q- • Complex karyotype |
| Failure to achieve any cytogenetic or molecular response to 2G-TKI after a minimum of 3 months of therapy |
| Recurrent grade IV cytopenias despite TKI dose interruptions, dose modifications, and cytokine support, especially within the first 3 months of therapy, leading to EMR failure or ELN-defined treatment failure |
| Recurrent grade 4 toxicity preventing consistent TKI dose intensity, resulting in EMR failure or ELN-defined treatment failure on 2 or more lines of TKI therapy |
| Compound kinase domain mutations involving T315I |
| Lymphoblasts >5% at diagnosis |
| High-risk features indicating the need to initiate a donor search for transplant-eligible patients . |
|---|
| The presence of specific cytogenetic abnormalities at diagnosis or acquisition while on therapy, including • Isochromosome 17q • 3q26.2 • Monosomy 7/7q- • Complex karyotype |
| Failure to achieve any cytogenetic or molecular response to 2G-TKI after a minimum of 3 months of therapy |
| Recurrent grade IV cytopenias despite TKI dose interruptions, dose modifications, and cytokine support, especially within the first 3 months of therapy, leading to EMR failure or ELN-defined treatment failure |
| Recurrent grade 4 toxicity preventing consistent TKI dose intensity, resulting in EMR failure or ELN-defined treatment failure on 2 or more lines of TKI therapy |
| Compound kinase domain mutations involving T315I |
| Lymphoblasts >5% at diagnosis |
ELN, European LeukemiaNet; EMR, early molecular response.
While the classification of AP-CML is hotly debated between the 2 recent updates to the ICC and the WHO, BP-CML remains relatively unchanged, although the definition now encompasses lymphoblasts in the peripheral blood/bone marrow as a BP-defining criteria in both guidelines. The ICC goes a step further, including a ≥5% cutoff for circulating lymphoblasts (Table 2).3,4 The data supporting this change are limited and largely restricted to retrospective case series and are somewhat conflicting, with some reports not able to demonstrate a link between progression to lymphoid BP-CML,12 whereas others indicate a high propensity for early progression.13-16 This may be linked to increasing reliance on sensitive flow cytometry and improved discrimination between lymphoblasts and hematogones but also defining a blast threshold below which progression to lymphoid BP is less likely. Our suggestion would be to perform flow cytometry at diagnosis to ensure patients with excess lymphoblasts are identified to enable appropriate treatment to be promptly initiated. However, this may not be a cost-effective screening tool for most institutions globally as an internal audit (unpublished data) has demonstrated that diagnostic flow cytometry only altered the treating approach in <1% of newly diagnosed CML.
CLINICAL CASE 2
A 58-year-old man presents to a peripheral center with 7% lymphoblasts in the peripheral blood with associated leukocytosis with neutrophilia. BCR::ABL1 positivity was confirmed, but bone marrow biopsy a few days later demonstrated CP-CML with no excess of blasts. The peripheral blood blast population also spontaneously cleared. Cytogenetics revealed a deletion of 13q, encompassing RB1, in addition to the standard Ph+ chromosome. NGS confirmed the presence of a low-level RUNX1 nonsense mutation in addition to the BCR::ABL1 translocation. He was treated as CP-CML and commenced 100 mg/d dasatinib. While he demonstrated a complete hematologic response and an initial significant decline in BCR::ABL1 within the first few months, there was rapid progression to lymphoid BP at 6 months with emergence of an F317L mutation. Lymphoblasts carried the same phenotype as observed at presentation. Cytogenetic analysis revealed clonal evolution, including formation of dicentric chromosomes 7 and 12, partial loss of 7p, and an isochromosome derivative 9. He was referred for an allogeneic stem cell transplant workup and commenced on combination chemotherapy with hyperCVAD in addition to 30 mg/d ponatinib, entering a second CP. He underwent a reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic transplant but relapsed within 5 months, necessitating treatment with blinatumomab. Unfortunately, despite achieving a morphologic remission with blinatumomab, he succumbed to septic shock 2 months following treatment completion.
