Abstract
Intrinsic factors such as genetic lesions, anti-apoptotic proteins, and aberrant signaling networks within leukemia cells have long been the main focus of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) research. However, over the past decade, it became increasingly clear that external signals from the leukemia microenvironment make pivotal contributions to disease progression in CLL and other B-cell malignancies. Consequently, increasing emphasis is now placed on exploring and targeting the CLL microenvironment. This review highlights critical cellular and molecular pathways of CLL-microenvironment cross-talk. In vitro and in vivo models for studying the CLL microenvironment are discussed, along with their use in searching for therapeutic targets and in drug testing. Clinically, CXCR4 antagonists and small-molecule antagonists of B cell receptor (BCR)-associated kinases (spleen tyrosine kinase [Syk], Bruton's tyrosine kinase [Btk], and PI3Kδ) are the most advanced drugs for targeting specific interactions between CLL cells and the miocroenvironment. Preclinical and first clinical evidence suggests that high-risk CLL patients can particularly benefit from these alternative agents. These findings indicate that interplay between leukemia-inherent and environmental factors, nature and nurture determines disease progression in CLL.
Introduction
In the bone marrow (BM) and secondary lymphatic tissues, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells engage in complex yet incompletely defined cellular and molecular interactions with stromal cells and matrix, collectively referred to as the “microenvironment.”1 In vitro models and gene-expression profiles (GEPs) have defined critical pathways for cross-talk between CLL cells and the microenvironment (Figure 1). These interactions affect CLL-cell survival and proliferation and confer drug resistance that may be responsible for residual disease after conventional therapy. Key cellular players are mesenchymal stromal cells, monocyte-derived nurse-like cells (NLCs), and T cells. The BCR plays a central role in the maintenance and expansion of the CLL clone, involving critical downstream kinases such as the spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk), Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk), and PI3Kδ. Chemokine receptors such as CXCR4 and CXCR5, in concert with adhesion molecules (VLA-4 and others), regulate CLL-cell trafficking and tissue homing via tissue gradients of the respective ligands. TNF family members such as the CD40 ligand, B cell-activating factor of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family (BAFF), and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) activate CLL cells via corresponding receptors, promoting immune recognition and/or survival and expansion of the leukemia cells. Another layer of complexity is added by the fact that CLL cells are not simply “seeds” that grow in the supportive soil of the microenvironment. Upon BCR activation, CLL cells secrete cytokines such as CCL3, which shape the microenvironment by attracting accessory cells such as T cells and monocytes. Clinically, the most advanced approaches for molecular targeting of the microenvironment are CXCR4 antagonists and B-cell kinase inhibitors, which disrupt regulatory loops between CLL cells and the microenvironment and have shown encouraging results in first, ongoing clinical trials. These findings demonstrate that the CLL microenvironment has become a highly dynamic translational research field.
