Abstract
Dyskeratosis congenita (DC) is a multisystem inherited syndrome exhibiting marked clinical and genetic heterogeneity. In its classic form, it is characterized by mucocutaneous abnormalities, BM failure, and a predisposition to cancer. BM failure is the principal cause of premature mortality. Studies over the last 15 years have led to significant advances, with 8 DC genes (DKC1, TERC, TERT, NOP10, NHP2, TIN2, C16orf57, and TCAB1) having been characterized. Seven of these are important in telomere maintenance either because they encode components of the telomerase enzyme complex (DKC1, TERC, TERT, NOP10, NHP2, and TCAB1) or the shelterin complex (TINF2). DC is therefore principally a disease of defective telomere maintenance and patients usually have very short telomeres. The genetic advances have led to the unification of DC with several other disorders, including the severe multisystem disorders Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson and Revesz syndromes, as well as a subset of patients with aplastic anemia, myelodysplasia, leukemia, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. This wide spectrum of diseases ranging from classic DC to aplastic anemia can be regarded as disorders of defective telomere maintenance—“the telomereopathies.” These advances have increased our understanding of normal hematopoiesis and highlighted the important role of telomerase and telomeres in human biology. They are also facilitating the diagnosis (especially when presentation is atypical) and management of DC.
Clinical features of DC
The spectrum of diseases encompassed by the term dyskeratosis congenita (DC) has expanded considerably since its initial description in 1910. In its classic form, it is usually characterized by the mucocutaneous triad of abnormal skin pigmentation, nail dystrophy, and leucoplakia (Figure 1). A wide spectrum of features (Table 1 and Figure 1) affecting every system in the body, particularly the BM, have been associated with DC.1–3 Three modes of inheritance have been recognized: X-linked recessive (OMIM, 305000), autosomal dominant (OMIM, 127550), and autosomal recessive (OMIM, 224230). The clinical phenotype associated with each of these genetic forms can vary widely. The main causes of mortality in DC are BM failure (∼ 60%-70%), pulmonary disease (∼ 10%-15%), and malignancy (∼ 10%).
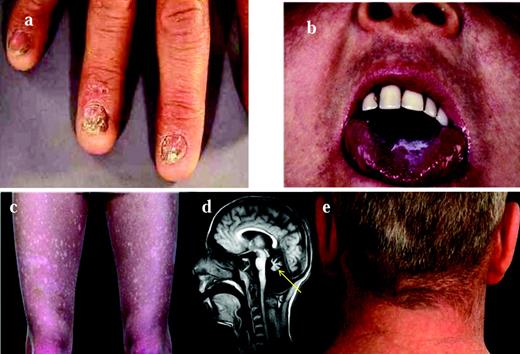
Clinical features of DC. The clinical features of DC are: nail dystrophy (A), oral leucoplakia (B), abnormal skin pigmentation (C), cerebellar hypoplasia (D; highlighted by the arrow), and premature hair loss/greying (E).
Clinical features of DC. The clinical features of DC are: nail dystrophy (A), oral leucoplakia (B), abnormal skin pigmentation (C), cerebellar hypoplasia (D; highlighted by the arrow), and premature hair loss/greying (E).
Multisystem clinical features of DC
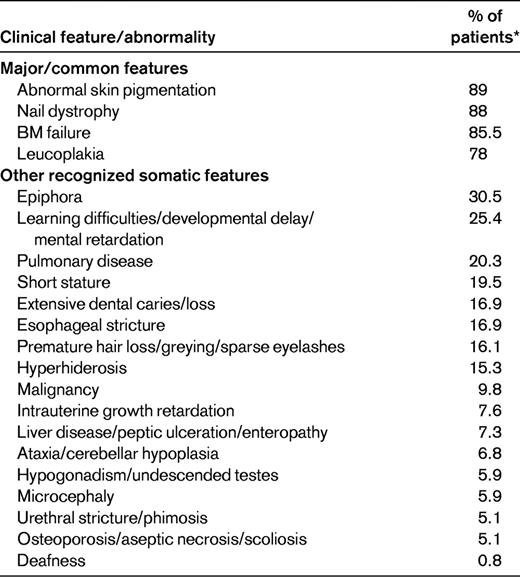
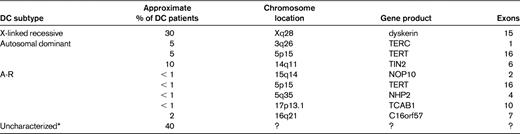
*These percentages refer to 118 DC patients recruited to the registry in London before the identification of any DC genes.