Discussion points
1. Consider the need for flow cytometry at diagnosis
We recommend flow cytometry to be performed at diagnosis to enable accurate enumeration of the blast percentage but also confirmation of the phenotype of identified blasts. The presence of lymphoblasts should prompt concern that this patient is of high risk of progression lymphoid BP-CML, necessitating more frequent monitoring, including repeat bone marrow biopsies as well as a donor search for consideration of an allogeneic stem cell transplant, especially in light of the recent WHO and ICC updates. Persistence of lymphoblasts should be treated as for lymphoid BP.
2. What is the optimal central nervous system prophylaxis in this scenario?
While this was not specifically addressed in the case vignette, the issue of central nervous system (CNS) prophylaxis is highly relevant. The CNS and testes remain a sanctuary site from conventional chemotherapy, and CNS relapses, while rare, do occur. Whichever chemotherapy protocol is used, CNS-penetrating drugs (such as higher-dose cytarabine and methotrexate) need to be included in the regimen. CNS sampling and imaging are also key to exclude current involvement, and regular intrathecal chemotherapy should also be considered. In the event of CNS disease, regular intrathecal chemotherapy administration is recommended. TKI selection is also vital in this setting as not all agents can cross the blood-brain barrier. Imatinib is not preferred for this reason, but both dasatinib and ponatinib can penetrate the blood-brain barrier, resulting in therapeutic levels in the cerebrospinal fluid in murine models.17,18 Furthermore, in the setting of pediatric Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), the incidence of CNS relapse following intensive chemotherapy was less in the dasatinib arm compared with the imatinib cohort.19 Therefore, to maximize CNS prophylaxis, either dasatinib or ponatinib would be the preferred TKI in conjunction with CNS-penetrating chemotherapy.
3. Is myeloablative (or reduced intensity) conditioning preferred for an allogeneic stem cell transplant in BP-CML?
Reduced intensity conditioning is becoming an acceptable option for older patients who are unable to tolerate the intensity of myeloablative conditioning (MAC) with similar OS between the 2 regimens.20 This is largely due to the improved relapse- free survival with myeloablative conditioning balancing out with the lower nonrelapse mortality but higher relapse rate associated with reduced intensity conditioning.20,21 These data are mostly in the setting of CP-CML, with patients with BP-CML being specifically avoided in these studies. Alternative donors were also generally excluded from these studies. Therefore, in the setting of BP-CML, we recommend myeloablative conditioning, if possible, due to the lower risk of relapse. In this scenario, due to age and comorbidities, reduced intensity conditioning was selected.
Differentiating lymphoid blast phase CML from Ph+ ALL
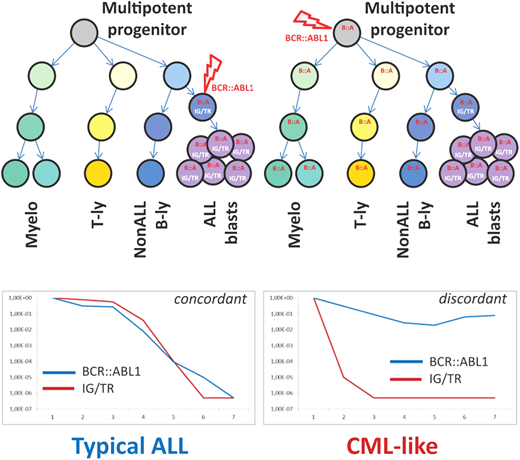
The possibility that some patients diagnosed with Ph+ ALL actually had de novo lymphoid BP and vice versa has been an ongoing issue that, until recently, could only be the subject of conjecture. In the era of minimal residual disease (MRD) monitoring, some advancement in this area has been possible. Parallel MRD monitoring with immunoglobulin/T-cell receptor (Ig/TCR) gene rearrangements and with IKZF1 deletion quantification in a population of pediatric Ph+ ALL had excellent concordance.22 However, in a proportion of patients, DNA-based monitoring of the unique BCR::ABL1 genomic breakpoint revealed consistently higher levels of BCR::ABL1 fusion compared to Ig/TCR and/or IKZF1 deletion MRD quantification.22 Subsequent cell sorting of diagnostic material from patients with discordant MRD results confirmed the presence of the BCR::ABL1 fusion in other hematopoietic cells, such as T lymphocytes, and other myeloid cells, confirming the involvement of a Ph+ pluripotent hematopoietic progenitor similar to CML (Figure 1).22
Schematic illustration of key differences between “typical ALL” and “CML-like” disease. Adapted from Zuna et al. with permission.23