Molecular interactions in the CLL microenvironment. Molecular interactions between CLL and stromal cells in the BM and/or lymphoid tissue microenvironments that are considered important for CLL-cell survival and proliferation, CLL-cell homing, and tissue retention. Contact between CLL cells and NLCs or BMSCs is established and maintained by chemokine receptors and adhesion molecules expressed on CLL cells. NLCs express the chemokines CXCL12 and CXCL13, whereas BMSCs predominantly express CXCL12. The chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CCR7 are additional chemokine receptors on CLL cells that are involved in lymphatic tissue homing. NLCs and BMSCs attract CLL cells via the G protein–coupled chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CXCR5, which are expressed at high levels on CLL cells. Integrins, particularly VLA-4 integrins (CD49d), expressed on the surface of CLL cells cooperate with chemokine receptors in establishing cell-cell adhesion through respective ligands on the stromal cells (VCAM-1 and fibronectin). NLCs also express the TNF family members BAFF and APRIL, providing survival signals to CLL cells via corresponding receptors (BCMA, TACI, and BAFF-R). CD38 expression allows CLL cells to interact with CD31, the ligand for CD38 that is expressed by stromal and NLCs. Ligation of CD38 activates ZAP-70 and downstream survival pathways. Self- and/or environmental Ags are considered key factors in the activation and expansion of the CLL clone by activation of the BCR and its downstream kinases. Stimulation of the BCR complex (BCR and CD79a,b) induces downstream signaling by recruitment and activation of Syk, Btk, and PI3Ks. Finally, BCR stimulation and coculture with NLCs also induces CLL cells to secrete chemokines (CCL3, CCL4, and CCL22) for the recruitment of immune cells (T cells and monocytes) for cognate interactions. CD40L+ (CD154+) T cells are preferentially found in CLL-proliferation centers,38 and can interact with CLL cells via CD40. (Modified with permission from Burger et al.1 )
Molecular interactions in the CLL microenvironment. Molecular interactions between CLL and stromal cells in the BM and/or lymphoid tissue microenvironments that are considered important for CLL-cell survival and proliferation, CLL-cell homing, and tissue retention. Contact between CLL cells and NLCs or BMSCs is established and maintained by chemokine receptors and adhesion molecules expressed on CLL cells. NLCs express the chemokines CXCL12 and CXCL13, whereas BMSCs predominantly express CXCL12. The chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CCR7 are additional chemokine receptors on CLL cells that are involved in lymphatic tissue homing. NLCs and BMSCs attract CLL cells via the G protein–coupled chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CXCR5, which are expressed at high levels on CLL cells. Integrins, particularly VLA-4 integrins (CD49d), expressed on the surface of CLL cells cooperate with chemokine receptors in establishing cell-cell adhesion through respective ligands on the stromal cells (VCAM-1 and fibronectin). NLCs also express the TNF family members BAFF and APRIL, providing survival signals to CLL cells via corresponding receptors (BCMA, TACI, and BAFF-R). CD38 expression allows CLL cells to interact with CD31, the ligand for CD38 that is expressed by stromal and NLCs. Ligation of CD38 activates ZAP-70 and downstream survival pathways. Self- and/or environmental Ags are considered key factors in the activation and expansion of the CLL clone by activation of the BCR and its downstream kinases. Stimulation of the BCR complex (BCR and CD79a,b) induces downstream signaling by recruitment and activation of Syk, Btk, and PI3Ks. Finally, BCR stimulation and coculture with NLCs also induces CLL cells to secrete chemokines (CCL3, CCL4, and CCL22) for the recruitment of immune cells (T cells and monocytes) for cognate interactions. CD40L+ (CD154+) T cells are preferentially found in CLL-proliferation centers,38 and can interact with CLL cells via CD40. (Modified with permission from Burger et al.1 )
The Cellular microenvironment in CLL
BMSCs and other MSCs
BM stromal cells (BMSCs) were the first stromal cells characterized to support CLL cells.2–4 Normal hematopoiesis depends on BMSCs, which provide attachment sites and growth factors to hematopoietic precursors. In CLL, BMSCs are thought to function in a similar fashion, creating niches within the BM in which CLL cells lodge and are nourished and protected from cytotoxic agents. CLL cells have a high affinity for BMSCs: coculture with BMSCs results in the adhesion and rapid, spontaneous migration of a fraction of CLL cells beneath and underneath the BMSCs (pseudoemperipolesis), inducing a cobblestone-like appearance4 that depends upon CXCR4 and VLA-4 expression by leukemia cells.4 Consequently, the protective effects of BMSCs are largely dependent on close proximity between CLL and stromal cells.3,5 Murine and human BMSCa are very similar in their capacity to protect CLL cells,5 and a recent murine in vivo model of CLL6 also demonstrated that the murine BM microenvironment was adequate for supporting CLL-cell growth, suggesting that key cellular and molecular pathways in the BM are evolutionarily conserved between mice and humans.