Clinical features of classic DC often appear in childhood. The abnormal skin pigmentation and nail changes usually appear first, often below the age of 10 years, and then BM failure develops frequently below the age of 20 years, with up to 80% of patients showing signs of BM failure by the age of 30 years. However, there is considerable variation between patients with respect to age of onset and disease severity even within the same family and this causes difficulty in making a diagnosis. It is also not uncommon for BM failure or an abnormality in another system to present before the more classic mucocutaneous features, and this is being recognized increasingly since the advances in DC genetics.
The minimal clinical criteria for diagnosis of DC include the presence of at least 2 of the 4 major features (abnormal skin pigmentation, nail dystrophy, leukoplakia, and BM failure) and 2 or more of the other somatic features (Table 1) known to occur in DC.3 Since 1998, 8 DC genes have been identified, and these account for approximately 60% of DC cases (Table 2).
X-linked DC and the Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome
The gene (DKC1) responsible for X-linked DC was mapped to Xq28 in 1986 and identified through positional cloning in 1998. The DKC1 gene is highly conserved and encodes the protein dyskerin.4 With the identification of mutations in DKC1, the first diagnostic tests became available. It also provided the first firm evidence that DC was not a homogenous disorder and that other syndromes with overlapping presentation can share the same genetic mutations (Figure 2). The first such example was the Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson (HH) syndrome,5 a severe multisystem disorder characterized by growth retardation of prenatal onset, microcephaly, cerebellar hypoplasia, aplastic anemia, and immunodeficiency. Due to the overlap in features, it was suggested and subsequently proved that HH is a severe variant of DC due to the presence of DKC1 mutations in males with the classical presentation of HH.6 A diagnosis of HH can be made if a patient presents with 4 of the 6 most commonly recognized features of HH: intrauterine growth retardation, developmental delay, microcephaly, cerebellar hypoplasia, immunodeficiency, or aplastic anemia.3 However, DKC1 mutations are not the only cause of HH; mutations in other genes can also lead to a phenotype of HH. The majority of patients with DKC1 mutations have a classic DC phenotype, but a subgroup of DKC1 mutations are associated with the HH phenotype. It is also notable that some patients with DKC1 mutations have features that overlap with both classic DC and HH.
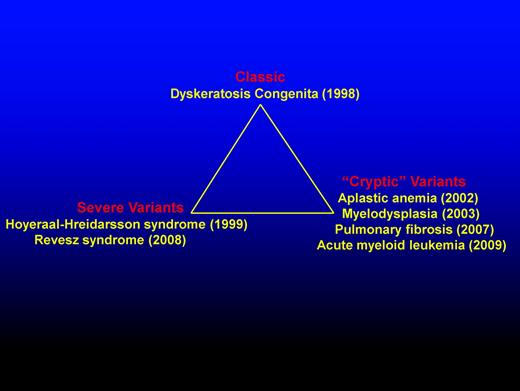
Schematic representation highlighting the diverse presentations of DC. DC presentation includes classic, severe variants, and “cryptic” variants. The year (in brackets) indicates first genetic recognition.
Schematic representation highlighting the diverse presentations of DC. DC presentation includes classic, severe variants, and “cryptic” variants. The year (in brackets) indicates first genetic recognition.
Autosomal dominant DC and its link to telomerase, telomeres, and shelterin
Autosomal dominant DC is heterogeneous. To date, heterozygous mutations in 3 genes (TERC, TERT, and TINF2) have been characterized. The identification of heterozygous mutations in TERC (telomerase RNA component) in 2001 was a major advance in the DC field because it provided a direct link between DC and telomerase (Figure 3).7 Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein composed of 2 core components: a catalytic component that adds the repeats, telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), and TERC, which acts as the template. Telomerase functions as a specialized polymerase that adds the telomeric repeat TTAGGG to the end of the 3′ lagging strand of DNA after replication. Due to the semiconservative nature of DNA replication, telomerase is essential to maintain telomere length in rapidly dividing cells such as cells of the hematopoietic system. Without telomerase, the telomeres shorten with each successive round of replication, and when they reach a critical length the cells enter senescence. Telomerase is mainly restricted to cells such as germ cells, stem cells, and their immediate progeny, activated T cells and monocytes; however, in cells in which telomerase is not present, telomere shortening is part of the normal process of cellular aging.8
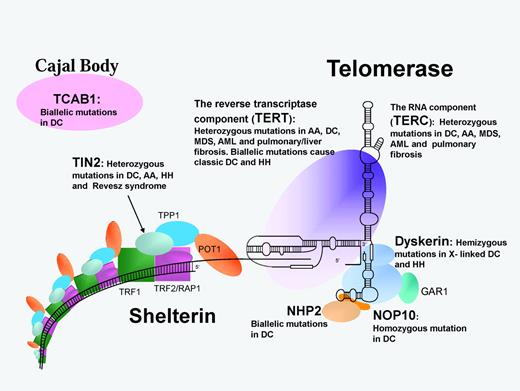
Schematic representation of the telomerase and shelterin complexes involved in telomere maintenance. Protein/RNA names in bold are mutated in DC and related disorders as listed. AA indicates aplastic anemia; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; and RS, Revesz syndrome.