Schematic illustration of key differences between “typical ALL” and “CML-like” disease. Adapted from Zuna et al. with permission.23
Whether these patients, referred to as having CML-like ALL, follow a distinct disease trajectory was explored in a larger cohort of 147 pediatric patients with Ph+ ALL.23 Patients were defined as having CML-like disease (n = 48) if ≥1 MRD time point had >1 log discordance between BCR::ABL1 and Ig/TCR- measured MRD.23 There was no significant difference in the 5-year survival parameters, specifically event-free survival and OS, between patients with CML-like ALL and typical Ph+ ALL. However, the level of MRD in patients with typical Ph+ ALL appeared to correlate with event-free survival and OS, with higher levels of MRD (≥10–3) indicating markedly inferior outcomes.23 In comparison, the MRD level was less concerning and not informative for therapy adjustment in CML-like disease.23 Hyperleukocytosis at diagnosis remains a poor prognostic feature in typical Ph+ ALL, whereas there was no association with outcome in CML-like ALL.23 Further investigation is required to validate these findings on a larger scale, but given the trend to alter therapy in ALL based on rising MRD, there is clearly a subset of patients with CML-like disease in whom a rising level of BCR::ABL1 may not have the same ominous implications.
Investigating advanced CML—the role of NGS
At the time of BP-CML, standard investigation to identify why these specific patients progressed involves cytogenetic analysis and investigation for kinase domain mutations, which remain the best understood mechanism of resistance. However, cytogenetic analysis does not often reveal karyotypic abnormalities in addition to the standard Ph translocation while kinase domain mutations are only identified in ~50% of patients.24 Targeting the BCR::ABL1 kinase domain via NGS has improved sensitivity and therefore detection of kinase domain mutations, observed in almost 80% of AP/BP-CML enrolled in the Next-in-CML study,25 but not all patients are found to harbor these mutations.
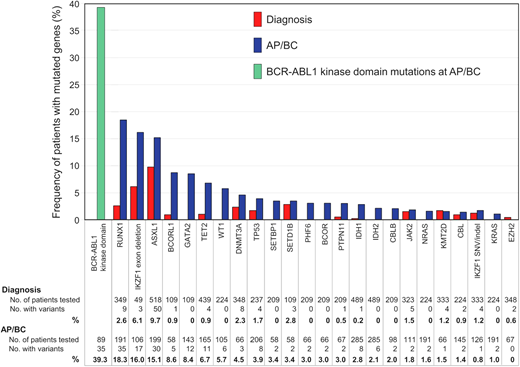
With increasing availability of NGS, our appreciation of the contribution of additional genomic defects in BP-CML has rapidly expanded. While early investigation focused on single gene studies, more recent evaluation includes unbiased interrogation of the whole exome or transcriptome.26,27 All patients at progression to BP-CML harbor additional genetic abnormalities, either involving cancer gene variants or rearrangements involving the Ph chromosome, although the Ph-associated rearrangements are present from diagnosis as opposed to being acquired at progression.26-28 Genomic analysis to date suggests that there are only a relatively small number of clinically relevant genes recurrently mutated in CML, enabling targeted capture of select candidate genes.2,29,30 Genes recurrently mutated in AP/BP-CML are RUNX1, IKZF1, and ASXL1 in descending order, but others have been described (Figure 2).2 Even when kinase domain mutations are identified, a high proportion of these cases is found to have co-occurring additional genetic abnormalities.2 What is also clear is that the mutational subtypes observed in BP-CML are not limited to single nucleotide variants and small insertions and deletions but also involve larger gene deletions, aberrant splicing, and fusions.27,31 Furthermore, the presence of additional genetic abnormalities at diagnosis of CP-CML was more frequent in patients who progressed to BP-CML compared to those with optimal outcomes.26 Interestingly, the presence of genomic abnormalities at diagnosis of CP-CML also predicted for inferior survival and molecular response in patients treated with imatinib,32 suggesting that genomic investigation at diagnosis of CP-CML has the potential to identify higher-risk patients, including those who with a high risk of progressing to BP-CML. However, recent interim data suggest that more potent 2G-TKIs can perhaps ameliorate the adverse impact of additional genetic abnormalities, although not completely negate their effect.33 This adds weight for the inclusion of NGS to the repertoire of tests that could be performed at diagnosis in order to enable optimal TKI selection.