BMSCs are of mesenchymal origin and are similar to actin (αSMA+)–positive mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) in other tissues such as the secondary lymphatic tissues. Dense infiltration with αSMA+ stromal cells in lymphatic tissues from CLL patients7 suggests that interactions between CLL cells and this type of stromal cells plays an important role even outside of the BM. Follicular dendritic cells (FDCs), another cell type present in lymphatic tissues, can also support CLL cells,8 although the comparability of the FDC cell line used in this study to FDCs in vivo is questionable. Interestingly, the cross-talk between CLL and MSCs is bidirectional, causing activation of both CLL cells and MSCs.9 CLL cells have a high affinity for BMSCs and the CXCR4-CXCL12 axis is critical for this interaction.
NLCs
NLCs differentiate in vitro from monocytes into large, round, adherent cells that attract CLL cells and protect them from undergoing spontaneous or drug-induced cell death in a contact-dependent fashion.10,11 Because these cells share features in common with thymic nurse cells that nurture developing thymocytes, we designated these cells “nurse-like cells,” or NLCs.10 NLCs can be found in the spleen and secondary lymphoid tissue of patients with CLL,11,12 and thus represent a model for the microenvironment in secondary lymphatic tissues. This is supported by the notion that GEPs of CLL cells after NLC coculture13 are strikingly similar to GEPs of CLL cells isolated from secondary lymphatic tissues,14 which show signs of BCR and NF-κB activation and up-regulation of BCR target genes such as CCL3 and CCL4.13,14 The diverse molecular mechanisms of CLL-NLC cross-talk have been extensively studied,10–13,15–20 and have revealed important pathways and therapeutic targets of CLL-microenvironment cross-talk. For example, NLCs express CXCL12,21 CXCL13,12 CD31, plexin B1,16 BAFF, APRIL,15 and vimentin.10,18 These findings, along with the GEP data, suggest that NLCs represent a highly relevant in vitro model for studying the CLL lymphatic tissue microenvironment. High levels of CD68 make NLCs comparable to CD68+ lymphoma-associated macrophages in follicular lymphoma and other B-cell lymphomas, and suggest that NLCs could be a model system for studying the lymphatic tissue microenvironment in other B-cell malignancies.
T lymphocytes
The importance of T cells remains one of the most controversial areas in CLL research. In untreated CLL patients, the overall number of circulating T cells, oligoclonal in both the CD4 and the CD8 compartment, is increased. It is unresolved whether these T cells are expanded because of interactions with the CLL clone, with microbial antigens that are more prevalent in CLL patients, or for other reasons. To make matters more complex, T cells can either suppress or stimulate the expansion of the CLL clone. Another layer of complexity is added by functional impairments of T cells from CLL patients, which fail to form appropriate immunological synapses with CLL cells,22 a dysfunction that can be reversed with the immunomodulatory drug lenalidomide.22,23 In tissue areas of CLL-cell proliferation, called proliferation centers or pseudofollicles, activated CD4+ T cells colocalize with proliferating CD38+ CLL cells,24 suggesting that T-cell subpopulations promote the expansion of the CLL clone. This is supported by recent in vivo evidence in a CLL-transfer model into immunodeficient mice demonstrating that activated CD4+ T cells support CLL-cell proliferation.6
Selected molecular pathways in the CLL microenvironment
The CXCR4-CXCL12 axis
The CXCR4 chemokine receptor (CD184) is expressed at high levels on the surface of peripheral blood CLL cells4 and mediates leukemia cell chemotaxis, migration across vascular endothelium, actin polymerization, and migration beneath and underneath BMSCs in response to CXCL12 gradients (pseudoemperipolesis).4 CXCL12 also displays a direct prosurvival effect in CLL.10,15 CXCR4 surface expression is regulated by its ligand CXCL12 (previously called stromal cell-derived factor-1/SDF-1) via receptor endocytosis (Table 1).4 This characteristic can be used to distinguish tissue (lymphatic and BM derived) from blood CLL cells, which express low or high CXCR4 levels, respectively.4,14 