Schematic representation of the telomerase and shelterin complexes involved in telomere maintenance. Protein/RNA names in bold are mutated in DC and related disorders as listed. AA indicates aplastic anemia; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; and RS, Revesz syndrome.
Mutations in patients with autosomal dominant DC were identified in TERC initially, and it was the identification of mutations within this molecule that led to significant expansion of the DC phenotype to include other hematological and nonhematological disorders (Figure 2). First, heterozygous mutations in TERC were identified in patients with aplastic anemia9 and soon after in patients with myelodysplasia.10 This started to push the original clinical diagnosis away from the classical mucocutaneous manifestations to BM failure being the initial presenting feature.
The identification of mutations in DKC1 and TERC established the pathology of defective telomere maintenance as being the principal underlying cause of DC. Both dyskerin (encoded by DKC1) and TERC are now recognized to be core components of telomerase,11 and patients with DKC1 and TERC mutations have very short telomeres compared with their age-matched controls. This led to the further study of the telomerase complex to determine the genetic basis of the remaining uncharacterized patients. The next gene to have mutations identified was TERT, which encodes the enzymatic component of the telomerase complex. The clinical presentation in patients with TERT mutations is highly variable, ranging from a nearly DC phenotype to just aplastic anemia.12–13 Heterozygous mutations in TERT and TERC have also been identified in some patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis,14 liver disease,15 and acute leukemia.16–17
In 2008, mutations in a component (TIN2) of the shelterin complex were identified in one subtype of autosomal dominant DC. The shelterin complex has at least 3 effects on telomeres: it determines the structure of the telomeric terminus, it has been implicated in the generation of t-loops, and it controls the synthesis of telomeric DNA by telomerase. Without the protective activity of shelterin, telomeres are no longer hidden from DNA damage-repair mechanisms and therefore chromosome ends are incorrectly processed by the DNA-repair pathways. The shelterin complex is composed of 6 proteins: telomeric-repeat binding protein 1 (TRF1), telomeric-repeat binding protein 2 (TRF2), TRF1-interacting nuclear factor 2 (TIN2), TERF2-interacting protein (RAP1), TIN2-interacting protein 1 (TPP1), and protection of telomeres (POT1).18 TRF1, TRF2, and POT1 of the shelterin complex (Figure 3) bind directly to the telomeric DNA, TRF1 and TRF2 bind to double-stranded DNA, and POT1 to the single-stranded DNA overhang. The composition and protein interaction of the components of the shelterin complex appears to be highly ordered, with TIN2 playing a pivotal role
In a subset of patients with DC, HH, aplastic anemia, and Revesz syndrome heterozygous mutations in the TIN2 component of shelterin have been identified.19–20 This discovery extends the range of the DC spectrum of diseases even further. Revesz syndrome is characterized by bilateral exudative retinopathy, BM hypoplasia, nail dystrophy, fine hair, cerebellar hypoplasia, and growth retardation.21 Patients with TIN2 mutations tend to have severe disease and this is associated with very short telomere lengths. Interestingly, nearly all patients have de novo TIN2 mutations that give rise to a different mechanism that causes the disease. In patients with heterozygous TERC and TERT mutations, studies have shown that the phenomenon of genetic anticipation is frequently involved; a parent of an affected child has the same telomerase mutation, but usually no overt signs of disease. However, in the child with the same heterozygous telomerase mutation, the disease manifests itself at a much younger age and is usually more severe.22–23 This adds another level of complexity to DC. Mutations in one gene (TERC or TERT) that take a generation to cause a significant clinical effect can cause the same disease as mutations in another gene (TINF2) that arise instantly.