Frequency of mutated cancer genes at diagnosis and AP/BP. The data from 15 studies of patients at diagnosis and 20 studies at AP/BP are reported where cancer genes were mutated in more than 1 patient at diagnosis and/or BP. Only genes listed in the COSMIC Cancer Gene Census are included. Adapted from Branford et al. with permission.2
Frequency of mutated cancer genes at diagnosis and AP/BP. The data from 15 studies of patients at diagnosis and 20 studies at AP/BP are reported where cancer genes were mutated in more than 1 patient at diagnosis and/or BP. Only genes listed in the COSMIC Cancer Gene Census are included. Adapted from Branford et al. with permission.2
CLINICAL CASE 1 (continued)
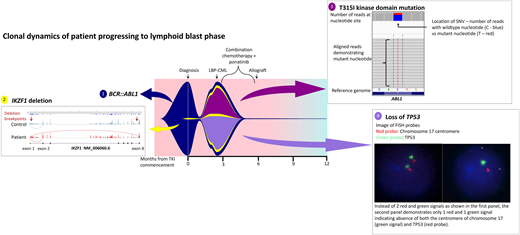
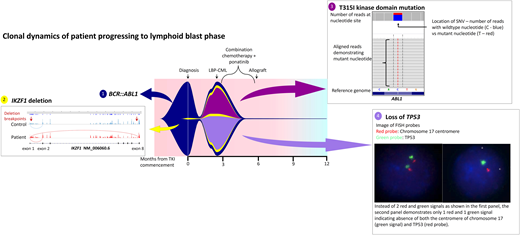
While the bone marrow biopsy specimen confirmed the presence of CD19+ CD20+ CD34+ lymphoblasts, fluorescence in situ hybridization confirmed the loss of 17p and TP53, and kinase domain mutation screening demonstrated emergence of T315I mutations. He was treated with hyperCVAD chemotherapy in combination with ponatinib 45 mg/d and was able to enter a second CP prior to proceeding to an unrelated donor transplant with MAC. Two years post-allograft, he remains in remission with 100% chimerism and undetectable BCR::ABL1 transcripts. He has not been able to commence post-transplant TKI maintenance due to various cytopenias. Interestingly, retrospective NGS investigation demonstrated expansion of a low-level IKZF1 deletion at progression that was detectable at diagnosis (Figure 3).
Fish plot illustrating mutation profile and clonal dynamics of patient 1. This patient progressed to lymphoid blast crisis within 3 months of diagnosis. This figure illustrates the complex clonal dynamics involved, with the fish plot highlighting the primary BCR::ABL1 clone in addition to the 3 subclones, including expansion of the IKZF1 subclone detectable at diagnosis in addition to the acquisition of T315I as well as loss of TP53. Detection of all variants involved NGS, Sanger sequencing, and cytogenetic analysis. The IKZF1 deletion is indicated by aberrant splicing, with the breakpoints indicated by the red arrows. The T315I mutation is shown on NGS while the loss of TP53 is indicated via fluorescence in situ hybridization probes. Combination chemotherapy in addition to ponatinib enabled clearance of the leukemic clone; LBP, lymphoid blast phase.