Proliferating Ki-67+ CLL cells from BM and lymphatic tissue display significantly lower levels of CXCR4 and CXCR5 than nonproliferating CLL cells.25 In vivo deuterium (2H) labeling of CLL cells revealed an enrichment of CLL cells expressing lower CXCR4 surface levels in the CD38+/CD5bright fraction, along with increased 2H incorporation.26 These in vivo data indicate that CLL subclones with lower blood CXCR4 surface levels are a fraction of cells that has recently exited the tissues into the blood. BCR signaling results in the down-modulation of CXCR4,17,27 along with enhanced chemotaxis toward CXCL12 and CXCL13.17 This may explain why ZAP-70+ CLL cells display increased chemotaxis and survival in response to CXCL12 compared with ZAP-70− CLL cells,28 given that ZAP-70 expression is associated with a higher responsiveness to BCR stimulation.29 CD38+ CLL cells also display higher levels of chemotaxis,30 and CD38 activation enhances chemotaxis toward CXCL12, whereas a blocking anti-CD38 mAb inhibits chemotaxis.31 CXCR4 signaling in CLL cells is pertussis toxin–sensitive and induces calcium mobilization, activation of PI3Ks,4 p44/42 MAPKs,10 and serine phosphorylation of STAT3.32 CXCR4 signaling can be inhibited by isoform-selective PI3K inhibitors,33 Syk inhibitors,17 and Btk inhibitors,34 leading to impaired migration of normal B cells and CLL cells.
Chemokine receptors (top) and inducible chemokines (bottom) involved in cross-talk between CLL cells and the microenvironment

CXCR4 can be specifically blocked by CXCR4 antagonists,35 which inhibit CLL-cell activation by CXCL12 and reverse, at least in part, stomal cell–mediated drug resistance.32 These data are the basis for an ongoing clinical trial in relapsed CLL patients, in which patients are treated with a combination of rituximab and plerixafor, a small-molecule CXCR4 antagonist. This is a proof-of-principle trial to determine whether leukemia cells can be mobilized from the tissues using a CXCR4 antagonist and then be targeted outside of the protective tissues. Preliminary data from this trial indicate a plerixafor dose–dependent mobilization of CLL cells from the tissues to the blood.36
The CXCR5-CXCL13 axis
CXCR5 (CD185) is the receptor for the chemokine CXCL13, which regulates lymphocyte homing and positioning within lymph follicles (Table 1). CXCR5 gene-deleted mice display defective formation of primary follicles and germinal centers in the spleen and Payer patches and lack inguinal lymph nodes. CXCL13 gradients induce recruitment of circulating naive B cell to follicles,37 and are involved in the microanatomic positioning of B cells within the germinal center.37 CLL cells express high levels of CXCR5,12 and stimulation with CXCL13 induces activation via Gi proteins, PI3Ks, and p44/42 MAPK, resulting in actin polymerization, CXCR5 endocytosis, and chemotaxis.12 CXCL13 mRNA and protein are expressed by NLC in vitro and in vivo.12 These data suggest that CXCR5 plays a role in CLL-cell positioning and cognate interactions between CLL and CXCL13-secreting NLCs in lymphoid tissues.
CCL3, CCL4, and CCL22
Activated CLL cells secrete CCL3, CCL4,13 and CCL22,38 which are chemoattractants for T lymphocytes and monocytes (Table 1). CCL3 and CCL4 normally are secreted by B cells after activation via the BCR and CD40 ligand.39 CLL cells secrete CCL3 and CCL4 in response to BCR stimulation and in coculture with NLCs,13 which are sensitive to inhibition of BCR signaling, using, for example, a Syk or Btk inhibitor.13,17 CLL patients display elevated plasma levels of CCL3 and CCL4,13 and plasma levels of CCL3 were strongly associated with established prognostic markers and time to treatment.40 A multivariable analysis revealed that CCL3, advanced clinical stage, poor-risk cytogenetics, and CD38 expression were independent prognostic markers in a cohort of 351 CLL patients.40 Conceivably, CLL cell–derived CCL3 may induce trafficking of T cells to activated, CD38+/Ki-67+ CLL cells for cognate T-CLL cell interactions that foster CLL-cell proliferation.13,24,41 Conceptually, by attracting T cells and other immune cells, CLL-cell–derived chemokines foster the coevolution of CLL cells and their supportive microenvironment, thereby actively creating a favorable microenvironment.