AR-DC
Since 2007, progress has been made in the investigation on the genetic basis of autosomal-recessive DC (AR-DC). A large linkage study of 16 consanguineous families comprising 25 affected individuals did not identify a single common locus, suggesting that there is genetic heterogeneity within this subtype of DC.24 Since this observation, mutations in 5 genes have been identified as causing AR-DC. The first AR-DC gene24 to be identified was NOP10. The homozygous NOP10 mutation identified in a large family affected a highly conserved residue. As a result of this mutation, all of the affected individuals had reduced telomere length and reduced TERC levels. To date, no additional NOP10 mutations have been described. In a subset of AR-DC patients, biallelic mutations have been identified in TERT. These mutations result in a very different profile regarding TRAP activity and telomere length, with both being greatly reduced compared with heterozygous TERT mutations.25
Biallelic mutations in NHP2 have been identified in a subset of AR-DC patients. Telomere lengths and TERC levels are reduced in these patients compared with healthy controls.26 Both NOP10 and NHP2 are components of the H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex (H/ACA RNP). This complex is composed of an RNA molecule and 4 proteins: dyskerin, GAR1, NOP10, and NHP2. These 4 proteins are highly conserved and have been shown to be involved in ribosome biogenesis, pre-mRNA splicing, and telomere maintenance.27 Mutations have been identified in all components of this H/ACA RNP complex in patients with DC except for GAR1. The reason for this is unclear, but it may be due to its location relative to the RNA component. Modeling of the telomerase complex has shown that GAR1 makes no contact with the RNA molecule and is not required for the structural integrity of the H/ACA RNP.
In 2011, biallelic mutations in the TCAB1 gene were identified in 2 patients with AR-DC.28 TCAB1 is a telomerase holoenzyme protein that facilitates trafficking of telomerase to Cajal bodies, the nuclear sites of nucleoprotein complex modification and assembly. Compound heterozygous mutations in TCAB1 disrupt telomere localization to Cajal bodies, resulting in misdirection of telomerase RNA to nucleoli, and this in turn prevents telomerase from elongating telomeres, thereby resulting in short telomeres.
In another subgroup of AR-DC, biallelic mutations have been found in the C16orf57 gene.29 Mutations in this gene have unified this subgroup of DC with patients classified as having poikiloderma with neutropenia and Rothmund-Thomson syndrome. This subgroup of AR-DC patients appear to have normal length telomeres and therefore represent a biologically different subtype from the 7 other characterized DC subgroups. The precise function of the C16orf57 gene remains unknown. Clinically, patients with C16orf57 mutations can be identical/similar to those with genetic defects in telomere length maintenance. Further studies are needed to establish the precise biology of this group; it is possible that C16orf57 has some role in maintaining telomere structure rather than telomere length.
Hematological involvement in DC
Over the years, it has become clear that BM failure is a frequent complication in DC. Often this develops in the second or third decade, but it can develop from any time after birth to the sixth or even the seventh decade of life. The BM failure can initially involve a single lineage (frequently associated with initial thrombocytopenia) and then become more global and evolve into severe BM failure. The progressive development of BM failure (in up to 80% of patients) resulting in significant reduction in mature blood cells is one of the major causes of premature mortality in DC. Features of dysplasia in one or more lineage are common and in some cases it can be trilineage. The BM abnormalities can evolve into myelodysplasia and leukemia. The initial clinical presentation may be with BM failure, especially in patients with TERC, TERT, and TIN2 mutations.
In vitro studies have shown that there is a reduction or absence of the multilineage colony-forming cells in DC patients, which is consistent with a hematopoietic stem cell defect.30–31 There are also differences in progenitor colonies according to the mutation; for example, patients with TERC mutations show a greater a reduction in peripheral blood colony number compared with those with DKC1 mutations. This correlation is noteworthy because patients with TERC mutations often present with BM failure before mucocutaneous features, whereas in those with DKC1 mutations, the presentation usually tends to be more classical.
Telomere lengths and pathophysiology of DC
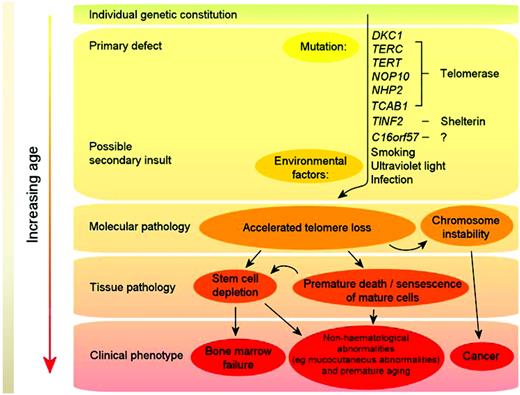
Telomeres consist of long TTAGGG repeats and the associated proteins of the shelterin complex at the ends of chromosomes that are essential for maintaining chromosome integrity by preventing chromosome ends from being recognized as DNA breaks. The association between shortened telomere length and DC was first observed by Mitchell et al in cells from patients with DKC1 mutations.32 Regardless of the genetic basis, many DC patients have short telomeres compared with healthy, age-matched individuals,33 and DC is now regarded principally as a disorder of telomere maintenance. A model for the pathophysiology of DC is given in Figure 4. Mutations in telomerase and shelterin components (primary defects) cause excessive telomere attrition, and this together with environmental factors (eg, smoking) in the context of the overall genetic constitution of the individual, leads to premature cell death and chromosome instability. With increasing age, this eventually either reduces/exhausts the stem cell reserve (thereby leading to clinical features such as BM failure) or results in hematological and nonhematological cancers.