Fish plot illustrating mutation profile and clonal dynamics of patient 1. This patient progressed to lymphoid blast crisis within 3 months of diagnosis. This figure illustrates the complex clonal dynamics involved, with the fish plot highlighting the primary BCR::ABL1 clone in addition to the 3 subclones, including expansion of the IKZF1 subclone detectable at diagnosis in addition to the acquisition of T315I as well as loss of TP53. Detection of all variants involved NGS, Sanger sequencing, and cytogenetic analysis. The IKZF1 deletion is indicated by aberrant splicing, with the breakpoints indicated by the red arrows. The T315I mutation is shown on NGS while the loss of TP53 is indicated via fluorescence in situ hybridization probes. Combination chemotherapy in addition to ponatinib enabled clearance of the leukemic clone; LBP, lymphoid blast phase.
Discussion points
1. What is the optimal dose of ponatinib in this situation?
The MATCHPOINT study suggested that 30 mg/d ponatinib was the optimal dose in conjunction with chemotherapy to minimize associated toxicity based on the EffTox model. However, in this setting, the presence of the T315I mutation dictated the use of the higher ponatinib dose to maximize a response and enhance the prospects of achieving a second CP.
2. Would identification of the IKZF1 deletion at diagnosis trigger any alteration to the approach?
This patient was deemed high ELTS risk at diagnosis and so a 2G-TKI was selected for frontline therapy. While detection of a low-level IKZF1 deletion would not necessarily alter the initial management of this patient at diagnosis beyond ensuring appropriate TKI selection (such as a 2G-TKI as opposed to frontline imatinib) and maintaining TKI intensity, the presence of the IKZF1 clone, often seen in BP-CML (Figure 2), may have indicated the potential for progression to BP-CML despite the early response to TKI. It may have been prudent to perform early tissue typing, although there is no definitive evidence to support this.
3. Is there benefit to TKI maintenance after allograft?
TKI administration after allograft has been demonstrated to be beneficial in Ph+ ALL, improving leukemia-free survival,34 but similar utility in CML is less evident. A recent Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research study analyzed clinical outcomes for 390 CML transplants, with 89 patients receiving TKI maintenance after allograft.35 A range of TKIs were used posttransplant, including imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib. Outcome measures did not significantly differ between those who received maintenance compared with those who did not. For patients who had evaluable data following day +100, the 5-year OS was 61% respectively in the maintenance TKI group vs 57% if patients did not receive TKI posttransplant (P = .61).35 Likewise, the 5-year leukemia-free survival did not differ between the 2 groups either.35 This study carries inherent bias, as only patients who survived to day +100 were evaluable, and early relapses would not have been captured by the landmark analysis in addition to higher-risk individuals being selected for maintenance treatment. Furthermore, while this study did not demonstrate a benefit for maintenance TKI after allograft, specific additional considerations may influence this decision. The selection of conditioning regimen may be a factor as while there is no difference in OS between a MAC compared to a RIC protocol, there is a higher potential for early relapse with RIC.20 Measurable BCR::ABL1 and/or history of BP-CML prior to transplant can support TKI maintenance, whereas the presence of posttransplant complications, such as poor engraftment, infection, and graft-versus-host disease, may curtail the potential for TKI initiation altogether.