Adhesion molecules
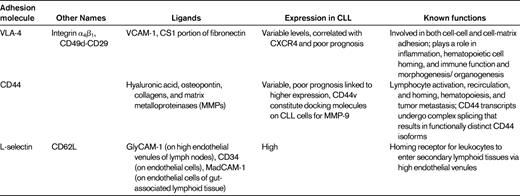
Integrins are heterodimeric glycoproteins consisting of various α and β subunits, the function of which is to mediate cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion. β1 integrins are very late activation antigens (VLAs) that have the same β1 subunit but various α chains (α1-α6). The α4β1 integrin VLA-4 (CD49d) is a receptor for fibronectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1/CD106). VLA-4 plays a particularly important role in interactions between normal and malignant hematopoietic cells and the BM microenvironment. VLA-4 integrins cooperate with CXCR4 in CLL-cell adhesion to BMSCs.4 Moreover, VLA-4 expression on CLL cells has prognostic impact,42,43 indicating the relevance of these interactions in vivo. These studies indicate that VLA-4 integrins play a key role in the adhesion of CLL and other leukemia cells to stromal cells and the extracellular matrix. Other important adhesion molecules in CLL include L-selectin (CD62L) and CD44 (Table 2).
CD40-CD154 interactions
Within proliferation centers, a significant number of T cells display CD40 ligand (CD154)38,44 that can bind to CD40 on CLL cells, rescuing them from apoptosis.45 Conversely, CD40 cross-linking also induces up-regulation of CD80 and CD54 and turns nonimmunogenic CLL cells into effective T-cell stimulators.46 CLL cells engineered to express CD154 by adenoviral gene transfer can cross-link CD40 on bystander CLL cells and induce the same sequence of activation and immune recognition. CLL patients infused with CLL cells transduced in vitro with an adenovirus encoding CD40L (Ad-CD154)47 can make antibodies to ROR1,48 an oncofetal antigen restricted to CLL cells, indicating that this approach can overcome immune tolerance. These data suggest that CD40 activation of CLL cells can result in different outcomes that are not mutually contradictory: activation of prosurvival and proliferation pathways if triggered by CD154+ T-cells in the context of proliferation centers, or immune recognition and induction of a specific immune response if triggered in the context of Ad-CD154–transduced CLL cells.
BAFF and APRIL
BAFF and APRIL are related TNF family ligands that bind to members of the TNF receptor family such as B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) and transmembrane activator and calcium modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI). BAFF also binds another TNF receptor, the BAFF receptor (BAFF-R). Binding to heparin sulfate proteoglycans allows for tissue retention of APRIL. Via BCMA, TACI, and BAFF-R expressed on the CLL cells, NLC-derived BAFF and APRIL induce activation of the canonical NF-κB pathway and protect CLL cells from apoptosis.15,49 Male v-Myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog (c-Myc) transgenic mice develop a CD5 B-cell leukemia resembling CLL after cross-breeding with Baff-transgenic mice,50 with Baff-induced enhancement of c-Myc, suggesting an important relationship between BAFF and c-MYC in CLL. Aging April-transgenic mice develop an expansion of CD5+ B1 B cells with organ infiltration, which can be reversed with anti-April mAbs.51
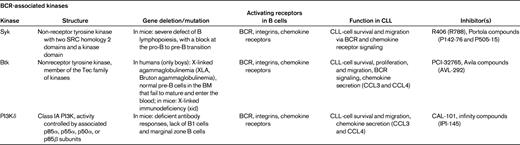
BCR and BCR-associated kinases (Syk, Btk, and PI3K delta)
Currently, we assume that in an appropriate microenvironment, the BCRs of CLL cells become engaged by microbial or auto-antigens,52–54 which, along with other costimulatory signals, promote the expansion of the CLL clone. Several lines of evidence suggest that antigen stimulation and BCR-derived signals play a critical role in the pathogenesis and prognosis of CLL.44,52 First, the prognosis of CLL patients is correlated with the number of somatic mutations in the variable regions of the BCR. Second, CLL cells express a restricted set of BCRs with Ig heavy-chain variable gene sequences that are identical or stereotyped in subsets of patients, suggesting that these BCRs bind similar antigens that are relevant to the pathogenesis of