Model of DC pathophysiology. Mutations in telomerase and shelterin components (primary defects) cause excessive telomere attrition; this, together with environmental factors (eg, smoking), in the context of the overall genetic constitution of the individual, leads to premature cell death and chromosome instability. With increasing age, this eventually either reduces/exhausts the stem cell reserve (thereby leading to clinical features such as BM failure) or results in cancer.
Model of DC pathophysiology. Mutations in telomerase and shelterin components (primary defects) cause excessive telomere attrition; this, together with environmental factors (eg, smoking), in the context of the overall genetic constitution of the individual, leads to premature cell death and chromosome instability. With increasing age, this eventually either reduces/exhausts the stem cell reserve (thereby leading to clinical features such as BM failure) or results in cancer.
A study by Alter et al measured telomere length in various blood cell types in patients with DC, their relatives, and other patients with different inherited BM failure syndromes34 and found that DC patients had very short telomeres in the majority of the leukocyte subset studied (< the first centile compared with normal controls). Telomere lengths in the DC patient group also tended to be shorter than in patients with other BM failure syndromes, so telomere length can, with caution, be treated as a surrogate marker for DC but only in the context of BM failure.35 It remains to be validated whether up-front telomere length measurements in new patients with one or more features of DC can be used to identify the cryptic forms of DC.
Therapy of hematological complications of DC
BM failure is the main cause of premature mortality in DC. The anabolic steroid oxymetholone can produce improvement in hematopoietic function. However, the precise mechanism of action of oxymetholone is not well understood but it is thought to function by promoting the growth of hematopoietic progenitors indirectly through the effect of cytokine production and by supporting hemopoietic production in times of stress. It has also been recently established that sex hormones can increase telomerase activity by action on the TERT gene.36 Approximately 2/3 of patients with DC will respond to oxymetholone and in some cases this response can last several years and involve all lineages. Patients with DC can respond to a dose as low as 0.25 mg of oxymetholone/kg/d, and this can be increased, if necessary, to 2-5 mg/kg/d (Dokal I, personal observation). It is important to monitor for side effects (eg, liver toxicity) when using oxymetholone, but it is possible to maintain reasonable blood counts in many patients using this approach.
The only long-term cure for the hemopoietic abnormalities associated with DC is allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, but this is not without risk. There is significant mortality associated with BM transplantations in DC patients—more so than with other BM failure syndromes. One of the main reasons for this is the high level of pulmonary/vascular complications that present in these patients, probably as a result of the underlying telomere defect. The conditioning regimen appears to have an impact on patient survival. The standard myeloablative conditioning regimes are associated with frequent and severe adverse effects such as pulmonary complications and venoocclusive disease. Recently, the adoption of nonmyeloablative fludarabine-based protocols has allowed for successful engraftment in some patients, which is associated with fewer complications and lower toxicity.37–38 Although the long-term survival after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is unknown, the initial response is encouraging as a more effective treatment for DC patients.
In the future, new treatments for DC may emerge. In this context, it is noteworthy that exogenous TERC alone can correct the telomerase defect, restore telomere length, and improve cell growth in DKC1- and TERC-mutated lymphocytes.39 It will be important to establish whether increased TERC expression, using this or other approaches,40 can lead to a viable new treatment for DC.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks all colleagues past (Stuart Knight, Anna Marrone, David Stevens, and Philip Mason) and present (Richard Beswick, Mike Kirwan, Upal Hossain, Amanda Walne, and Tom Vulliamy) and all of the patients and clinicians upon whom the research in our laboratory depends. This work is supported by funding from The Wellcome Trust.
Disclosures
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The author declares no competing financial interests. Off-label drug use: None disclosed.
Correspondence
Professor Inderjeet Dokal, Centre for Paediatrics, Blizard Institute of Cell and Molecular Science, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry, 4 Newark Street, London E1 2AT, United Kingdom; Phone: 44-0-20-7882-2205; Fax: 44-0-20-7882-2195; e-mail: i.dokal@qmul.ac.uk.