Novel therapeutic strategies in BP-CML
The primary goal of therapy in BP-CML, irrespective of whether the disease has progressed from CP or presents in de novo BP-CML, is to return to CP-CML once more and proceed to an allogeneic transplant if patients are eligible. However, there is no consistent strategy recommended to achieve this. The low frequency of de novo BP-CML but also transformed disease contributes to the difficulty of developing high-powered clinical trials to investigate therapeutic options in BP-CML. TKI alone is generally inadequate to revert BP-CML to CP36 as only 31% of patients achieve a major hematologic response even with ponatinib monotherapy.37 Multiagent chemotherapy in conjunction with TKI is required if patients can tolerate therapy intensity to maximize entering a second CP.38 The chemotherapy regimen is generally dictated by the blast lineage, with more myeloid-directed combinations being used in myeloid BP-CML, whereas lymphoid BP-CML is generally treated with ALL-directed regimens, such as hyperCVAD. The choice and dose of TKI are not always clear, but combination therapy using more potent TKIs does correlate with improved outcomes, including relapse-free survival.38 Consequently, a more efficacious and uniform treatment model is required.
CLINICAL CASE 3
A 70-year-old woman presents with marked leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 213 × 109/L) with circulating myeloblasts of 5%. There was associated splenomegaly, with the splenic edge extending 10 cm below the costal margin. The bone marrow biopsy specimen confirmed 10% myeloblasts and a standard Ph-chromosome alone. She was diagnosed with CP-CML and commenced on nilotinib 300 mg twice daily on a clinical trial. She developed marked pancytopenia (hemoglobin <70 g/L, neutrophil count <0.2 × 109/L, and platelets <20 × 109/L) with nilotinib, and despite dose reduction and treatment interruption, this failed to resolve. She was withdrawn from the study and switched to imatinib with recurrence of pancytopenia, necessitating long treatment interruptions. Transitioning to 50 mg/d dasatinib had the same outcome, and her BCR::ABL1 slowly increased in the presence of persistent pancytopenia. She was transitioned to the phase 1 asciminib study where treatment intensity was maintained with aggressive transfusion support. However, following 6 months of asciminib with dose interruption and modification for pancytopenia, she progressed to myeloid BP with acquisition of trisomy 8 on cytogenetic analysis. By this stage, she was 72 years old and not fit for intensive chemotherapy, nor was she an allogeneic stem cell transplant candidate. Ponatinib 45 mg/d was commenced, and to maintain treatment intensity, she was once more supported aggressively with transfusions. She was able to enter a second CP within 6 months, achieving a complete cytogenetic remission for the first time and maintained a good response on ponatinib monotherapy for a further 3 years before progressing to a second myeloid BP, succumbing to her disease shortly after.
Discussion points
1. Maintaining TKI intensity in patients with marked pancytopenia
While this patient was high risk by ELTS score, treatment intensity could not be maintained due to the associated marked cytopenia. This would have contributed to the risk of progression. Patients with high-risk disease and cytopenia would ideally be considered for an allogeneic stem cell transplant at an early stage (Table 3) if fitness was adequate. However, this patient was not a transplant candidate, and so when progression to myeloid BP occurred, the preference was to maintain ponatinib dose intensity to maximize a response.
2. Role of transfusions and cytokines to enable dose intensity to be maintained
Maintaining dose intensity is vital to maximize response and minimize transformation potential. Managing grade 3 cytopenias may necessitate platelet and red cell transfusion support to permit adequate TKI intensity as opposed to dose interruptions. Judicious use of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor to manage neutropenia is also recommended. Early cytopenias are often secondary to eradication of the CML clones that are primarily responsible for most hematopoiesis in the bone marrow, and not maintaining treatment intensity will essentially leave the CML inadequately treated. The benefits of maintaining treatment intensity need to be balanced with the competing risks of bleeding and infection. While this is largely an evidence-free zone, we used this strategy to manage this patient's BP and maximize ponatinib dosing.