CLL. Third, Ig-unmutated and/or ZAP-70+ patients preferentially respond to BCR stimulation29 and display GEPs suggesting activation downstream of the BCR.55 BCR signaling is a complex process. The BCR is composed of an antigen-specific membrane Ig paired with Ig-α/Ig-β heterodimers (CD79α/CD79β). Engagement of BCRs by antigen induces phosphorylation of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs in the cytoplasmic tails of Ig-α and Ig-β, with subsequent recruitment of Syk to BCR microclusters, followed by downstream activation of Btk and PI3Ks (Table 3). Upon phosphorylation, Syk, Btk, and PI3Ks propagate BCR-derived signals by activating downstream signaling pathways, including calcium mobilization and activation of AKT kinase, ERK1/2, and myeloid cell leukemia-1 (MCL-1). The notion that ZAP-70+29 and unmutated CLL cells20,56 are more responsive to BCR stimulation and other microenvironmental signals28 suggests that patients with high-risk disease features may be particularly well suited for alternative treatments that target the microenvironment. Indeed, early clinical data from ongoing trials with the Btk inhibitor PCI-3276557 and the PI3K inhibitor CAL-10158 suggest that high-risk CLL patients respond well to these agents that disrupt CLL-microenvironment interactions.
In vivo evidence
In vivo studies of the CLL microenvironment have been decelerated by the lack of suitable mouse models and limited access to primary CLL tissue samples. However, this has recently changed after publication of a landmark paper.14 Herishanu et al explored GEPs of CLL cells isolated from different tissues (blood, BM, and lymphatic tissues)14 which revealed BCR and NF-κB activation in CLL cells in the lymphatic tissues,14 indicating that the lymphatic tissues are a key site of CLL activation and proliferation. Activation of these pathways was particularly prominent in high-risk CLL patients, suggesting more effective BCR signaling in this subtype in vivo. Recent studies using mouse models are also starting to explore the question of how different elements of the microenvironment contribute to CLL pathogenesis. For example, a recent murine adoptive-transfer model demonstrated a central role of T cells in the progression of CLL in this setting.6
Therapeutic targeting of CLL-microenvironment cross-talk
The CXCR4-CXCL12 axis
CXCR4 antagonists, such as plerixafor (Mozobil, AMD3100) and T140 analogs, disrupt CLL-cell adhesion to BMSCs32 and mobilize CLL cells from protective tissue microenvironments to the blood, making them more accessible to conventional drugs. Targeting the CXCR4-CXCL12 axis is currently being explored in a first clinical trial in CLL patients.36 CXCR4 antagonists were initially developed for the treatment of HIV, in which CXCR4 functions as a coreceptor for virus entry into T cells. In these first trials, CXCR4 antagonists were observed to induce leukocytosis and thus were developed for mobilization of hematopoietic progenitors in the context of autologous stem cell mobilization in myeloma and lymphoma patients. This is the currently approved indication for plerixafor. The ongoing CLL trial combines plerixafor with rituximab, and preliminary data indicate a plerixafor dose–dependent CLL-cell mobilization to the blood and show the safety of this drug combination.36 Future studies in CLL could combine a CXCR4 antagonist with established cytotoxic agents or antibodies or in the setting of minimal residual disease, in which these agents could help to mobilize and eliminate residual CLL cells from tissue sanctuaries.35
BCR-associated kinase inhibitors
Orally bioavailable inhibitors of kinases downstream of the BCR are currently tested in first clinical trials in CLL patients, and are generating excitement because of promising early response data and benign side effect profiles, particularly the lack of myelosuppression.57–59 These new targeted agents are the Syk inhibitor fostamatinib disodium,59 the Btk inhibitor PCI-32765,60 and the PI3Kδ inhibitor CAL-10161 (Table 3). Characteristically, these kinase inhibitors induce rapid lymph node shrinkage, along with a transient lymphocytosis during the first weeks of treatment, which is presumably due to mobilization of CLL cells from the tissues into the blood. Inhibition of signaling through CXCR4, and potentially other chemokine receptors and adhesion molecules,17,33,34 has been proposed as the basis for this remarkable phenomenon. Future research on these agents will need to address the question of whether CLL-cell mobilization is a prerequisite for the efficacy of these agents. Mobilized into the blood, CLL cells may simply die from neglect (ie, a lack of tissue-derived survival and growth signals). However, in vitro data suggest that these agents also effectively block signaling downstream of the BCR and other surface receptors,17,62 implying dual effects on CLL cells: deprivation from exogenous survival signals and blockade of prosurvival signaling.
Targeting of BCR signaling interferes not only with pathways related to survival, but also with tissue homing and retention of CLL cells. Specifically, BCR signaling within the lymphatic tissues can enhance responsiveness of CLL cells to chemokines, which then can result in the retention of such activated CLL cells. We previously reported that BCR engagement on CLL cells induces an adhesive phenotype with increased expression of adhesion and costimulatory molecules, along with increased chemotaxis toward the chemokines CXCL12 and CXCL13 and increased migration beneath BM stromal cells.17 These responses were more noticeable in ZAP-70+ cases and were sensitive to inhibition by R406, a small-molecule Syk inhibitor.17 A question remaining is what is the mode of BCR activation and the nature of antigen(s) that stimulate CLL BCRs. Indirect evidence based on cytokine (CCL3 and CCL4) secretion and GEPs of CLL cells cultured with NLCs,13 which are remarkably similar to GEPs of activated CLL cells isolated from lymph nodes, suggests that such BCRs can react with antigen on stromal cells (ie, NLCs).14 Direct binding of CLL BCRs to vimentin on the surface of stromal cells (BMSCs and NLCs) and vimentin-induced activation support this concept.18 Nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA (MYHIIA) is an alternative antigen derived from apoptotic cells that is recognized by CLL-cell mAbs.53
Conclusion
During the coming years, increasing emphasis will be placed on targeting the microenvironment in CLL. Clinically, CXCR4 and the BCR-associated kinases Syk, Btk, and PI3Kδ represent the most advanced therapeutic targets in the complex cross-talk between CLL cells and their microenvironment. Despite the current enthusiasm for these new targeted approaches, which is justified based on the clinical activity and the lack of major side effects such as myelosuppression,57–59 the precise mechanism of action of these agents and the potential benefit of combinations with conventional agents remain to be explored. Additional in vivo and in vitro studies will accelerate the development of these new concepts and will help to define the best drug combinations. Moreover, numerous other pathways of CLL-microenvironment interactions, such as VLA-4 or BAFF and APRIL, represent alternative therapeutic targets that are likely to be explored in the near future.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a CLL Global Research Foundation grant and by a Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) grant.
Disclosures
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The author has received research funding from Noxxon, Calistoga, and Pharmacyclics and has consulted for Noxxon, Pharmacyclics, Genzyme, and Celgene. Off-label drug use: Plerixafor for leukemia cell mobilization.
Correspondence
Jan A. Burger, MD, PhD, Department of Leukemia, Unit 428, The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center, PO Box 301402, Houston, TX 77230; Phone: (713) 563-1487 or (713) 792-1865; Fax: (713) 794-4297; e-mail: jaburger@mdanderson.org.