MATCHPOINT
While ponatinib is certainly an attractive choice of TKI for use in BP-CML given potency and ability to overcome a number of highly resistant kinase domain mutations, optimal dosing and the ideal chemotherapy regimen to be combined with ponatinib needs clarity. The combination of ponatinib in addition to fludarabine, cytarabine, idarubicin chemotherapy was investigated in a phase 1/2 study that recruited across the United Kingdom. Recruited patients (n = 17) had myeloid, lymphoid, or mixed-lineage BP-CML and had a combination of de novo and progressed disease with a median age of 33 years (range, 16-64 years).39 The aim of the study was to identify the optimal dose of ponatinib in combination with conventional chemotherapy and capitalized on an EffTox design, which is a Bayesian adaptive dose-finding schedule that rigorously investigates both efficacy and toxicity.40 The optimal dose of ponatinib was identified to be 30 mg/d, and of the 16 patients evaluable for the primary outcome, 69% (n = 11) entered a second CP-CML following 1 cycle of treatment, including 5 patients achieving a BCR::ABL1 ≤0.1%IS.39 Dose-limiting toxicity was observed in 4 patients, including 1 episode of fulminant cardiomyopathy and another with cerebral vein sinus thrombosis. Twelve patients were able to proceed to an allogeneic stem cell transplant with a median follow-up of 41 months. All 5 patients not transplanted died within 7 months of study entry, which included 3 of the 4 patients with dose-limiting toxicity.39 Five of the transplanted patients also died, 2 from disease relapse and the remainder secondary to transplant-related complications.39 While further investigation is required, this study demonstrates that the MATCHPOINT approach of combining 30 mg/d ponatinib with FLAG-Ida chemotherapy is a feasible strategy to salvage patients in BP-CML in order to bridge to an allogeneic stem cell transplant. However, the long-term OS remains <50% despite this intense treatment strategy.
Dasatinib and decitabine
Another recent study examined the combination of dasatinib and decitabine in advanced phase CML. Using a 3 + 3 design, doses of either 10 or 20 mg/m2 decitabine for 10 days with either 100 or 140 mg dasatinib daily were investigated.41 Thirty patients (including 19 in BP-CML, 7 AP-CML, and 4 Ph+ AML) were enrolled with a median age of 51 years (range, 18-89 years).41 Dose- limiting toxicity was observed in only 2 patients, but this was only with the higher dasatinib dose of 140 mg, one with grade 3 cardiac failure and another with a cardiac arrest following a myocardial infarction. Twenty-seven patients completed the minimum 2 cycles for response evaluation, and 19 patients achieved a hematologic response, whereas no response was observed in patients with Ph+ AML.41 A complete cytogenetic response and major molecular response were observed in 10 and 9 patients, respectively. Median OS was 13.8 months, with a superior survival among patients who achieved a hematologic response compared to nonresponders (median not reached vs 4.65 months, respectively; P < .001).41 However, 6 of the 19 responders relapsed at a median of 1.4 months, including 5 patients with BP-CML who all succumbed to their disease.41 Eight patients were successfully bridged to an allograft, and while <50% of responders proceeded to a transplant, there was a trend to improved OS if an allograft was performed. These preliminary data demonstrate that dasatinib combined with decitabine can be a safe and feasible option in advanced CML, even in older patients who may not be able to tolerate intensive chemotherapy.
Future directions
CML that presents or advances beyond the chronic phase remains the biggest challenge for CML clinicians, and frustratingly, very limited progress has been made in this setting. Unfortunately, very few clinical trials have been conducted to provide some level of consensus about the best approach. Ongoing genomic investigation in CML in all phases will continue to improve our understanding of the biology of BP-CML, hopefully eventually identifying a genetic signature for patients that is sufficiently high risk for progression to justify testing novel approaches designed to modify that risk. While more data are required, the preliminary findings from the studies investigating novel approaches will hopefully stimulate further innovative trials in the setting of blast phase aiming to make meaningful progress in improving outcomes in this challenging setting.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
Naranie Shanmuganathan received research funding from Novartis and honoraria from Takeda.
Timothy P. Hughes has received research funding and honoraria from Novartis and Bristol-Myers Squibb and honoraria from Takeda.
Off-label drug use
Naranie Shanmuganathan: No off label drug use discussed.
Timothy P. Hughes: No off label drug use discussed.